Abstract
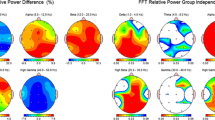
Screening alcohol use disorder (AUD) patients has been challenging due to the subjectivity involved in the process. Hence, robust and objective methods are needed to automate the screening of AUD patients. In this paper, a machine learning method is proposed that utilized resting-state electroencephalography (EEG)-derived features as input data to classify the AUD patients and healthy controls and to perform automatic screening of AUD patients. In this context, the EEG data were recorded during 5 min of eyes closed and 5 min of eyes open conditions. For this purpose, 30 AUD patients and 15 aged-matched healthy controls were recruited. After preprocessing the EEG data, EEG features such as inter-hemispheric coherences and spectral power for EEG delta, theta, alpha, beta and gamma bands were computed involving 19 scalp locations. The selection of most discriminant features was performed with a rank-based feature selection method assigning a weight value to each feature according to a criterion, i.e., receiver operating characteristics curve. For example, a feature with large weight was considered more relevant to the target labels than a feature with less weight. Therefore, a reduced set of most discriminant features was identified and further be utilized during classification of AUD patients and healthy controls. As results, the inter-hemispheric coherences between the brain regions were found significantly different between the study groups and provided high classification efficiency (Accuracy = 80.8, sensitivity = 82.5, and specificity = 80, F-Measure = 0.78). In addition, the power computed in different EEG bands were found significant and provided an overall classification efficiency as (Accuracy = 86.6, sensitivity = 95, specificity = 82.5, and F-Measure = 0.88). Further, the integration of these EEG feature resulted into even higher results (Accuracy = 89.3 %, sensitivity = 88.5 %, specificity = 91 %, and F-Measure = 0.90). Based on the results, it is concluded that the EEG data (integration of the theta, beta, and gamma power and inter-hemispheric coherence) could be utilized as objective markers to screen the AUD patients and healthy controls.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya UR, Sree SV, Chattopadhyay S, Suri JS (2012) Automated diagnosis of normal and alcoholic EEG signals. Int J Neural Syst 22(03):1250011
Alcoholism NIAAA (2012) Alcohol use disorder. http://www.niaaa.nih.gov/alcohol-health/overview-alcohol-consumption/alcohol-use-disorders
Alhassoon OM, Sorg SF, Stern MJ, Hall MG, Wollman SC (2015) Neuroimaging in alcohol-use disorders: clinical implications and future directions. Future Neurol 10(4):345–356
Babor TF, Higgins-Biddle JC, Saunders JB, Monteiro MG, World Health Organization (2001) AUDIT: the alcohol use disorders identification test: guidelines for use in primary health care. World Health Organization, Geneva
Bajaj V, Guo Y, Sengur A, Siuly S, Alcin OF (2016) A hybrid method based on time–frequency images for classification of alcohol and control EEG signals. Neural Comput Appl 27:1–7
Bauer LO (2001) Predicting relapse to alcohol and drug abuse via quantitative electroencephalography. Neuropsychopharmacology 25(3):332–340
Bush K, Kivlahan DR, McDonell MB, Fihn SD, Bradley KA (1998) The AUDIT alcohol consumption questions (AUDIT-C): an effective brief screening test for problem drinking. Arch Intern Med 158(16):1789–1795
Campanella S, Petit G, Maurage P, Kornreich C, Verbanck P, Noël X (2009) Chronic alcoholism: insights from neurophysiology. Neurophysiol Clin Clin Neurophysiol 39(4):191–207
Coutin-Churchman P, Moreno R, Añez Y, Vergara F (2006) Clinical correlates of quantitative EEG alterations in alcoholic patients. Clin Neurophysiol 117:740–751
de Bruin EA, Bijl S, Stam CJ, Böcker KB, Kenemans JL, Verbaten MN (2004) Abnormal EEG synchronisation in heavily drinking students. Clin Neurophysiol 115(9):2048–2055
de Bruin EA, Stam CJ, Bijl S, Verbaten MN, Kenemans JL (2006) Moderate-to-heavy alcohol intake is associated with differences in synchronization of brain activity during rest and mental rehearsal. Int J Psychophysiol 60(3):304–314
Ehlers CL, Phillips E (2007) Association of EEG alpha variants and alpha power with alcohol dependence in Mexican American young adults. Alcohol 41(1):13–20
Ehlers CL, Phillips E, Schuckit MA (2004) EEG alpha variants and alpha power in Hispanic American and white non-Hispanic American young adults with a family history of alcohol dependence. Alcohol 33(2):99–106
Eisinga R, Grotenhuis MT, Pelzer B (2013) The reliability of a two-item scale: Pearson, Cronbach, or Spearman-Brown? Int J Public Health 4:1–6
Ek Z, Akg A, Bozkurt MR (2013) The classification of EEG signals recorded in drunk and non-drunk people. Int J Comput Appl 68(10):40
Faust O, Yanti R, Yu W (2013a) Automated detection of alcohol related changes in electroencephalograph signals. J Med Imaging Health Inform 3(2):333–339
Faust O, Yu W, Kadri NA (2013b) Computer-based identification of normal and alcoholic eeg signals using wavelet packets and energy measures. J Mech Med Biol 13(03):1350033
Fründ I, Schadow J, Busch NA, Naue N, Körner U, Herrmann CS (2008) Anticipation of natural stimuli modulates EEG dynamics: physiology and simulation. Cogn Neurodyn 2(2):89–100
Guntaka R, Tcheslavski GV (2013) On the EEG-based automated detection of alcohol dependence. 17:167–176
Gutiérrez D, Ramírez-Moreno MA (2016) Assessing a learning process with functional ANOVA estimators of EEG power spectral densities. Cogn Neurodyn 10(2):175–183
Guyon I, Elisseeff A (2003) An introduction to variable and feature selection. J Mach Learn Res 3:1157–1182
Herrera-Díaz A, Mendoza-Quiñones R, Melie-Garcia L, Martínez-Montes E, Sanabria-Diaz G, Romero-Quintana Y, Caballero-Moreno A (2015) Functional connectivity and quantitative EEG in women with alcohol use disorders: a resting-state study. Brain Topogr 29:1–14
Hosmer DW Jr, Lemeshow S (2004) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, New York
Huys QJ, Maia TV, Frank MJ (2016) Computational psychiatry as a bridge from neuroscience to clinical applications. Nat Neurosci 19(3):404–413
Kanna PS, Palaniappan R, Ravi K (2005) Classification of alcohol abusers: an intelligent approach. In: Paper presented at the information technology and applications, 2005. Third international conference on ICITA 2005
Kiebel SJ, Garrido MI, Moran RJ, Friston KJ (2008) Dynamic causal modelling for EEG and MEG. Cogn Neurodyn 2(2):121–136
Klem GH, Lüders HO, Jasper H, Elger C (1999) The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 52(3):3–6
Klimesch W (1999) EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: a review and analysis. Brain Res Rev 29(2):169–195
Kousarrizi MN, Ghanbari AA, Gharaviri A, Teshnehlab M, Aliyari M (2009) Classification of alcoholics and non-alcoholics via EEG using SVM and neural networks. In: Paper presented at the bioinformatics and biomedical engineering, 2009. 3rd international conference on ICBBE 2009
Kuncheva LI, Rodríguez JJ (2013) Interval feature extraction for classification of event-related potentials (ERP) in EEG data analysis. Prog Artif Intell 2(1):65–72
Liao J, Chin K-V (2007) Logistic regression for disease classification using microarray data: model selection in a large p and small n case. Bioinformatics 23(15):1945–1951
Lopes CD, Mainardi JO, Zaro MA, Susin AA (2004) Classification of event-related potentials in individuals at risk for alcoholism using wavelet transform and artificial neural network. In: Paper presented at the computational intelligence in bioinformatics and computational biology, 2004. Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE symposium on CIBCB’04
Lopes CD, Schuler E, Engel P, Susin AA (2005) ERP signal identification of individuals at risk for alcoholism using learning vector quantization network. In: Paper presented at the computational intelligence in bioinformatics and computational biology, 2005. Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE symposium on CIBCB’05
Maisto SA, Saitz R (2003) Alcohol use disorders: screening and diagnosis. Am J Addict 12(s1):s12–s25
Mamitsuka H (2006) Selecting features in microarray classification using ROC curves. Pattern Recogn 39(12):2393–2404
Michael A, Mirza K, Mukundan C, Channabasavanna S (1993) Interhemispheric electroencephalographic coherence as a biological marker in alcoholism. Acta Psychiatr Scand 87(3):213–217
Moss HB, Chen CM, Yi H-Y (2007) Subtypes of alcohol dependence in a nationally representative sample. Drug Alcohol Depend 91(2):149–158
Mumtaz W, Vuong PL, Xia L, Malik AS, Rashid RBA (2016) Automatic diagnosis of alcohol use disorder using EEG features. Knowl Based Syst 105:48–59
Ng EP, Lim T-C, Chattopadhyay S, Bairy M (2012) Automated identification of epileptic and alcoholic EEG signals using recurrence quantification analysis. J Mech Med Biol 12(05):1240028
Ong K-M, Thung K-H, Wee C-Y, Paramesranle R (2005) Selection of a subset of EEG channels using PCA to classify alcoholics and non-alcoholics. In: Paper presented at the proceedings of the 2005 IEEE engineering in medicine and biology 27th Annual Conference, Shanghai, China
Ozaki TJ, Sato N, Kitajo K, Someya Y, Anami K, Mizuhara H, Yamaguchi Y (2012) Traveling EEG slow oscillation along the dorsal attention network initiates spontaneous perceptual switching. Cogn Neurodyn 6(2):185–198
Padmanabhapillai A, Porjesz B, Ranganathan M, Jones KA, Chorlian DB, Tang Y, Begleiter H (2006) Suppression of early evoked gamma band response in male alcoholics during a visual oddball task. Int J Psychophysiol 60(1):15–26
Palaniappan R (2003) Improved automated classification of alcoholics and non-alcoholics. Int J Inf Technol 2(3)
Palaniappan R (2005) Discrimination of alcoholic subjects using second order autoregressive modelling of brain signals evoked during visual stimulus perception. In: Paper presented at the IEC, Prague
Palaniappan R (2007) Screening for chronic alcoholic subjects using multiple gamma band EEG: a pilot study. J Comput Sci Technol 7:182–185
Palaniappan R, Raveendran P, Omatu S (2002) VEP optimal channel selection using genetic algorithm for neural network classification of alcoholics. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 13(2):486–491
Parsons OA, Nixon SJ (1998) Cognitive functioning in sober social drinkers: a review of the research since 1986. J Stud Alcohol 59(2):180–190
Parvaz MA, Alia-Klein N, Woicik PA, Volkow ND, Goldstein RZ (2011) Neuroimaging for drug addiction and related behaviors. Rev Neurosci 22(6):609–624
Popham RE, Schmidt W (1981) Words and deeds: the validity of self-report data on alcohol consumption. J Stud Alcohol 42(3):355–358
Porjesz B, Begleiter H (2003) Alcoholism and human electrophysiology. Alcohol Res Health 27(2):153–160
Porjesz B, Rangaswamy M, Kamarajan C, Jones KA, Padmanabhapillai A, Begleiter H (2005) The utility of neurophysiological markers in the study of alcoholism. Clin Neurophysiol 116(5):993–1018
Rangaswamy M, Porjesz B, Chorlian DB, Wang K, Jones KA, Bauer LO, Reich T (2002) Beta power in the EEG of alcoholics. Biol Psychiatry 52(8):831–842
Rangaswamy M, Porjesz B, Chorlian DB, Choi K, Jones KA, Wang K, Reich T (2003) Theta power in the EEG of alcoholics. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27(4):607–615
Ritsner MS (2009) The handbook of neuropsychiatric biomarkers, endophenotypes and genes: volume I: neuropsychological endophenotypes and biomarkers (vol 1). Springer Science & Business Media, New York
Saletu-Zyhlarz GM, Arnold O, Anderer P, Oberndorfer S, Walter H, Lesch OM, Böning J, Saletu B (2004) Differences in brain function between relapsing and abstaining alcohol-dependent patients, evaluated by EEG mapping. Alcohol Alcohol 39:233–240
Shalbaf R, Behnam H, Moghadam HJ (2015) Monitoring depth of anesthesia using combination of EEG measure and hemodynamic variables. Cogn Neurodyn 9(1):41–51
Shooshtari MA, Setarehdan SK (2010) Selection of optimal EEG channels for classification of signals correlated with alcohol abusers. In: Paper presented at the signal processing (ICSP), 2010 IEEE 10th international conference on
Sinha R (2016) Automated identification of chronic alcoholism from brain signals. Online J Health Allied Sci 14(4):20
Solomon J, Vanga N, Morgan J, Joseph P (1980) Emergency-room physicians’: recognition of alcohol misuse. J Stud Alcohol 41(5):583–586
Son K, Choi J, Lee J, Park S, Lim J, Lee J, Kwon J (2015) Neurophysiological features of Internet gaming disorder and alcohol use disorder: a resting-state EEG study. Transl Psychiatry 5(9):e628
Tavakoli HR, Hull M, Michael Okasinski L (2011) Review of current clinical biomarkers for the detection of alcohol dependence. Innov Clin Neurosci 8(3):26–33
Tcheslavski GV, Gonen FF (2012) Alcoholism-related alterations in spectrum, coherence, and phase synchrony of topical electroencephalogram. Comput Biol Med 42(4):394–401
Thatcher R (2008) NeuroGuide manual and tutorial, St. Petersburg, FL. Applied Neuroscience. http://www.AppliedNeuroscience.com/NeuroGuide_Deluxe.pdf
Thatcher RW, Biver CJ, North D, To SRR (2004) EEG coherence and phase delays: comparisons between single reference, average reference and current source density. Univ. South Florida College of Medicine, Tampa, FL, USA, Technical Report A-1
Timmerman D, Testa AC, Bourne T, Ferrazzi E, Ameye L, Konstantinovic ML, Van Huffel S (2005) Logistic regression model to distinguish between the benign and malignant adnexal mass before surgery: a multicenter study by the International Ovarian Tumor Analysis Group. J Clin Oncol 23(34):8794–8801
Van Rijsbergen CJ (2004) The geometry of information retrieval. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wan L, Baldridge RM, Colby AM, Stanford MS (2010) Association of P3 amplitude to treatment completion in substance dependent individuals. Psychiatry Res 177(1):223–227
Watson CG, Tilleskjor C, Hoodecheck-Schow E, Pucel J, Jacobs L (1984) Do alcoholics give valid self-reports? J Stud Alcohol 45(4):344–348
Winterer G, Klöppel B, Heinz A, Ziller M, Dufeu P, Schmidt LG, Herrmann WM (1998) Quantitative EEG (QEEG) predicts relapse in patients with chronic alcoholism and points to a frontally pronounced cerebral disturbance. Psychiatry Res 78(1):101–113
Yazdani A, Setarehdan SK (2007) Classification of EEG signals correlated with alcohol abusers. In: Paper presented at the signal processing and its applications, 2007. 9th International Symposium on ISSPA 2007
Zhang XL, Begleiter H, Porjesz B, Litke A (1997) Electrophysiological evidence of memory impairment in alcoholic patients. Biol Psychiatry 42(12):1157–1171
Zhong S, Ghosh J (2002) HMMs and coupled HMMs for multi-channel EEG classification. In: Paper presented at the proceedings of the IEEE international joint conference on neural networks
Zhu J, Hastie T (2004) Classification of gene microarrays by penalized logistic regression. Biostatistics 5(3):427–443
Zhu G, Li P, Wen PP, Wang S (2014) Analysis of alcoholic EEG signals based on horizontal visibility graph entropy. Brain Inform 1:19–25
Zúquete A, Quintela B, Cunha JPS (2010) Biometric authentication using electroencephalograms: a practical study using visual evoked potentials. Electrónica e Telecomunicações 5(2):185–194
Acknowledgments
This research work is supported by the HICoE Grant for CISIR (0153CA-005), Ministry of Education (MOE), Malaysia, National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61572076), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant (No. 2015M570940), BIT Fundamental Research Grant (No. 20150442009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mumtaz, W., Vuong, P.L., Xia, L. et al. An EEG-based machine learning method to screen alcohol use disorder. Cogn Neurodyn 11, 161–171 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-016-9416-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11571-016-9416-y