Abstract
The novel anode material for lithium-ion batteries, silicon–oxygen–carbon (Si–O–C) composite, is prepared by a liquid solidification combined with following pyrolysis process, in which silicon dioxide (SiO2) is used as an additive agent to enhance the electrochemical performance of the composite. While the structure of the composite is confirmed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared spectra (FT-IR), the morphology and microstructure were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), respectively. SEM and TEM observations reveal that the Si–O–C powders are about 1 μm in diameter, and there is a homogenous pyrolyzed carbon layer about 5 nm thick on the surface of the particle. The Si–O–C sample as anode material can deliver a high initial charge capacity of 753.4 mAh g−1, and the capacity keeps above 500.0 mAh g−1 after 40 cycles at 100.0 mA g−1. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy results show that the composite exhibits lower charge transfer resistance and higher lithium-ion diffusion rate compared with the Si–C anode, which indicates that the composite Si–O–C could be used as a promising anode material for lithium-ion batteries.

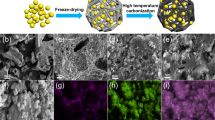
SEM images of the Si-C (a) and Si-O-C (b) samples and the TEM (c) and HRTEM (d) image of the Si-O-C sample





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kasavajjula U, Wang C, Appleby AJ (2007) J Power Sources 163:1003–1039
Tao H-C, Fan L-Z, Qu X (2012) Electrochim Acta 71:194–200
Su M, Wang Z, Guo H, Li X, Huang S, Xiao W, Gan L (2014) Electrochim Acta 116:230–236
Li X, Meduri P, Chen X, Qi W, Engelhard MH, Xu W, Ding F, Xiao J, Wang W, Wang C, Zhang J-G, Liu J (2012) J Mater Chem 22:11014–11017
Su M, Wang Z, Guo H, Li X, Huang S, Gan L, Xiao W (2013) Powder Technol 249:105–109
Song J, Chen S, Zhou M, Xu T, Lv D, Gordin ML, Long T, Melnyk M, Wang D (2014) J Mater Chem 2:1257–1262
Zhu S, Zhu C, Ma J, Meng Q, Guo Z, Yu Z, Lu T, Li Y, Zhang D, Lau WM (2013) RSC Advan 3:6141–6146
Kim J-H, Sohn H-J, Kim H, Jeong G, Choi W (2007) J Power Sources 170:456–459
Lee J-I, Lee E-H, Park J-H, Park S, Lee S-Y (2014) Advan Energ Mater 4:n/a-n/a
Wu F, Kim H, Magasinski A, Lee JT, Lin H-T, Yushin G (2014) Advan Energ Mater 4:n/a-n/a
Lai J, Guo H, Wang Z, Li X, Zhang X, Wu F, Yue P (2012) J Alloys Compd 530:30–35
Gan L, Guo H, Wang Z, Li X, Peng W, Wang J, Huang S, Su M (2013) Electrochim Acta 104:117–123
Xiao W, Wang Z, Guo H, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Gan L (2013) J Alloys Compd 560:208–214
de Guzman RC, Yang J, Cheng MM-C, Salley SO, Simon Ng KY (2014) J Power Sources 246:335–345
Lv P, Zhao H, Wang J, Liu X, Zhang T, Xia Q (2013) J Power Sources 237:291–294
Wu L, Lu J, Wei G, Wang P, Ding H, Zheng J, Li X, Zhong S (2014) Electrochim Acta 146:288–294
Terranova ML, Orlanducci S, Tamburri E, Guglielmotti V, Rossi M (2014) J Power Sources 246:167–177
Yue L, Zhang W, Yang J, Zhang L (2014) Electrochim Acta 125:206–217
Xu H, Hu X, Luo W, Sun Y, Yang Z, Hu C, Huang Y (2014) Chem Electro Chem 1:611–616
Acknowledgments
This work has been carried out with the financial support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Contract Number 51404038, National Natural Science Foundation of China under Contract Number 51472034 and Scientific Research and Development Funds of Basic Subject in Yangtze University under Contract Number 2013cjp20.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, W., Miao, C., Yan, X. et al. Novel silicon–oxygen–carbon composite with excellent cycling steady performance as anode for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 21, 2149–2153 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1391-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-015-1391-5