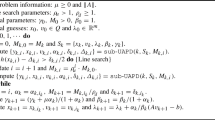Abstract
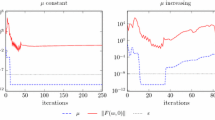
We propose a new class of incremental primal–dual techniques for solving nonlinear programming problems with special structure. Specifically, the objective functions of the problems are sums of independent nonconvex continuously differentiable terms minimized subject to a set of nonlinear constraints for each term. The technique performs successive primal–dual increments for each decomposition term of the objective function. The primal–dual increments are calculated by performing one Newton step towards the solution of the Karush–Kuhn–Tucker optimality conditions of each subproblem associated with each objective function term. We show that the resulting incremental algorithm is q-linearly convergent under mild assumptions for the original problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abello, J., Pardalos, P.M., Resende, M. (eds): Handbook of Massive Data Sets. Series: Massive Computing, vol. 4. Springer, New York (2002)
Bertsekas D.P.: Incremental least squares methods and the extended Kalman filter. SIAM J. Optim. 6(3), 807–822 (1996)
Bertsekas D.P.: A new class of incremental gradient methods for least squares problems. SIAM J. Optim. 7(4), 913–926 (1997)
Bersekas, D.P.: Incremental gradient, subgradient, and proximal methods for convex optimization: a survey. Technical Report LIDS-2848, Laboratory for Information and Decision Systems, MIT, Cambridge, MA (2010)
Couellan, N.P.: Primal-dual techniques for nonlinear programming and applications to artificial neural network training. Ph.D. Dissertation, School of Industrial Engineering, University of Oklahoma, Norman, OK (1997)
Couellan, N.P., Trafalis, T.B: Online SVM learning via an incremental primal-dual technique. Optim. Methods Soft. (2011) (submitted)
Davidon W.C.: New least-square algorithms. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 18(2), 187–197 (1976)
Dennis J.E., Schnabel R.B.: Numerical Methods for Unconstrained Optimization and Nonlinear Equations. Classics in Applied Mathematics. SIAM, Philadelphia (1996)
El-Bakry A.S., Tapia R.A., Tsuchiya T., Zhang Y.: On the formulation and theory of the primal-dual Newton interior point method for nonlinear programming. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 89, 507–541 (1996)
Kallrath J.: Polylithic modeling and solution approaches using algebraic modeling systems. Optim. Lett. 5(3), 453–466 (2011)
Kohn W., Zabinsky Z.B., Brayman V.: Optimization of algorithmic parameters using a meta-control approach. J. Glob. Optim. 34(2), 293–316 (2006)
Lustig I.J., Marsten R.E., Shanno D.F.: Computational experiences with a primal-dual interior point method for linear programming. Linear Algebra Appl. 152, 191–222 (1991)
Nocedal J., Wright S.J.: Numerical Optimization. Springer, New York (1999)
Pardalos P.M., Resende M.: Handbook of Applied Optimization. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2002)
Söderstrom T., Stoica P.: System Identification. Prentice Hall International (UK), Englewood Cliffs (1989)
Trafalis, T.B., Couellan, N.P.: An incremental nonlinear primal-dual algorithm and applications to artificial neural networks training. In: Large Scale Systems: Theory and Applications, 1995. 7th IFAC/IFORS/IMACS Symposium, Oxford, UK (1995) (postprint volume)
Tseng, P.: Incremental gradient(-projection) method with momentum term and adaptive stepsize rule. Technical Report, Department of Mathematics, University of Washington, Seattle, WA (1995)
Yamashita, H.: A globally convergent primal-dual interior point method for constrained optimization. Technical Report, Mathematical System Institute, Inc., Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Couellan, N.P., Trafalis, T.B. An incremental primal–dual method for nonlinear programming with special structure. Optim Lett 7, 51–62 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-011-0393-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-011-0393-0