Abstract
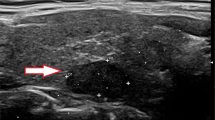
A 19-year-old female underwent two radiofrequency ablation procedures for a thyroid tumor that was proven to be nodular hyperplasia versus a follicular neoplasm by fine-needle aspiration. Two years after the last follow-up, the thyroid mass had grown and a newly developed mass was detected in the platysma muscle. After surgery, the thyroid mass was revealed to be a solid papillary thyroid carcinoma, and the subplatysmal mass was tumor seeding.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howenstein Matthew J, Sato Kent T. Complications of radiofrequency ablation of hepatic, pulmonary, and renal neoplasms. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2010;27(3):285–95.
Na DG, Lee JH, Jung SL, Kim JH, Sung JY, Shin JH, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules and recurrent thyroid cancers: consensus statement and recommendations. Korean J Radiol. 2012;13(2):117–25.
Polyzos SA, Anastasilakis AD. A systematic review of cases reporting needle tract seeding following thyroid fine needle biopsy. World J Surg. 2010;34(4):844–51.
Uchida N, Suda T, Inoue T, Fujiwara Y, Ishiguro K. Needle track dissemination of follicular thyroid carcinoma following fine-needle aspiration biopsy: report of a case. Surg Today. 2007;37(1):34–7.
Kumar N, Gaba RC, Knuttinen MG, Omene BO, Martinez BK, Owens CA, et al. Tract seeding following radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: prevention, detection, and management. Semin Interv Radiol. 2011;28(2):187–92.
Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE, Parikh PM, Pezzullo JA, Cronan JJ. Imaging-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of solid renal masses: techniques and outcomes of 38 treatment sessions in 32 consecutive patients. AJR. 2003;180:1503–8.
Arora N, Scognamiglio T, Zhu B, Fathey TJ 3rd. Do benign thyroid nodules have malignant potential? An evidence-based review. World J Surg. 2008;32(7):1237–46.
Alexander EK, Hurwitz S, Heering JP, Benson CB, Frates MC, Doubilet PM, et al. Natural history of benign solid and cystic thyroid nodules. Ann Intern Med. 2003;138(4):315–8.
Obara K, Matsumoto N, Okamoto M, Kobayashi M, Ikeda H, Takahashi H, et al. Insufficient radiofrequency ablation therapy may induce further malignant transformation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hep Intl. 2008;2(1):116–23.
Kim HY, Ryu WS, Woo SU, Son GS, Lee ES, Lee JB, et al. Primary papillary thyroid carcinoma previously treated incompletely with radiofrequency ablation. J Cancer Res Ther. 2010;6(3):310–2.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C.U., Kim, S.J., Sung, J.Y. et al. Needle track tumor seeding after radiofrequency ablation of a thyroid tumor. Jpn J Radiol 32, 661–663 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-014-0350-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-014-0350-9