Summary
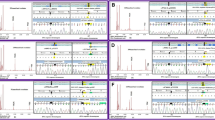
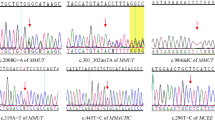
Methylmalonic aciduria (MMA) is a common inherited autosomal recessive disorder resulting from defects in the enzyme methylmalonyl CoA mutase (MCM, mut complementation group) or in the synthesis of the MCM cofactor adenosylcobalamin (cbl complementation groups). The defects in the mut complementation group accounts for the largest number of patients with isolated MMA. At least 200 mutations in the MUT gene on chromosome 6p12 have been identified in MMA patients until now. This study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics of MMA and genomic variations in the MUT gene of Chinese patients. Genomic DNA was extracted from 18 patients who were diagnosed as having isolated MMA by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry (GC-MS), and from some of their parents as well. Amplification and direct sequencing of the MUT coding regions (exon 2–13) and their adjacent intronic consensus splice sites were performed in order to identify the disease causing mutations. In this group, six novel mutations in the MUT gene, c.424A>G (p.T142A), c.786T>G (p.S262R), c.808G>C (p.G270R), c.1323_1324insA, c.1445-1G>A and c.1676+77A>C were identified. p.T142A and p.G270R were respectively detected at a heterozygous level in one patient. Two previously reported mutations, c.682C>T (p.R228X) and c.323G>A (p.R108H) were also found in this study. In addition, six previously described single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), c.636A>G (p.K212K), c.1495G>A (p.A499T), c.1595A>G (p.H532R), c.1992G>A (p.A664A), c.2011G>A (p.V671I) and c.1677-53A>G were identified. In this study, we updated the spectrum of MUT mutations and identified the main MMA-causing mutations in Chinese MMA patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dionisi-Vici C, Deodato F, Röschinger W, et al. ’Classical’ organic acidurias, propionic aciduria, methylmalonic aciduria and isovaleric aciduria: Long-term outcome and effects of expanded newborn screening using tandem mass spectrometry. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2006,29(2–3): 383–389
Kobayashi A, Kakinuma H, Takahashi H. Three novel and six common mutations in 11 patients with methylmalonic academia. Pediatr Int, 2006,48(1):1–4
Cavicchi C, Donati MA, Funghini S, et al. Genetic and biochemical approach to early prenatal diagnosis in a family with mut methylmalonic aciduria. Clin Genet, 2006,69(1):72–76
Martínez MA, Rincón A, Desviat LR, et al. Genetic analysis of three genes causing isolated methylmalonic acidemia: identification of 21 novel allelic variants. Mol Genet Metab, 2005,84(4):317–325
Janata J, Kogekar N, Fenton WA. Expression and kinetic characterization of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase from patients with the mutphenotype: evidence for naturally occurring interallelic complementation. Hum Mol Genet, 1997, 6(9):1457–1464
Nham SU, Wilkemeyer MF, Ledley FD. Structure of the human methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MUT) locus. Genomics, 1990,8(4):710–716
Richard E, Monteoliva L, Juarez S, et al. Quantitative analysis of mitochondrial protein expression in methylmalonic acidemia by two-dimensional difference gel electrophoresis. J Proteome Res, 2006,5(7):1602–1610
Ledley FD, Lumetta MR, Zoghbi HY. Mapping of human methylmalonyl CoA mutase (MUT) locus on chromosome 6. Am J Hum Genet, 1998,42(6):839–846
Cavicchi C, Donati MA, Pasquini E, et al. Mutational spectrum in ten Italian patients affected by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2005, 28(6):1175–1178
Fowler B, Leonard JV, Baumgartner MR. Causes of and diagnostic approach to methylmalonic acidurias. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2008,31(3):350–360
Hörster F, Hoffmann GF. Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of methylmalonic aciduria-recent advances and new challenges. Pediatr Nephrol, 2004,19(10):1071–1074
Zwickler T, Lindner M, Aydin HI, et al. Diagnostic work-up and management of patients with isolated methylmalonic acidurias in European metabolic centres. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2008, 31(3):361–367
Lerner-Ellis JP, Gradinger AB, Watkins D, et al. Mutation and biochemical analysis of patients belonging to the cblB complementation class of vitamin B12-dependent methylmalonic aciduria. Mol Genet Metab, 2006,87(3): 219–225
Suormala T, Baumgartner MR, Coelho D, et al. The cblD defect causes either isolated or combined deficiency of methylcobalamin and adenosylcobalamin synthesis. J Biol Chem, 2004,279(41):42742–42749
Touati G, Valayannopoulos V, Mention K, et al. Methylmalonic and propionic acidurias: management without or with a few supplements of specific amino acid mixture. J Inherit Metab Dis, 2006,29(2–3):288–298
Fuchshuber A, Mucha B, Baumgartner ER, et al. mut0 methylmalonic acidemia: eleven novel mutations of the methylmalonyl CoA mutase including a deletion-insertion mutation. Hum Mutat, 2000, 16(2):179
Fenton WA, Rosenberg LE. Disorders of propionate and methylmalonate metabolism. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WM, et al, eds. The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease. New York: McGraw-Hill, 1995,1423–1450
Ying YQ, Wei H, Cao LZ, et al. Clinical features and growth hormone receptor gene mutations of patients with Laron syndrome from a Chinese family. Chin J Contemp Pediatr, 2007, 9(4):335–338
Acquaviva C, Benoist JF, Pereira S, et al. Molecular basis of methylmalonyl-CoA mutase apoenzyme defect in 40 European patients affected by mut(o) and mut- forms of methylmalonic acidemia: identification of 29 novel mutations in the MUT gene. Hum Mutat, 2005,25(2):161–176
Worgan LC, Niles K, Tirone JC, et al. Spectrum of mutations in mut methylmalonic acidemia and identification of a common Hispanic mutation and haplotype. Hum Mutat, 2006,27(1):31–43
Wajner M, Coelho Dde M, Ingrassia R, et al. Selective screening for organic acidemias by urine organic acid GC-MS analysis in Brazil: fifteen-year experience. Clin Chim Acta, 2009,400(1–2):77–81
Nakagawa K, Kawana S, Hasegawa Y, et al. Simplified method for the chemical diagnosis of organic aciduria using GC/MS. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci, 2010,878(13–14):942–948
Wasant P, Liammongkolkul S, Kuptanon C, et al. Organic acid disorders detected by urine organic acid analysis: twelve cases in Thailand over three-year experience. Clin Chim Acta, 2008,392(1–2):63–68
Cosson MA, Benoist JF, Touati G, et al. Long-term outcome in methylmalonic aciduria: A series of 30 French patients. Mol Genet Metab, 2009,97(3):172–178
Peters HL, Nefedov M, Lee LW, et al. Molecular studies in mutase-deficient (MUT) methylmalonic aciduria: identification of five novel mutations. Hum Mutat, 2002, 20(5):406–410
Berger I, Shaag A, Anikster Y, et al. Mutation analysis of the MCM gene in Israeli patients with mut(0) disease. Mol Genet Metab, 2001,73(1):107–110
Chang HB, Wu JX, Liu ZW, et al. Molecular analysis of two novel mut gene mutations in Chinese patient with methylmalonic academia. Zhonghua Shen Jing Ke Za Zhi (Chinese), 2006,39(11):742–744
Wang F, Han L, Ye J, et al. Analysis of the MUT gene mutations in patients with methylmalonic academia. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi (Chinese), 2009, 26(5):485–489
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This project was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (2005CB522507) and the 11th Five-year Plan of National Science & Technology (2006BAI05A07).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yi, Q., Lv, J., Tian, F. et al. Clinical characteristics and gene mutation analysis of methylmalonic aciduria. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 31, 384–389 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0386-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-011-0386-3