Abstract
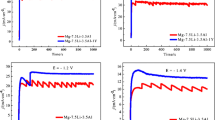
MnO2 doped with Ce was hydrothermally synthesized and the as-made breathable waterproof membrane used outside the cathode was prepared for improving the lithium-air battery performance in air. The samples were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectrum analysis (EDS), charge–discharge cycle tests, charge–discharge cycle tests of limited capacity, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) tests. The result showed that Ce x Mn1-x O2 can effectively reduce the charge overpotential of the cathode. The charge and discharge electrical potential difference of Ce0.1Mn0.9O2 was only 700 mV while MnO2’s was 2100 mV. And Ce0.1Mn0.9O2 that exhibited high discharge capacity of 400 mAh g−1 in air had a stable discharge platform of 2.5 V and then the more obvious charge phenomenon appeared after 3.5 V. The excellent catalysis, the effect of cathode catalytic materials named Ce x Mn1-x O2, may attribute to the decrease of reaction potential energy of oxygen reduction reaction and oxygen evolution reaction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Girishkumar G, McCloskey B, Luntz AC, Swanson S, Wilcke W (2010) Lithium air battery: promise and challenges. J Phys Chem Lett 1:2193–2203
Bruce PG, Freunberger SA, Hardwick LJ, Jean-Marie T (2011) Li-O2 and Li-S batteries with high energy storage. Nat Mater 11:19–29
Zhang YN, Zhang HM, Li J, Wang MR, Nie HJ, Zhang FX (2013) The use of mixed carbon materials with improved oxygen transport in a lithium-air battery. J Power Sources 240:390–396
Yang XH, He P, Xia YY (2009) Preparation of mesocellular carbon foam and its application for lithium/oxygen battery. Electrochem Commun 11(6):1127–1130
Xiao J, Wang D, Xu W, Wang DY, Willifird RE, Liu J (2010) Optimization of air electrode for Li/air batteries. J Electrochem Soc 157(4):487–492
Sun B, Huang K, Qi X et al (2015) Rational construction of a functionalized V 2 O 5, nanosphere/MWCNT layer-by-layer nanoarchitecture as cathode for enhanced performance of lithium-ion batteries. J Adv Funct Mater 25(35):5716–5716
Sun F, Huang K, Qi X et al (2013) A rationally designed composite of alternating strata of Si nanoparticles and graphene: a high-performance lithium-ion battery anode. J Nanoscale 5(18):8586–8592
Ren L, Liu Y, Qi X et al (2012) An architectured TiO2 nanosheet with discrete integrated nanocrystalline subunits and its application in lithium batteries. J Mater Chem 40(40):21513–21518
Tang H, Qi X, Han W et al (2015) SnS2 nanoplates embedded in 3D interconnected graphene network as anode material with superior lithium storage performance. J Appl Surf Sci 355:7–13
Arango-Diaz A, Cecilia JA, Marrero-Jerez J et al (2016) Freeze-dried Co3O4-CeO2 catalysts for the preferential oxidation of CO with the presence of CO2 and H2O in the feed. J Ceram Int 42(6):7462–7474
Mizuno F, Nakanishi S, Kotani Y, Yokoishi S, Iba H (2010) Rechargeable Li-air batteries with carbonate-based liquid electrolytes. Electrochemistry 78(5):403–405
Qin Y, Lu J, Du P, Chen Z, Ren Y, Wu TP, Miller JT, Wen JG, Miller DJ, Zhang ZC, Amine K (2013) In situ fabrication of porous-carbon-supported alpha-MnO2 nanorods at room temperature: application for rechargeable Li-O2 batteries. Energy Environ Sci 6:519–531
Li J, Wang N, Zhao Y, Ding Y, Guan L (2011) MnO2 nanoflakes coated on multi-walled carbon nanotubes for rechargeable lithium-air batteries. Electrochem Commun 13(7):698–700
Thapa AK, Hidaka Y, Hagiwara H, Ida S, Ishihara T (2011) Mesoporous β-MnO2 air electrode modified with Pd for rechargeability in lithium-air battery. J Electrochem Soc 158(12):1483–1489
Yang Y, Sun Q, Li YS, Li YS, ZW F (2013) A CoO x /carbon double-layer thin film air electrode for nonaqueous Li-air batteries. J Power Sources 223:312–318
Minowa H, Hayashi M, Hayashi K, Kobayashi R, Takahashi K (2013) Mn-Fe-based oxide electrocatalysts for air electrodes of lithium-air batteries. J Power Sources 244:17–22
Shitta-Bey GO, Mirzaeian M, Halla PJ (2012) The electrochemical performance of phenol-formaldehyde based activated carbon electrodes for lithium/oxygen batteries. J Electrochem Soc 159:A315–A320
Zhang LL, Zhang XB, Wang ZL, JJ X, Xu D, Wang LM (2012) High aspect ratio γ-MnOOH nanowires for high performance rechargeable nonaqueous lithium–oxygen batteries. Chem Commun 48(61):7598–7600
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, K., Zhu, Y. & Shi, H. Effect of Ce-doped MnO2 catalyst on the lithium-air batteryperformance in the ambient atmosphere. Ionics 23, 385–393 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1832-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-016-1832-9