Abstract
Background
An alternative approach to lateral internal sphincterotomy in the management of chronic anal fissure is presented and its potential advantages are described.
Methods
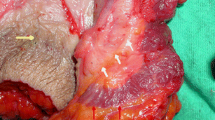
Using the conventional diathermy, the internal sphincter along with its overlying anoderm is cut to the caudal border of the dentate line.
Results
This prospective study included 350 patients. Twenty-six patients (7.4%) reported spotting of blood with defecation and 266 patients (76%) reported minimal perianal discharge. The cessation of the discharge and spotting of blood correlated with the complete healing of the sphincterotomy wound. Urine retention requiring temporary catheterization was encountered in 19 patients (5.4%). Neither abscesses nor fistulae were encountered. Cure was achieved in all patients. Neither recurrences nor permanent fecal incontinence were encountered throughout the study period.
Conclusion
The alternative approach is efficient and safe and may be added to the surgeon's armamentarium when attempting lateral internal sphincterotomy for chronic anal fissure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nelson RL. Meta-analysis of operative techniques for fissure-in-ano. Dis Colon Rectum 42:1424–1431,1999.
Corman ML. Anal fissure. In Corman ML (Ed). Colon and rectal surgery, 4th Ed. Philadelphia. Lippincott-Raven 206–223. 1998
Keighley MRD, Williams NS. Fissure-in-ano. In: Keighley MRD and Williams NS (Eds.). Surgery of the Anus, Rectum and Colon, 2nd Ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders 428–455,1991
Nelson R. A systematic review of medical therapy for anal fissure. Dis Colon Rectum 47(4):422–431, 2004
Oliveira L, Wexner SD. Anal incontinence. In Beck DE and Wexner SD (Eds). Fundamentals of Anorectal surgery, 2nd Ed. London: WB Saunders Company 115–152, 1998.
Practice parameters for the management of anal fissures (Revised). Dis Colon Rectum 53(8): 1110–1115, 2010.
Maria G, Brisinda G, Bentivoglio AR et al. Influence of Botulinum toxin site of injections on healing rate in patients with chronic anal fissure. Am J Surg 179:46–50, 2000
Minguez M, Melo F, Espi A et al. Therapeutic effects of different doses of Botulinum toxin in chronic anal fissure. Dis Colon Rectum 42: 1016–1021, 1999.
Nyam DC, Pemberton JH. Long-term results of lateral sphincterotomy for chronic anal fissure with particular reference to incidence of fecal incontinence. Dis Colon Rectum 42:1306–1310, 1999.
Hyman N. Incontinence after lateral internal sphincterotomy: A prospective study and quality of life assessment. Dis Colon Rectum 47:35–38, 2004.
Garcia-Aguilar J, Belmonte C, Wong WD et al. Open vs. closed sphincterotomy for chronic anal fissure: long-term results. Dis Colon Rectum 39:440–443, 1996.
Keighley MR, Greca F, Nevah E et al. Treatment of anal fissure by lateral subcutaneous sphincterotomy should be under general anesthesia.Br J Surg 68:400–401, 1981
Leong AF, Husain MJ, Seow-Choen F et al. Performing internal sphincterotomy with other anorectal procedures. Dis Colon Rectum 37:1130–1132, 1994.
Tjandra JJ, Han WR, Ooi BS et al. Fecal incontinence after lateral internal sphincterotomy is often associated with coexisting occult sphincter defects: a study using endoanal ultrasonography. ANZ J Surg 71:598–602, 2001
Garcia-Aguilar J, Belmonte Montes C et al. Incontinence after lateral internal sphincterotomy: anatomic and functional evaluation. Dis Colon Rectum 41:423–427, 1998
Sultan AH, Kamm MA, Nicholls RJ et al. Prospective study of the extent of internal anal sphincter division during lateral sphincterotomy. Dis Colon Rectum 37:1031–1033, 1994
Lindsey I, Jones OM, Smiligin-Humphreys MN et al. Patterns of fecal incontinence after anal surgery. Dis Colon Rectum 47:1643–1649, 2004
Garcia- Granero E, Sanahuja A, Garcia-Armengol J et al. Anal endosonographic evaluation after closed lateral subcutaneous sphincterotomy. Dis Colon Rectum 41(5):598–601, 1998 E,
Khubcchandani IT, Reed JF. Sequelae of internal sphincterotomy for chronic fissure in ano. Br J Surg 76:431–434, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
No competing financial interests exist.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bessa, S.S. Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy for Chronic Idiopathic Anal Fissure: An Alternative Approach. J Gastrointest Surg 15, 466–470 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-010-1407-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-010-1407-4