Abstract
Background
Electrothermal injury of common bile duct is a frequent type of biliary injury. A long-term postoperative course and biliary leakage after removing T-tube are associated with external drainage. A method was developed to repair the injury with a degradable biliary stent instead of T-tube insertion.
Methods
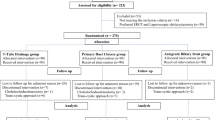
Pigs were divided into a stent repair (SR) group (n = 18), a T-tube repair (TR) group (n = 4), and a suturing repair (SUR) group (n = 4). An electrothermal injury model was made by electric coagulation. Pigs in the SR group were further divided into five subgroups according to the observation time (2 weeks and 1, 3, 6, and 18 months). Pigs in the TR group and SUR group were observed for 6 months. Cholangiography was repeated and bilirubin level was monitored. Pigs were reoperated for further evaluation at the end of observation.
Results
No biliary stricture, bile leakage, or bile duct necrosis occurred in the SR group. The stent could be detected in the first 2 months. No stent migration or stent-related obstruction was observed. Three pigs in the SUR group had biliary stricture with elevated bilirubin levels.
Conclusions
These results suggested that the developed method for repairing electrothermal injury of common bile duct is feasible and safe.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Waage A, Nilsson M. Iatrogenic bile duct injury: a population-based study of 152 776 cholecystectomies in the Swedish Inpatient Registry. Arch Surg 2006;141:1207–1213
Nuzzo G, Giuliante F, Giovannini I, Ardito F, D’Acapito F, Vellone M, Murazio M, Capelli G. Bile duct injury during laparoscopic cholecystectomy: results of an Italian national survey on 56 591 cholecystectomies. Arch Surg 2005;140:986–992
Mirza DF, Narsimhan KL, Ferraz Neto BH, Mayer AD, McMaster P, Buckels JA. Bile duct injury following laparoscopic cholecystectomy: referral pattern and management. Br J Surg 1997;84:786–790
Soper NJ. Prevention of biliary leaks. J Gastrointest Surg 2011;15:1005–1006
Humes DJ, Ahmed I, Lobo DN. The pedicle effect and direct coupling: delayed thermal injuries to the bile duct after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Arch Surg 2010;145:96–98
Gharaibeh KI, Heiss HA. Biliary leakage following T-tube removal. Int Surg 2000;85:57–63
Maghsoudi H, Garadaghi A, Jafary GA. Biliary peritonitis requiring reoperation after removal of T-tubes from the common bile duct. Am J Surg 2005;190:430–433
Tang CN, Tai CK, Ha JP, Tsui KK, Wong DC, Li MK. Antegrade biliary stenting versus T-tube drainage after laparoscopic choledochotomy—a comparative cohort study. Hepatogastroenterology 2006;53:330–334
Liang YL, Yu YC, Liu K, Wang WJ, Ying JB, Wang YF, Cai XJ. Repair of bile duct defect with degradable stent and autologous tissue in a porcine model. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18: 5205–5210
Wang Y, Cai X, Cai H, Liang Y, Huang D, Liang X. Experimental study of colonic anastomosis with a degradable stent in a porcine model. Am J Surg 2010;199:833–839
Wang Y, Cai X, Jin R, Liang Y, Huang D, Peng S. Experimental study of primary repair of colonic leakage with a degradable stent in a porcine model. J Gastrointest Surg 2011;15:1995–2000
Freeman RK, Ascioti AJ, Wozniak TC. Postoperative esophageal leak management with the Polyflex esophageal stent. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2007;133:333–338
Langer FB, Wenzl E, Prager G, Salat A, Miholic J, Mang T, Zacherl J. Management of postoperative esophageal leaks with the Polyflex self-expanding covered plastic stent. Ann Thorac Surg 2005;79:398–403
Gelbmann CM, Ratiu NL, Rath HC, Rogler G, Lock G, Schölmerich J, Kullmann F. Use of self-expandable plastic stents for the treatment of esophageal perforations and symptomatic anastomotic leaks. Endoscopy 2004;36:695–699
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Liqun Wang and the members of his research team at the Institute of Polymer Science at Zhejiang University for their work in manufacturing the stent. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81101152) and International Program of China (2012DFA30410).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
YiFan Wang and YueLong Liang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Liang, Y., Wang, W. et al. Management of Electrothermal Injury of Common Bile Duct with a Degradable Biliary Stent: an Experimental Study in a Porcine Model. J Gastrointest Surg 17, 1760–1765 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2316-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2316-0