Abstract
Purpose
While microsurgical resection plays a central role in the management of ACMs, extensive surgery may be associated with substantial morbidity particularly for tumors in intimate association with critical structures. In this study, we evaluated the use of HFSRT in the management of ACM.
Materials and methods
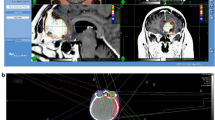
A total of 22 patients with ACM were treated using HFSRT. Frameless image guided volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) was performed with a 6 MV linear accelerator (LINAC). The total dose was 25 Gy delivered in five fractions over five consecutive treatment days. Local control (LC) and progression free survival (PFS) rates were calculated using the Kaplan–Meier method. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events, version 4.0 was used in toxicity grading.
Results
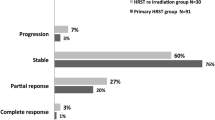
Out of the total 22 patients, outcomes of 19 patients with at least 36 months of periodic follow-up were assessed. Median patient age was 40 years old (range 24–77 years old). Median follow-up time was 53 months (range 36–63 months). LC and PFS rates were 100 and 89.4 % at 1 and 3 years, respectively. Only two patients (10.5 %) experienced clinical deterioration during the follow-up period.
Conclusion
LINAC-based HFSRT offers high rates of LC and PFS for patients with ACMs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee JH, Sade B. Anterior clinoidal meningiomas. In: Lee JH, editor. Meningiomas. London : Springer; 2009. p. 347–54.
Tzekov C, Spiriev T, Cherninkova S, Bussarsky V, Laleva L, Cekov A, et al. Characteristics and prognosis of visual deficit caused by parasellar meningiomas. Khirurgiia (Sofiia). 2010;2–3:19–23.
Al-Mefty O. Clinoidal meningiomas. J Neurosur. 1990;73:840–9.
Al-Mefty O. Clinoidal meningiomas. In: Al-Mefty O, editor. Meningiomas. New York: Raven Press; 1991. p. 427–43.
Risi P, Uske A, de Tribolet N. Meningiomas involving the anterior clinoid process. Br J Neurosurg. 1994;8:295–305.
Samii M, Ammirati M. Medial sphenoidal wing meningiomas. In: Samii M, editor. Surgery of skull base meningiomas. Berlin: Springer; 1993. p. 35–41.
Mirimanoff RO, Dosoretz DE, Linggood RM, Ojemann RG, Martuza RL. Meningioma: analysis of recurrence and progression following neurosurgical resection. J Neurosurg. 1985;62(1):18–24.
Mathiesen T, Lindquist C, Kihlstrom L, Karlsson B. Recurrence of cranial base meningiomas. Neurosurgery. 1996;39(1):2–7.
Bassiouni H, Asgari S, Sandalcioglu IE, Seifert V, Stolke D, Marquardt G. Anterior clinoidal meningiomas: functional outcome after microsurgical resection in a consecutive series of 106 patients. Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2009;111(5):1078–90.
Kocher M, Treuer H, Hoevels M, Semrau R, Sturm V, Mueller RP. Endocrine and visual function after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy of perioptic tumors. Strahlenther Onkol. 2013;189(2):137–41.
Milker-Zabel S, Huber P, Schlegel W, Debus J, Zabel-du Bois A. Fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in the management of primary optic nerve sheath meningiomas. Neurooncology. 2009;94(3):419–24.
Nagai A, Shibamoto Y, Yoshida M, Wakamatsu K, Kikuchi Y. Treatment of single or multiple brain metastases by hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy using helical tomotherapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):6910–24.
Chen JC, Giannotta SL, Yu C, Petrovich Z, Levy ML, Apuzzo ML. Radiosurgical management of benign cavernous sinus tumors: dose profiles and acute complications. Neurosurgery. 2001;48(5):1022–32.
Correa SF, Marta GN, Teixeira MJ. Neurosymptomatic carvenous sinus meningioma: a 15-years experience with fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery. Radiat Oncol. 2014;9:27.
Dincoglan F, Beyzadeoglu M, Sager O, Demiral S, Gamsiz H, Uysal B, et al. Management of patients with recurrent glioblastoma using hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy. Tumori. 2015;101(2):179–84.
Sager O, Beyzadeoglu M, Dincoglan F, Gamsiz H, Demiral S, et al. Evaluation of linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of glomus jugulare tumors. Tumori. 2014;100(2):184–8.
Demiral S, Beyzadeoglu M, Sager O, Dincoglan F, Gamsiz H, Uysal B, et al. Evaluation of linear accelerator (linac)-based stereotactic radiosurgery (srs) for the treatment of craniopharyngiomas. UHOD. 2014;24(2):123–9.
Dincoglan F, Sager O, Gamsiz H, Uysal B, Demiral S, Oysul K, et al. Management of patients with ≥4 brain metastases using stereotactic radiosurgery boost after whole brain irradiation. Tumori. 2014;100(3):302–6.
Sager O, Beyzadeoglu M, Dincoglan F, Uysal B, Gamsiz H, Demiral S, et al. Evaluation of linear accelerator (LINAC)-based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for cerebral cavernous malformations: a 15-year single-center experience. Ann Saudi Med. 2014;34(1):54–8.
Sager O, Beyzadeoglu M, Dincoglan F, Demiral S, Uysal B, Gamsiz H, et al. Management of vestibular schwannomas with linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery: a single center experience. Tumori. 2013;99(5):617–22.
Dincoglan F, Beyzadeoglu M, Sager O, Uysal B, Demiral S, Gamsiz H, et al. Evaluation of linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery in the management of meningiomas: a single center experience. J BUON. 2013;18(3):717–22.
Surenkok S, Sager O, Dincoglan F, Gamsiz H, Demiral S, Uysal B, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery in pituitary adenomas: a single center experience. UHOD. 2012;22(4):255–60.
Sirin S, Oysul K, Surenkok S, Sager O, Dincoglan F, Dirican B, et al. Linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery in recurrent glioblastoma: a single center experience. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2011;68(11):961–6.
Hamm K, Henzel M, Gross MW, Surber G, Kleinert G, Engenhart-Cabillic R. Radiosurgery/stereotactic radiotherapy in the therapeutical concept for skull base meningiomas. Zentralbl Neurochir. 2008;69(1):14–21.
Minniti G, Amichetti M, Enrici RM. Radiotherapy and radiosurgery for benign skull base meningiomas. Radiat Oncol. 2009;4:42.
Minniti G, Clarke E, Cavallo L, Osti MF, Esposito V, Cantore G, et al. Fractionated stereotactic conformal radiotherapy for large benign skull base meningiomas. Radiat Oncol. 2011;6:36.
Onodera S, Aoyama H, Katoh N, Taguchi H, Yasuda K, Yoshida D, et al. Long-term outcome of fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for intracranial skull base meningiomas in single institution. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2011;41(4):462–8.
Maranzano E, Draghini L, Casale M, Arcidiacono F, Anselmo P, Trippa F, et al. Long-term outcome of moderate hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for meningiomas. Strahlenther Onkol. 2015;191(12):953–60.
Conti A, Pontoriero A, Midili F, Iatì G, Siragusa C, Tomasello C, et al. CyberKnife multisession stereotactic radiosurgery and hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for perioptic meningiomas: intermediate-term results and radiobiological considerations. Springerplus. 2015;30(4):37.
Navarria P, Pessina F, Cozzi L, Clerici E, Villa E, Ascolese AM, et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in skull base meningiomas. J Neurooncol. 2015;124(2):283–9.
Haghighi N, Seely A, Paul E, Dally M. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign intrakranial tumors of the cavernous sinus. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22(9):1450–5.
Mahadevan A, Floyd S, Wong E, Chen C, Kasper E. Clinical outcome after hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HSRT) for benign skull base tumors. Comput Aided Surg. 2011;16(3):112–20.
Fokas E, Henzel M, Surber G, Hamm K, Engenhart-Cabillic R. Stereotactic radiotherapy of benign meningioma in the elderly: clinical outcome and toxicity in 121 patients. Radiother Oncol. 2014;111(3):457–62.
Kaul D, Budach V, Wurm R, Gruen A, Graaf L, Habbel P, et al. Linac-based stereotactic radiotherapy and radiosurgery in patients with meningioma. Radiat Oncol. 2014;9:78.
Han J, Girvigian MR, Chen JC, Miller MJ, Lodin K, Rahimian J, et al. A comparative study of stereotactic radiosurgery, hypofractionated, and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of skull base meningioma. Am J Clin Oncol. 2014;37(3):255–60.
Lee JY, Niranjan A, McInerney J, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD. Stereotactic radiosurgery providing long-term tumor control of cavernous sinus meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2002;97(1):65–72.
Chang SD, Adler JR, Martin DP. LINAC radiosurgery for cavernous sinüs meningiomas. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1998;71(1):43–50.
Eustacchio S, Trummer M, Fuchs I, Schröttner O, Sutter B, Pendl G. Preservation of cranial nerve function following gamma knife radiosurgery for benign skull base meningiomas: experience in 121 patients with follow-up of 5 to 9.8 years. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 2002;84:71–6.
Pollock BE, Stafford SL, Utter A, Giannini C, Schreiner SA. Stereotactic radiosurgery provides equivalent tumor control to Simpson Grade 1 resection for patients with small- to medium-size meningiomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;55(4):1000–5.
Leber KA, Bergloff J, Pendl G. Dose-response tolerance of the visual pathways and cranial nerves of the cavernous sinus to stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg. 1998;88(1):43–50.
Choi Y, Lim DH, Jo K, Nam DH, Seol HJ, Lee JI. Efficacy of postoperative radiotherapy for high grade meningiomas. J Neurooncol. 2014;119(2):405–12.
Aboukais R, Zairi F, Lejeune JP, Le Rhun E, Vermandel M, Blond S, et al. Grade 2 meningioma and radiosurgery. J Neurosurg. 2015;122(5):1157–62.
Detti B, Scoccianti S, Di Cataldo V, Monteleone E, Cipressi S, Bordi L, et al. Atypical and malignant meningioma: outcome and prognostic factors in 68 irradiated patients. J Neurooncol. 2013;115(3):421–7.
Pollock BE, Stafford SL, Link MJ, Garces YI, Foote RL. Stereotactic radiosurgery of World Health Organization grades II and III intracranial meningiomas: treatment results on the basis of a 22-year experience. Cancer. 2012;118(4):1048–54.
Liscak R, Simonova G, Vymazal J, Janouskova L, Vladyka V. Gamma knife radiosurgery of meningiomas in the cavernous sinus region. Acta Neurochir. 1999;141(5):473–80.
Jalali R, Loughrey C, Baumert B, Perks J, Warrington AP, Traish D, et al. High precision focused irradiation in the form of fractionated stereotactic conformal radiotherapy (SCRT) for benign meningiomas predominantly in the skull base location. Clin Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol.). 2002;14(2):103–9.
Pan DH, Guo WY, Chang YC, Chung WY, Shiau CY, Wang LW, et al. The effectiveness and factors related to treatment results of gamma knife radiosurgery for meningiomas. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 1998;70:19–32.
Stafford SL, Pollock BE, Leavitt JA, Foote RL, Brown PD, Link MJ, et al. A study on the radiation tolerance of the optic nerves and chiasm after stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;55(5):1177–81.
Acknowledgments
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
About this article
Cite this article
Demiral, S., Dincoglan, F., Sager, O. et al. Hypofractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (HFSRT) for who grade I anterior clinoid meningiomas (ACM). Jpn J Radiol 34, 730–737 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-016-0581-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-016-0581-z