ABSTRACT
Background
Many seniors rely on paid non-familial caregivers to maintain their independence at home. Caregivers often assist with medication reminding and activities of daily living. No prior studies have examined the health literacy levels among paid non-familial caregivers.
Objectives
To determine health literacy levels and the health-related responsibilities of paid non-familial caregivers of seniors.
Design
One-on-one face-to-face surveys. The Test for Functional Health Literacy (TOFHLA) was administered to identify health literacy levels. Caregivers were asked to demonstrate their skill in medication use by following directions on pill bottles and sorting medications into pill boxes.
Participants
Ninety-eight paid unrelated caregivers of seniors recruited at physician offices, caregiver agencies, senior shopping areas, and independent living facilities.
Results
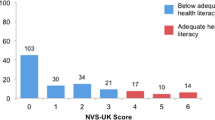
Average age of caregivers was 49.5 years, and 86.7% were female. Inadequate health literacy was found in 35.7% of caregivers; 60.2% of all caregivers made errors with the pillbox test medications, showing difficulty in following label directions. Health-related tasks (i.e., medication reminding, sorting, dispensing, and accompanying seniors to physician appointments) were performed by 85.7% of caregivers. The mean age of their seniors was 83.9 years (range 65–99 years), and 82.1% were female.
Conclusion
Paid non-familial caregivers are essential for many seniors to remain independent and maintain their health. Many caregivers perform health-related duties, but over 1/3 have inadequate health literacy and have difficulties following medication-related instructions. Educating caregivers and ascertaining their health literacy levels prior to assigning health-related tasks may be an important process in providing optimal care to seniors.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hanyok LA, Finucane T, Carrese J, et al. Potential caregivers for homebound elderly: more numerous than supposed? J Fam Pract. 2009;58(7):E1–6.
Kirsch I, Jungeblut A, Jenkins L, Kolstad A. Adult Literacy in America: a First Look at the Results of the National Adult Literacy Survey. Washington, DC: National Center for Education Statistics, US Department of Education; 1993.
Gazmararian J, Baker D, Williams M, et al. Health literacy among Medicare enrollees in a managed care organization. JAMA. 1999;281(6):545–51.
Baker DW, Gazmararian JA, Williams MV, et al. Health literacy and use of outpatient physician services by Medicare managed care enrollees.[see comment]. J Gen Intern Med. 2004;19(3):215–20.
Scott TL, Gazmararian JA, Williams MV, Baker DW. Health literacy and preventive health care use among Medicare enrollees in a managed care organization. Med Care. 2002;40(5):395–404.
BD WMV, Honig EG, Lee TM, Nowlan A. Inadequate literacy is a barrier to asthma knowledge and self-care. Chest. 1998;114:1008–15.
Gazmararian JA, Williams MV, Peel J, Baker DW. Health literacy and knowledge of chronic disease. Patient Educ Couns. 2003;51(3):267–75.
Juzych MS, Randhawa S, Shukairy A, et al. Functional health literacy in patients with glaucoma in urban settings. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008;126(5):718–24.
Williams MV, Baker DW, Parker RM, Nurss JR. Relationship of functional health literacy to patients' knowledge of their chronic disease. A study of patients with hypertension and diabetes. Arch Intern Med. 1998;158(2):166–72.
Gazmararian JA, Kripalani S, Miller MJ, et al. Factors associated with medication refill adherence in cardiovascular-related diseases: a focus on health literacy. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(12):1215–21.
Davis TC, Wolf MS, Bass PF 3rd, et al. Literacy and misunderstanding prescription drug labels. Ann Intern Med. 2006;145(12):887–94.
Persell SD, Osborn CY, Richard R, et al. Limited health literacy is a barrier to medication reconciliation in ambulatory care. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22(11):1523–6.
Baker DW, Parker RM, Williams MV, Clark WS. Health literacy and the risk of hospital admission.[see comment]. J Gen Intern Med. 1998;13(12):791–8.
Baker DW, Wolf MS, Feinglass J, et al. Health literacy and mortality among elderly persons. Arch Intern Med. 2007;167(14):1503–9.
Parker RM, Baker DW, Williams MV, Nurss JR. The test of functional health literacy in adults: a new instrument for measuring patients' literacy skills. J Gen Intern Med. 1995;10(10):537–41.
Baker DW, Williams MV, Parker RM, Gazmararian JA, Nurss J. Development of a brief test to measure functional health literacy. Patient Educ Couns. 1999;38(1):33–42.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to thank the Barney Family Foundation for their support and funding of this study.
Conflict of Interest
None disclosed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindquist, L.A., Jain, N., Tam, K. et al. Inadequate Health Literacy Among Paid Caregivers of Seniors. J GEN INTERN MED 26, 474–479 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-010-1596-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11606-010-1596-2