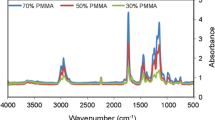
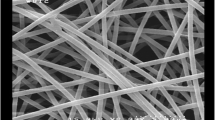
Abstract
Polyacrylonitrile/poly (vinylidene fluoride) fibrous membranes were prepared by electrospinning of PAN and PVdF solution and were soaked in 1 M lithium perchlorate (LiClO4) in ethylene carbonate (EC)/diethyle carbonate (DEC) (1:1 wt.%) solution in order to prepare polymer electrolyte membranes. Response surface method (RSM) was used to obtain a quantitative relationship between selected electrospinning parameters, i.e., applied voltage, solution concentration, and PVdF content. The measured response is ionic conductivity of electrolyte membranes. The Box–Behnken method was applied to design of experiments. Importance of parameters in the model was determined by analysis of variance (ANOVA). The model was used to find the maximum ionic conductivity of electrolyte membranes as optimum result. The morphology of fibers was investigated by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). FESEM results show that the PAN/PVdF membrane has interconnected multifibrous layers with ultrafine porous structure that leads to a high ionic conductivity and efficient lithium ion transport. Produced fibrious membranes show uniform morphology. Average fiber diameter lies between 116 and 379 nm, and membranes have high porosity of 48–90 % and electrolyte uptake of 303–493 %. The polymer electrolyte membranes show good ionic conductivity in the order of 10−3 S cm−1 at ambient temperature. Ionic conductivity decreases with increase of solution concentration and increases with increase of PVdF composition. Voltage has no significant effect on ionic conductivity of the membranes. The model predicted the maximum ionic conductivity of 7.98 mS cm−1 when the voltage was set at 21.57 kV, the solution concentration set at 14.02 wt.%, and the PVdF composition set at 69.48 wt.%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicotera I, Coppola L, Oliviero C, Russo A, Ranieri GA (2004) Some physicochemical properties of PAN-based electrolytes: solution and gel microstructures. Solid State Ion 167:213–220
Kim YW, Gong MS, Choi BK (2001) Ionic conduction and electrochemical properties of new poly (acrylonitrile-itaconate)-based gel polymer electrolytes. J Power sources 97:654–656
Sekhon SS, Arora N, Agnihotry SA (2000) PAN-based gel electrolyte with lithium salts. Solid State Ion 136:1201–1204
Deka M, Kumar A (2011) Electrical and electrochemical studies of poly (vinylidene fluoride)-clay nanocomposite gel polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. J Power sources 196:1358–1364
Saikia D, Chen-Yang YW, Chen YT, Li YK, Lin SI (2008) Investigation of ionic conductivity of composite gel polymer electrolyte membranes based on P(VDF-HFP), LiClO4 and silica aerogel for lithium ion battery. Desalination 234:24–32
Nunes-Pereira JC, Lopes A, Costa CM, Leones R, Silva MM, Lanceros-Méndez S (2012) Porous membranes of montmorillonite/poly (vinylidene fluoride-trifluorethylene) for Li-Ion battery separators. J Electroanalysis 24:2147–2156
Xiao W, Li X, Guo H, Wang Z, Li Y, Yang B (2014) Preparation and physicochemical performances of poly [(vinylidene fluoride)-co-hexafluoropropylene]-based composite polymer electrolytes doped with modified carbon nanotubes. J Polym Int 63:307–314
Nah C, Jeong K, Lee Y, Lee S, Abdul Kader M, Lee H, Ahn J (2013) Polymer electrolyte membranes composed of an electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) fibrous mat in a poly (4-vinylpyridine) matrix. J Polym Int 62:375–381
Zhu Y, Xiao S, Shi Y, Yang Y, Hou Y, Wu Y (2014) A Composite Gel Polymer Electrolyte with High Performance Based on Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) and Polyborate for Lithium Ion Batteries. J Adv Energy Mater 4:1300647. doi:10.1002/aenm.201300647
Kelley J, Simonsen J, Ding J (2013) Poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) nanocomposites incorporating cellulose nanocrystals with potential applications in lithium ion batteries. J Appl Polym Sci 127:487–493
Jeong K, Chae HD, Lim C, Lee HK, Ahn JH, Nah C (2010) Fabrication and characterization of electrolyte membranes based on organoclay/tripropyleneglycol diacrylate/poly (vinylidene fluoride) electrospun nanofiber composites. J Polym Int 59:249–255
Cha EH, Macfarlane DR, Forsyth M, Lee CW (2004) Ionic conductivity studies of polymeric electrolytes containing lithium salt with plasticizer, Electrochim. Acta 50:335–338
Kim JR, Choi SW, Jo SM, Lee WS, Kim BC (2004) Electrospun PVdF-based fibrous polymer electrolytes for lithium ion polymer batteris, Electrochim. Acta 50:69–75
Wang Z, Tang Z (2003) Characterization of the polymer electrolyte based on the blend of poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) and poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) for lithium ion battery. Mater Chem Phys 82:16–20
Tarascon JM, Gozdz AS, Schmutz C, Shokoohi F, Warren PC (1996) Performance of Bellcore’s plastic rechargeable Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ion 86–88:49–54
Choi JW, Kim JH, Cheruvally G, Ahn JH, Kim KW, Ahn HJ, Kim JU (2006) Microporous poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) polymer electrolytes for lithium/sulfur cells. J Ind Eng Chem 12:939–949
Subramania A, Kalyanasundaram NT, Vijykumar G (2006) Structural and electrochemical properties of micro-porous polymer blend electrolytes based on PVdF-co-HFP-PAN for Li-ion battery applications. J Power Sources 153:177–182
Saunier J, Alloin F, Sanchez JY, Caillon G (2003) Thin and flexible lithium-ion batteries: investigation of polymer electrolytes. J Power Sources 119–121:454–459
Pu W, He X, Wang L, Jiang C, Wan C (2006) Preparation of PVDF–HFP microporous membrane for Li-ion batteries by phase inversion. J Membr Sci 272:11–14
Choi JW, Kim JK, Cheruvally G, Ahn JH, Ahn HJ, Kim JU (2007) Rechargeable lithium/sulfur battery with suitable mixed liquid electrolytes, Electrochim. Acta 52:2075–2082
Doshi J, Reneker DH (1995) Electrospinning process and application of electrospun fibers. J Electrost 35:151–160
Huang ZM, Zhang YZ, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2003) A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 63:2223–2253
Li D, Xia Y (2004) Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the wheel? Adv Mater 16:1151–1170
Kong CS, Yoo WS, Jo NG, Kim HS (2010) Electrospinning mechanism for producing nanoscale polymer fibers. J Macromol Sci B Phys 49:122–131
Ramakrishna S, Tan SH, Inai R, Kotakil M (2005) Systematic parameter study for ultra-fine fiber fabrication via electro spinning process. Polymer 46:6128–6134
Myer RH, Montogomery DC (2002) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiment, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 343–350
Ray S (2006) RSM A statistical tool for process optimization. J Indian Text 117:24–27
Box GEP, Hunter WG, Hunter WS (1978) Statistics for experimenters: an introduction to design, data analysis and model building. Wiley, New York, pp 510–536
Prasanth R, Shubha N, Hng HH, Srinivasan M (2013) Effect of nano-clay on ionic conductivity and electrochemical properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride) based nanocomposite porous polymer membranes and their application as polymer electrolyte in lithium ion batteries. J European Poly 49:307–318
Lim DH, Manuel J, Ahn JH, Kim JK, Jacobsson P, Matic A, Ha JK, Cho KK, Kim KW (2012) Polymer electrolytes based on poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) nanofibrous membranes containing polymer plasticizers for lithium batteries. Solid State Ion 225:631–635
Raghavan P, Zhao X, Kim JK, Manuel J, Chauhan GS, Ahn JH, Nah C (2008) Ionic conductivity and electrochemical properties of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes based on electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoroprooylene) with nano-sized ceramic fillers, Electrochim. Acta 54:228–234
Appetecchi GB, Romagnoli P, Scrosati B (2001) Composite gel membranes: a new class of improved polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Electrochem Commun 3:281–284
Raghavan P, Manuel J, Zhao X, Kim DS, Ahn JH, Nah C (2011) Preparation and electrochemical characterization of gel polymer electrolyte based on electrospun polyacrylonitrile nonwoven membranes for lithium batteries. J Power Sources 196:6742–6749
Rao M, Geng X, Liao Y, Hu S, Li W (2012) Preparation and performance of gel polymer electrolyte based on electrospun polymer membrane and ionic liquid for lithium ion battery. J Membrane Sci 399–400:37–42
Yoon HK, Chung WS, Jo NJ (2004) Study on ionic transport mechanism and interactions between salt and polymer chain in PAN based solid polymer electrolytes containing LiCF3SO3, Electrochim. Acta 50:289–293
Li X, Cheruvally G, Kim JK, Choi JW, Ahn JH, Kim KW, Ahn HJ (2007) Polymer electrolytes based on an electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) membrane for lithium batteries. J Power sources 167:491–498
Hakkak F, Rafizadeh M (2013) Optimization of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/poly (vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber diameter using the response surface method. J Macromol Sci Phys 52:1250–1264
McKee MG, Wilkes GL, Colby RH, Long T (2004) Correlations of solution rheology with electrospun fiber formation of linear and branched polyester. Macromolecules 37:1760–1767
Koski A, Yim K, Shivkumar S (2004) Effect of molecular weight on fibrous PVA produced by electrospinning. Mater Lett 58:493–497
Hong PD, Chou CM, He CH (2001) Solvent effects on aggregation behavior of polyvinyl alcohol solutions. Polymer 42:6105–6112
Wang C, Cheng YW, Hsu CH, Chien HS, Tsou SY (2011) How to manipulate the electrospinning jet with controlled properties to obtain uniform fibers with the smallest diameter? a brief discussion of solution electrospinning process. J Polym Res 18:111–123
Kataoka H, Saito Y, Sakai T, Quartarone E, Mustarelli P (2000) Conduction mechanisms of PVDF-type Gel polymer electrolytes of lithium prepared by a phase inversion process. J Phys Chem B 104:11460–11464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hakkak, F., Rafizadeh, M., Sarabi, A.A. et al. Optimization of ionic conductivity of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/poly (vinylidene fluoride) (PAN/PVdF) electrolyte using the response surface method (RSM). Ionics 21, 1945–1957 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1363-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-014-1363-1