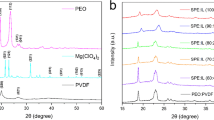
Abstract
Solid polymer electrolytes (SPEs) based on polyethylene oxide (PEO) complexed with magnesium triflate Mg(Tf)2 or Mg(CF3SO3)2) and incorporating the ionic liquid (IL) (1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (PYR14TFSI)) were prepared by solution cast technique. The electrolyte was optimized and characterized using electrical conductivity, cationic transport number measurements, and cyclic voltammetry. The highest conductivity of the PEO/Mg(Tf)2, 15:1 (molar ratio), electrolyte at room temperature was 1.19 × 10−4 S cm−1 and this was increased to 3.66 × 10−4 S cm−1 with the addition of 10 wt.% ionic liquid. A significant increase in the Mg2+ ion transport number was observed with increasing content of the ionic liquid in the PEO-Mg(Tf)2 electrolyte. The maximum Mg2+ ion transport number obtained was 0.40 at the optimized electrolyte composition. A battery of the configuration Mg/ and [(PEO)15:Mg(Tf)2+10%IL]/TiO2-C was assembled and characterized. Preliminary studies showed that the discharge capacity of the battery was 45 mA h g−1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2001) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. Nature 414:359–367
Kumar GG, Munichandraiah N (1999) Reversibility of Mg/Mg 2+ couple in a gel polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 44:2663–2666
Connor JH, Reid WE, Wood GB (1957) Electrodeposition of metals from organic solutions V. Electrodeposition of magnesium and magnesium alloys. J Electrochem Soc 104:38–41
Cheek G, O’Grady W, El Abedin SZ, Moustafa E, Endres F (2008) Studies on the electrodeposition of magnesium in ionic liquids. J Electrochem Soc 155:D91–DD5
Inamoto M, Kurihara H, Yajima T (2013) Vanadium pentoxide-based composite synthesized using microwave water plasma for cathode material in rechargeable magnesium batteries. Materials 6:4514–4522
Pandey G, Hashmi S (2009) Experimental investigations of an ionic-liquid-based, magnesium ion conducting, polymer gel electrolyte. J Power Sources 187:627–634
Yoshimoto N, Shirai T, Morita M (2005) A novel polymeric gel electrolyte systems containing magnesium salt with ionic liquid Electrochimica acta 50: 3866–3871
Kim JK, Matic A, Ahn JH, Jacobsson P (2010) An imidazolium based ionic liquid electrolyte for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 195:7639–7643
Armand M, Endres F, MacFarlan DR, Ohno H, Scrosati B (2009) Ionic-liquid materials for the electrochemical challenges of the future. Nat Mater 8:621–629
Pitawala J, Navarra MA, Scrosati B, Jacobsson P, Matic A (2014) Structure and properties of Li-ion conducting polymer gel electrolytes based on ionic liquids of the pyrrolidinium cation and the bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl) imide anion. J Power Sources 245:830–835
Kumar Y, Hashmi S, Pandey G (2011) Ionic liquid mediated magnesium ion conduction in poly (ethylene oxide) based polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 56:3864–3873
Evans J, Vincent CA, Bruce PG (1987) Electrochemical measurement of transference numbers in polymer electrolytes. Polymer 28:2324–2328
Kumar GG, Munichandraiah N (2002) Poly (methylmethacrylate)—magnesium triflate gel polymer electrolyte for solid state magnesium battery application. Electrochim Acta 47:1013–1022
Bruce P, Vincent C (1993) Polymer electrolytes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 89:3187–3203
Narayanan NV, Raj BA, Sampat S (2009) Magnesium ion conducting, room temperature molten electrolytes. Electrochem Commun 11:2027–2031
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarangika, H.N.M., Dissanayake, M.A.K.L., Senadeera, G.K.R. et al. Polyethylene oxide and ionic liquid-based solid polymer electrolyte for rechargeable magnesium batteries. Ionics 23, 2829–2835 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1870-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1870-3