Summary
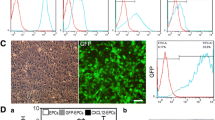
Various stem cells, including neural stem cells (NSCs), have been extensively studied in stroke models, but how to increase neuronal differentiation rate of NSCs remains unresolved, particularly in a damaged environment. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (CMECs) on the neurogenesis of NSCs with or without oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD). The NSCs acquired from primary culture were immunostained to prove cell purity. Survival and proliferation of NSCs were determined after the co-culture with CMECs for 7 days. After removing the CMECs, NSCs were randomly divided into two groups as follows: OGD and non-OGD groups. Both groups were maintained in differentiation culture for 4 days to evaluate the differentiation rate. Mouse embryo fibroblast (MEF) cells co-cultured with NSCs served as control group. NSCs co-cultured with CMECs had an increase in size (on the 7th day: 89.80±26.12 μm vs. 73.08±15.01 μm, P<0.001) (n=12) and number [on the 7th day: 6.33±5.61/high power objective (HP) vs. 2.23±1.61/HP, P<0.001] (n=12) as compared with those co-cultured with MEF cells. After further differentiation culture for 4 days, NSCs co-cultured with CMECs had an increase in neuronal differentiation rate in OGD and non-OGD groups, but not in the control group (15.16% and 16.07% vs. 8.81%; both P<0.001) (n=6). This study provided evidence that OGD could not alter the effects of CMECs in promoting the neuronal differentiation potential of NSCs. These findings may have important implications for the development of new cell therapies for cerebral vascular diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hicks A, Jolkkonen J. Challenges and possibilities of intravascular cell therapy in stroke. Acta Neurobiol Exp, 2009,69(1):1–10
Schwarz SC, Schwarz J. Translation of stem cell therapy for neurological diseases. Transl Res, 2010,156(3): 155–60
Liu YP, Lang BT, Baskaya MK, et al. The potential of neural stem cells to repair stroke-induced brain damage. Acta Neuropathol, 2009,117(5):469–80.
Reynolds BA, Weiss S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science, 1992,255(5052):1707–1710
Richards LJ, Kilpatrick TJ, Bartlett PF. De novo generation of neuronal cells from the adult mouse brain, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 1992,89(18):8591–8595
Koch P, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O, et al. Emerging concepts in neural stem cell research: autologous repair and cell-based disease modeling. Lancet Neurol, 2009,8(9): 819–829
Morgan PJ, Liedmann A, Hübner R, et al. Human neural progenitor cells show functional neuronal differentiation and regional preference after engraftment onto hippocampal slice cultures. Stem Cells Dev, 2012,21(9): 1501–1512
Zhang L, Jiang H, Hu Z. Concentration-dependent effect of nerve growth factor on cell fate determination of neural progenitors. Stem Cells Dev, 2011,20(10):1723–1731
Mitrecić D, Nicaise C, Gajović S, et al. Distribution, differentiation, and survival of intravenously administered neural stem cells in a rat model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell Transplant, 2010,19(5):537–548
Wurmser AE, Palmer TD, Gage FH. Cellular interactions in the stem cell niche. Neurosci, 2004,304(5675):1253
Ohlstein B, Kai T, Decotto E, et al. The stem cell niche: theme and variations. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2004,16(6): 693
Butcher J. Adult neural stem cells localised in SVZ. Lancet Neurol, 2004,3(4):198
Shen Q, Goderie S, Jin L, et al. Endothelial cells stimulate self-renewal and expand neurogenesis of neural stem cells. Science, 2004,304(5675):1338–1340
Cimarosti H, Henley JM. Investigating the mechanisms underlying neuronal death in ischemia using in vitro oxygen-glucose deprivation: potential involvement of protein SUMOylation, Neuroscientist, 2008, 14(6):626–636
Wu ZH, Hofman F, Zlokovic B. A simple method for isolation and characterization of mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Neurosci Methods, 2003,130(1): 53–63
Plane J, Andjelkovic A, Keep R, et al. Intact and injured endothelial cells differentially modulate postnatal murine forebrain neural stem cells. Neurobiol Dis, 2010,37(1): 218–227
Yu JY, Vodyanik M, Smuga-Otto K, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science, 2007,318(5858):1917–1920
Schmidta N, Koedera D, Messinga M, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-stimulated cerebral microvascular endothelial cells mediate the recruitment of neural stem cells to the neurovascular niche. Brain Res, 2009,1268:24–37
Kermani P, Hempstead B. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor: a newly described mediator of angiogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc Med, 2007,17(4):140–143
Christiea V, Maltmana D, Hendersona A, et al. Retinoid supplementation of differentiating human neural progenitors and embryonic stem cells leads to enhanced neurogenesis in vitro. J Neurosci Methods, 2010,193(2): 239–245
Wang G, Ao Q, Gong K, et al. Synergistic effect of neural stem cells and olfactory ensheathing cells on repair of adult rat spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant, 2010,19(10): 1325–1337
Habisch HJ, Liebau S, Lenk T et al. Neuroectodermally converted human mesenchymal stromal cells provide cytoprotective effects on neural stem cells and inhibit their glial differentiation. Cytotherapy, 2010,12(4):491–504
Wang YB, Liu YH, Liu LB, et al. Primary culture of brain microvascular endothelial cell and its biological behavior study. Chin J Neuroanat (Chinese), 2006,22(2): 224–228
Liu KM, Chi LX, Lu XH, et al. Primary culture of rat brain microvascular endothelial cell. Acta Academiae Medicinae Militaris Tertiae (Chinese), 2007,29(20): 2011–2013
Liang CF, Guo Y, Shi DJ, et al. Isolation and primary culture of rat brain microvascular endothelial cells. Chin J Pathophysiol (Chinese), 2008,24(5):1038–1040
Bürgers HF, Schelshorn DW, Wagner W, et al. Acute anoxia stimulates proliferation in adult neural stem cells from the rat brain. Exp Brain Res, 2008,188(1):33–43
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, Yj., Yin, B., Xiao, Lc. et al. Proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells co-cultured with cerebral microvascular endothelial cells after oxygen-glucose deprivation. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 33, 63–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1072-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-013-1072-4