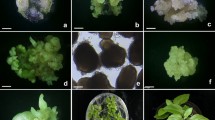
Summary
Embryogenic calluses were induced from 73% of Phalaenopsis shoot-tip explants excised from flower stalk buds by culturing for 7 mo. on New Dogashima Medium (NDM) containing 0.5 μM α-naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA), 4.4 μM 6-benzylaminopurine and 29.2 mM sucrose. The sucrose concentration was increased to 58.4 mM 4 mo. after initiation of the callus culture. These calluses were successfully subcultured as cell suspension cultures in liquid NDM supplemented with 5.4μM NAA and 58.4 mM sucrose. By simply reducing the sucrose concentration to 29.2 mM, the cells grew into plantlets through a developmental process similar to that of Phalaenopsis seedlings. The occurrence of somaclonal variants was less than 10% in six out of eight genotypes examined. These results suggest that the embryogenic callus and cell suspension culture could be utilized as the materials for micropropagation and breeding of Phalaenopsis orchids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arditti, J.; Ernst, R. Micropropagation of orchids: methods for specific genera. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1993: 87–607.
Belarmino, M. M.; Mii, A. Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation of a phalaenopsis orchid. Plant Cell Rep. 19:435–442; 2000.
George, E. E. Plant micropropagation of tissue culture: sugars—nutritional and regulatory effects. London: Exegetics; 1993:322–336.
Ichihashi, S. Micropropagation of Phalaenopsis throught the culture of lateral buds from young flower stalks. Lindleyana 7:208–215; 1992.
Ishii, Y.; Takamura, T.; Goi, M.; Tanaka, M. Callus induction and somatic embryogenesis of Phalaenopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 17:446–450; 1998.
Kobayashi, S.; Kameya, T.; Ichihashi, S. Plant regeneration from protoplasts derived from callus of Phalaenopsis. Plant Tiss. Cult. Lett. 10:267–270; 1993.
Morel, G. M. Producing virus-free Cymbidiums. Am. Orchid Soc. Bull. 29:495–497; 1960.
Sajise, J. U.; Sagawa, Y. Regeneration of plantlets from callus and protoplasts of Phalaenopsis sp. Malaysia Orchid Bull. 5:23–28; 1991.
Tokuhara, K.; Mii, M. Micropropagation of Phalaenopsis and Doritaenopsis by shoot tips of flower stalk buds. Plant Cell Rep. 13:7–11; 1993.
Tokuhara, K.; Mii, M. Somaclonal variation in flower and inflorescence axis in micropropagated plants through flower stalk bud culture of Phalaenopsis and Doritaenopsis. Plant Biotechnol. 15:23–28; 1998.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tokuhara, K., Mii, M. Induction of embryogenic callus and cell suspension culture from shoot tips excised from flower stalk buds of Phalaenopsis (Orchidaceae). In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Plant 37, 457–461 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-001-0080-4
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11627-001-0080-4