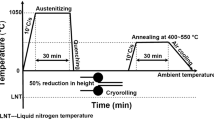
Abstract
A novel design scheme of hot stamping, quenching and partitioning process was conducted in a quenchable boron steel to obtain the nanometric duplex microstructure comprising ultrafine retained austenite and martensite. It is shown that the materials possess excellent mechanical properties and the ductility can be further improved without compromising the strength. The newly treated steel shows excellent mechanical properties and the total elongation of the steel increases from 6.6% to 14.8% compared with that of hot stamped and quenched steel. Therefore, this kind of steel has become another group of advanced high-strength steels. The microstructure which is mainly responsible for such excellent mechanical properties was investigated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Speer J G, De Moor E, Findley K O, et al. Analysis of Microstructure Evolution in Quenching and Partitioning Automotive Sheet Steel[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2011, 42(12): 3591–3601
Bhadeshia H. Computational Design of Advanced Steels[J]. Scripta Mater., 2014, 70: 12–17
Naderi M, Abbasi M, Saeed-Akbari A. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of a Hot-stamped Advanced High-Strength Steel via Tempering Treatment[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2013, 44(4): 1852–1861
Liu H, Lu X, Jin X, et al. Enhanced Mechanical Properties of a Hot Stamped Advanced High-Strength Steel Treated by Quenching and Partitioning Process[J]. Scripta Mater., 2011, 64(8): 749–752
Nikravesh M, Naderi M, Akbari G H. Influence of Hot Plastic Deformation and Cooling Rate on Martensite and Bainite Start Temperatures in 22MnB5 Steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2012, 540: 24–29
Kolleck R, Steinhoefer D, Feindt J A, et al. Manufacturing Method for Safety and Structural Body Parts for Lightweight Body Design[C]. Proceedings IDDRG, Sindelfingen, 2004
Liu H S, Xing Z W, Bao J, et al. Investigation of the Hot-Stamping Process for Advanced High-Strength Steel Sheet by Numerical Simulation[J]. J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2010, 19(3): 325–334
Kolleck R, Veit R, Merklein M, et al. Investigation on Induction Heating for Hot Stamping of Boron Alloyed Steels[J]. CIRP Annals-Manuf. Technol., 2009, 58(1): 275–278
Merklein M, Lechler J, Geiger M. Characterisation of the Flow Properties of the Quenchenable Ultra High Strength Steel 22MnB5[J]. CIRP Annals-Manuf. Technol., 2006, 55(1): 229–232
Heping Liu, Liu B, Li D, et al. Hot Deformation Behavior of Low Carbon Steel during Compression at Elevated Temperature[J]. J.Wuhan Univ.Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2014, 29(3): 601–605
Hoffmann H, So H, Steinbeiss H. Design of Hot Stamping Tools with Cooling System[J]. CIRP Annals-Manuf. Technol., 2007, 56(1): 269–272
Bardelcik A, Salisbury C P, Winkler S, et al. Effect of Cooling Rate on the High Strain Rate Properties of Boron Steel[J]. Int. J. Impact Eng., 2010, 37(6): 694–702
Lin N, Guo J, Xie F, et al. Comparison of Surface Fractal Dimensions of Chromizing Coating and P110 Steel for Corrosion Resistance Estimation[J]. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 311(9): 330–338
Lin N, Huang X, Zou J, et al. Effects of Plasma Nitriding and Multiple Arc Ion Plating TiN Coating on Bacterial Adhesion of Commercial Pure Titanium via in Vitro Investigations[J]. Surf. Coa. Technol., 2012, 209(38): 212–215
Speer J, Matlock D K, De Cooman B C, et al. Carbon Partitioning into Austenite after Martensite Transformation[J]. Acta Mater., 2003, 51(9): 2611–2622
De Moor E, Speer J G, Matlock D K, et al. Quenching and Partitioning of CMnSi Steels Containing Elevated Manganese Levels[J]. Steel Res. Int., 2012, 83(4): 322–327
Speer J G, Edmonds D V, Rizzo F C, et al. Partitioning of Carbon from Supersaturated Plates of Ferrite, with Application to Steel Processing and Fundamentals of the Bainite Transformation[J]. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci., 2004, 8(3): 219–237
Clarke A J, Speer J G, Matlock D K, et al. Influence of Carbon Partitioning Kinetics on Final Austenite Fraction during Quenching and Partitioning[J]. Scripta Mater., 2009, 61(2): 149–152
Edmonds D V, Speer J G. Martensitic Steels with Carbide Free Microstructures Containing Retained Austenite[J]. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26(4): 386–391
Edmonds D V, He K, Rizzo F C, et al. Quenching and Partitioning Martensite-A Novel Steel Heat Treatment[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2006, 438: 25–34
Liu H, Sun H, Liu B, et al. An Ultrahigh Strength Steel with Ultrafinegrained Microstructure Produced through Intercritical Deformation and Partitioning Process[J]. Mater. Des., 2015, 83: 760–767
Santofimia M J, Speer J G, Clarke A J, et al. Influence of Interface Mobility on the Evolution of Austenite-Martensite Grain Assemblies during Annealing[J]. Acta Mater., 2009, 57(15): 4548–4557
Liu H, Jin X, Dong H, et al. Martensitic Microstructural Transformations from the Hot Stamping, Quenching and Partitioning Process[J]. Mater. Charact., 2011, 62(2): 223–227
Martis C J, Putatunda S K, Boileau J, et al. The Static and Dynamic Mechanical Properties of a New Low-Carbon, Low-Alloy Austempered Steel[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2014, 589: 280–287
Naderi M. Hot Stamping of Ultra High Strength Steels[D]. Germany: RWTH Aachen University, 2007
Clarke A J, Speer J G, Miller M K, et al. Carbon Partitioning to Austenite from Martensite or Bainite during the Quench and Partition (Q&P) Process: A Critical Assessment[J]. Acta Mater., 2008, 56(1): 16–22
Caballero F G, Miller M K, Clarke A J, et al. Examination of Carbon Partitioning into Austenite during Tempering of Bainite[J]. Scripta Mater., 2010, 63(4): 442–445
Shipway P H, Bhadeshia H. Mechanical Stabilisation of Bainite[J]. Mater. Sci. Technol., 1995, 11(11): 1116–1128
Mukherjee K, Hazra S S, Militzer M. Grain Refinement in Dual-Phase Steels[J]. Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, 40(9): 2145–2159
Torralba J M, Navarro A, Campos M. From the TRIP Effect and Quenching and Partitioning Steels Concepts to the Development of New High-Performance, Lean Powder Metallurgy Steels[J]. Mater. Sci. Eng., A, 2013, 573: 253–256
Bouquerel J, Verbeken K, De Cooman B C. Microstructure-Based Model for the Static Mechanical Behaviour of Multiphase Steels[J]. Acta Mater., 2006, 54(6): 1443–1456
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Funded by the School Foundation of North University of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.51206081,51571141), Science and Technology Innovation Project of Shanxi Province(No.2016156), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation(No.2016M590214), Key Research and Development Program of Shanxi Province(No.201603D121002-3) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, China (Nos.2015011036, 2014011024-6)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Sun, F., Sun, H. et al. Analysis of microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrafine grained low carbon steel. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mat. Sci. Edit. 31, 1099–1104 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1496-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11595-016-1496-3