Abstract
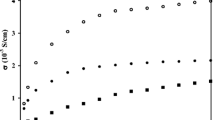
Nano-sized silica poly(methylmethacrylate)-based gel electrolyte containing lithium hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6) was synthesized by using different binary solvent mixture (propylene carbonate(PC) and dimethylformamide (DMF) in different volume ratio). Role of DMF in PC: Higher DMF content in PC-based electrolyte shows higher ionic conductivity at all polymer content and at wide temperature regions (10-70 °C). A small increment in ionic conductivity at lower content of polymer in liquid/gel electrolyte was observed and having maximum conductivity of 13.12 mS/cm at 25 °C. Stability (mechanically and electrically), viscosity and ionic conductivity of gel electrolytes were improved with the addition of nano-sized silica at ambient temperature. Ionic conductivity of nano-sized silica-based gel electrolyte does not change much over 5o–70 °C temperature range and is factor-wise only which make indispensable in different electrochemical devices. Also polymer gel electrolyte membranes as such and with dispersed silica nano-particles were characterized through scanning electron microscope to study the morphology of gel matrix.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schalkwijk W A, Scrosati B (2002) Advances in lithium-ion batteries. Springer: 1–5. ISBN 978–0–306-47508-5
Tarascon J-M, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367. doi:10.1038/35104644
Armand M, Tarascon J (2008) Building better batteries. Nature 451:652–657. doi:10.1038/451652a
Xu K (2004) Nonaqueous liquid electrolytes for lithium-based rechargeable batteries. Chem Rev 104:4303–4418. doi:10.1021/cr030203g
Stephan AM (2006) Review on gel polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Eur Polym J 42:21–42
Uma T, Mahalingam T, Stimming U (2005) Conductivity studies on poly(methyl methacrylate)–Li2SO4 polymer electrolyte systems. Mater Chem Phys 90:245–249
Adebahr J, Byrne N, Forsyth M, MacFarlane DR, Jacobsson P (2003) Enhancement of ion dynamics in PMMA-based gels with addition of TiO2 nano-particles. Electrochim Acta 48:2099. doi:10.1016/S0013-4686(03)00191-9
Nicotera I, Coppola L, Oliviero C, Castriota M, Cazzanelli E (2006) Nuclear magnetic resonance. Solid State Ionics 177:581–588
Bruce PG (1995) Structure and electrochemistry of polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 40(13–14):2077–2085. doi:10.1016/0013-4686(95)00144-4
Song JY, Wang YY, Wan CC (1999) Review of gel type polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. J Power Sources 77:183–187. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2005.09.017
Ito Y, Kanehori K, Miyauchi K, Kudo T (1987) Ionic conductivity of electrolytes formed from PEO-LiCF3SO3 complex low molecular weight poly (ethylene glycol). J Mater Sci 22:1845–1849
Feuillade G, Perche P (1975) Ion-conductive macromolecular gels and membranes for solid lithium cells. J Appl Electrochem 5:63–69 ISSN: 0021-891X
Choi B, Kim Y, Shin H (2000) Ionic conduction in PEO–PAN blend polymer electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 45:1371–1374. doi:10.1016/S0013-4686(99)00345-X
Ramesh S, Leen K, Kumutha K, Arof A (2007) FTIR studies of PVC/PMMA blend based polymer electrolytes. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 66:1237–1242. doi:10.1016/j.saa.2006.06.012
Lee H, Yoo J, Park J, Kim J, Kang K, Jung S (2012) A stretchable polymer–carbon nanotube composite electrode for flexible lithium-ion batteries: porosity engineering by controlled phase separation. Adv Energy Mater 2:976–982
Ahmad S, Bohidar HB, Ahmad S, Agnihotry SA (2006) Polymer nanocomposites handbook. Polymer 47:3583–3590
Singh B, Kumar R, Sekhon SS (2005) Conductivity and viscosity behavior of PMMA based gels and nano dispersed gels: Role of dielectric constant of solvent. Solid State Ionics 176:1577–1583. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2005.05.001
Sloop SE, Pugh JK, Kerr JB, Kinoshita K (2000) Chemical reactivity of PF5 and LiPF6 in ethylene carbonate/dimethyl carbonate solutions. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 4:A42–A44. doi:10.1149/1.1353158
Barlowz C (1999) Reaction of water with hexafluorophosphates and with Li bis (perfluoroethylsulfonyl) imide salt. Electrochem Solid-State Lett 2:362–364
Abraham K (1993) Directions in secondary lithium battery research and development. Electrochim Acta 38:1233–1248. doi:10.1016/0013-4686(93)80054-4
Chandra S, Sekhon SS, Arora N (2000) PMMA based protonic polymer gel electrolytes. Ionics 6:112–118. doi:10.1007/BF02375554
Shmukler LE, Thuc NV, Fadeeva YA, Safonova LP (2012) Proton conducting gel electrolytes based on polymethylmethacrylate doped with sulfuric acid solutions in N,N-dimethylformamide. J Polym Res 19:9770. doi:10.1007/s10965-011-9770-8
Xuan X, Wang J, Tang J, Qu G, Lu J (2000) Vibrational spectroscopic studies on ion solvation of lithium perchlorate in propylene carbonate + N,N-dimethylformamide mixtures. Spectrochim Acta A 56:2131–2139
Ericson H, Svanberg C, Brodin A, Grillone AM, Panero S, Scrosati B, Jacobsson P (2000) Poly(methyl methacrylate)-based protonic gel electrolytes: a spectroscopic study. Electrochim Acta 45:1409–1414
Grillone AM, Panero S, Retamal BA, Scrosati B (1999) Proton polymeric gel electrolyte membranes based on polymethylmethacrylate. J Electrochem Soc 146(1):27–31
Wieczorek W, Ukowska GZ, Borkowska R, Chung SH, Greenbaum S (2001) A basic investigation of anhydrous proton conducting gel electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 46:1427–1438
Sharma S, Dhiman N, Pathak D, Kumar R (2016) Effect of nano-size fumed silica on ionic conductivity of PVdF-HFP-based plasticized nano-composite polymer electrolytes. Ionics . doi:10.1007/s11581-016-1721-2in press
Palomares V, Serras P, Villaluenga I, Hueso KB, Gonzalez JC, Rojo T (2012) Na-ion batteries, recent advances and present challenges to become low cost energy storage systems. Energy Environ Sci 5:5884–5901. doi:10.1039/c2ee02781j
Stallworth PE, Fontanella JJ, Wintersgill MC, Scheidler CD, Immel JJ, Greenbaum SG, Gozdz AS (1999) NMR, DSC and high pressure electrical conductivity studies on liquid and hybrid electrolytes. J Power Sources 81:739–747. doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(99)00144-5
Arora N, Sharma A, Kumar A, Kumar R (2014) PMMA based polymer gel electrolyte containing LiCF3SO3 i-manager. J Mater Sci 2(1):24–26 ISSN -2347-2235
Lassegues JC, Desbat B, Trinquet O, Cruege F, Poinsignon C (1989) From model solid-state protonic conductor to new polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 35:17–25
Raducha D, Wieczorek W, Florjanczyk Z, Stevens JR (1996) Nonaqueous H3PO4-doped gel electrolytes. J Phys Chem 100(51):20126–20133
Wang X-L, Cai Q, Fan L-Z, Hua T, Lin Y-H, Nan C-W (2008) Gel-based composite polymer electrolytes with novel hierarchical mesoporous silica network for lithium batteries. Electrochim Acta 53:8001–8007. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2008.05.082
Zhang S, Sun N, He X, Lu X, Zhang X (2006) Physical properties of ionic liquids: database and evaluation. J Phys Chem 35(4):1475–1517. doi:10.1063/1.2204959
Kumar D, Hashmi SA (2010) Ion transport and ion-filler-polymer interaction in poly(methylmethacrylate)-based, sodium ion conducting, gel polymer electrolytes dispersed with silica nanoparticles. J Power Sources 195:5101–5108. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2010.02.026
Sun J, Bayley P, MaCfarlane DR, Forsyth M (2007) Gel electrolytes based on lithium modified silica nano-particles. Electrochim Acta 52:7083–7090. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2007.05.033
Sharma JP, Sekhon SS (2007) Nanodispersed polymer gel electrolytes: conductivity modification with the addition of PMMA and fumed silica. Solid State Ionics 178:439–445. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2007.01.017
Hashmi SA, Upadhyaya HM and Thakur AK (2000) Sodium ion conducting composite polymer electrolytes for battery applications. In: Chowdari BVR. Wang W (eds) Solid State Ionics: Materials and Devices, Fuzhou, China. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd, Singapore, p 461
Kumar B, Nellutla S, Thokchom J, Chen C (2006) Ionic conduction through heterogeneous solids: Delineation of the blocking and space charge effects. J Power Sources 160:1329–1335. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.02.062
Thomas H, Vinga SD (2010) Polymer-nanoparticle composites: from synthesis to modern applications. Materials 3(6):3468–3517
Ferrari S, Quartarone E, Mustarelli P, Magistris A, Fagnoni M, Protti S, Gerbaldi C, Spinella A (2010) Lithium ion conducting PVdF-HFP composite gel electrolytes based on N-methoxyethyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)-imide ionic liquid. J Power Sources 195:559–566. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.08.015
Kumar B (2004) From colloidal to composite electrolytes: properties, peculiarities, and possibilities. J. Power Sources 135:215–231. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.04.038
Ciosek M, Sannier L, Siekierski M, Golodnitsky D, Peled E, Scrosati B, Głowinkowski S, Wieczorek W (2007) On transport phenomena in polymeric electrolytes. Electrochim Acta 53:1409–1416. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2007.03.037
Salem N, Abu-Lebdeh Yaser (2013) Effect of Nano-particles on Electrolytes and Electrode/Electrolyte Interface. Springer US: 221–244.
Ahmad S, Deepa M, Agnihotry SA (2008) Effects of salts on the fumed silica-based composite polymer electrolytes. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 92:184–189. doi:10.1016/j.solmat.2007.03.036
Z Fang, Wang M, Liang C, Jiang H, Shen J, Li H (2014) Thin-layer polymer wrapped enzymes encapsulated in hierarchically mesoporous silica with high activity and enhanced stability. Nature.com Scientific Reports 4, Article number: 4421. doi:10.1038/srep04421
Zhang YH, Deng Y, Cai YH, Xiao W, Sun LL (2015) Simple synthesis for hierarchical SiO2 tubes with adjustable mesoporous. International Conference on Power Electronics and Energy Engineering, Hong Kong (ed.: A. Leung), China, 19–20 April 2015 (PEEE 2015; Published by Atlantis Press) Advances in Engineering Research Volume 20: 215–218. doi: 10.2991/peee-15.2015.57, ISBN: 978–1–5108-0764-8
Guo X, Deng Y, Tu B, Zhao D (2010) Facile synthesis of hierarchically mesoporous silica particles with controllable cavity in their surfaces. Langmuir 26(2):702–708. doi:10.1021/la9023647
Ramesh S, Wen LC (2010) Investigation on the effects of addition of SiO2 nanoparticles on ionic conductivity, FTIR, and thermal properties of nanocomposite PMMA–LiCF3SO3–SiO2. Ionics 16:255–262. doi:10.1007/s11581-009-0388-3
Kumar D, Suleman M, Hashmi SA (2011) Studies on poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) based gel electrolyte nanocomposite for sodium–sulfur batteries. Solid State Ionics 202:45–53. doi:10.1016/j.ssi.2011.09.001
Choudhury S, Mangal R, Agrawal A, Archer LA (2015) A highly reversible room-temperature lithium metal battery based on crosslinked hairy nanoparticles. Nat Commun 6:10101. doi:10.1038/ncomms10101
Hong S, Lee M, Song H-J, Jun Y, Han C-H (2016) Preparation of pyridinium iodide-grafted nano-silica and its application to nano-gel systems for dye sensitized solar cells. Synth Met 215:14–20. doi:10.1016/j.synthmet.2016.01.023
Kim D-W (2000) Electrochemical characterization of poly(ethylene-co-methylacrylate)-based gel polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion polymer batteries. J Power Sources 87:78–83. doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(99)00363-8
Li Y, Yerian J-A, Khan S-A, Fedkiw P-S (2006) Crosslinked fumed silica-based nanocomposite electrolytes for rechargeable lithium batteries. J Power Sources 161:1288–1296. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.06.015
Chen H-W, Chiang Y-D, Kung C-W, Sakai N, Ikegami M, Yamauchi Y, Wu Kevin C-W, Miyasaka T, Ho K-C (2014) Highly efficient plastic-based quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cells with light-harvesting mesoporous silica nanoparticles gel-electrolyte. J Power Sources 245:411–417. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2013.06.142
Dey A, Karan S, De SK (2013) Effect of nano-additives on ionic conductivity of solid polymer electrolyte. Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Physics 51:281–288
Singh THJ, Bhat SV (2003) Morphology and conductivity studies of a new solid polymer electrolyte: (PEG)xLiClO4. Bull Mater Sci 26(7):707–714 © Indian Academy of Sciences
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Bhuvaneswari MS (2004) Vibrational, ac impedance and dielectric spectroscopic studies of poly(vinylacetate)–N, N–dimethylformamide–LiClO4 polymer gel electrolytes. J Power Sources 134:235–240
Jiang J, Gao D, Li Z, Su G (2006) Gel polymer electrolytes prepared by in situ polymerization of vinyl monomers in room-temperature ionic liquids. Reactive & Functional Polymers 66:1141–1148
Chand N, Rai N, Agrawal SL, Patel SK (2011) Morphology, thermal, electrical and electrochemical stability of nano aluminium-oxide-filled polyvinyl alcohol composite gel electrolyte. Bull Mater Sci 34(7):1297–1304 © Indian Academy of Sciences
Yang M, Hou J (2012) Membranes in lithium ion batteries. Membranes 2:367–383. doi:10.3390/membranes2030367
Chew KW, Tan KW (2011) The effects of ceramic fillers on PMMA-based polymer electrolyte salted with lithium Triflate, LiCF3SO3. Int J Electrochem Sci 6:5792–5801
Zhang J, Sun B, Huang X, Chen S, Wang G (2014) Honeycomb-like porous gel polymer electrolyte membrane for lithium ion batteries with enhanced safety. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4(6007):1–7. doi:10.1038/srep06007
Sabrina Q, Majid N, Prihandoko B (2016) Application of PVDF composite for lithium-ion battery separator. Journal of Physics: Conference Series; 8th International Conference on Physics and its Applications (ICOPIA) IOP Publishing Ltd 776:1–6 . doi:10.1088/1742-6596/776/1/012062012062
HariHaraPriya G, Suganya N, Jaisankar V (2015) A study on the ionic conductivity and structural properties of plasticised polymer nanocomposite electrolyte on the addition of nano CeO2. International Journal of Advanced Chemical Science and Applications (IJACSA) 3(1):6–14 ISSN (Online): 2347-761X
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank UGC, New Delhi and Principal, D.A.V College, Amritsar for providing research facilities via UGC-CPE grant. The authors are thankful to Ms. Monica Nanda and Mr. Viney Sharma (research fellow) from PG Department of Physics, D.A.V. College, Amritsar for the help in the experimental work and fruitful manuscript discussions. Authors are also thankful to Dr. Kamaldeep Paul, School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Thapar University, Patiala for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arora, N., Singh, S. & Kumar, R. Effect of nano-dispersed silica on the ion-conducting behavior of PMMA-based polymer gel electrolytes containing LiPF6 . Ionics 23, 2685–2695 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2038-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-017-2038-5