Abstract
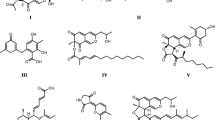
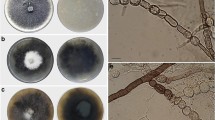
A specimen of the Hypoxylon rubiginosum complex featuring unusual bicoloured stromata was collected in northern Thailand and examined by means of classical morphological methodology, complemented by studies of its secondary metabolites using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with diode array and electrospray mass spectrometric detection (HPLC-DAD/MS), and molecular phylogenetic analysis of its ITS and partial beta-tubulin DNA sequences. In addition, the ultrastructure of its ascospores was examined by SEM. The chemotaxonomic studies revealed the presence of two putatively unknown, apparently specific azaphilone pigments in the stromata. These metabolites were consequently isolated to purity by preparative HPLC and identified by means of nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and high resolution mass spectrometry as the novel natural products, (+)-6″-hydroxymitorubrinol acetate (1) and (+)-6″-hydroxymitorubrinol (3).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bills GF, Gonzalez-Menendez V, Martın J, Platas G, Fournier J, Persoh D, Stadler M (2012) Hypoxylon pulicicidum sp. nov. (Ascomycota, Xylariales), a pantropical insecticide-producing endophyte. PLoS ONE 7:e46687. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046687
Bitzer J, Köpcke B, Stadler M, Hellwig V, Ju YM, Seip S, Henkel T (2007) Accelerated dereplication of natural products, supported by reference libraries. Chimia 51:332–338
Bitzer J, Læssøe T, Fournier J, Kummer V, Decock C, Tichy HV, Piepenbring M, Persǒh D, Stadler M (2008) Affinities of Phylacia and the daldinoid Xylariaceae, inferred from chemotypes of cultures and ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol Res 112:251–270
Fournier J, Köpcke B, Stadler M (2010a) New species of Hypoxylon from Western Europe and Ethiopia. Mycotaxon 113:209–235
Fournier J, Stadler M, Hyde KD, Duong ML (2010b) The new genus Rostrohypoxylon and two new Annulohypoxylon species from Northern Thailand. Fungal Divers 40:23–36
Gao JM, Yang SX, Qin JC (2013) Azaphilones: chemistry and biology. Chem Rev 113:4755–4811
Halecker S, Surup F, Kuhnert E, Mohr KI, Brock NL, Dickschat JS, Junker C, Schulz B, Stadler M (2014) Hymenosetin, a 3-decalinoyltetramic acid antibiotic from cultures of the ash dieback pathogen, Hymenoscyphus pseudoalbidus. Phytochemistry 100:86–91
Hellwig V, Ju YM, Rogers JD, Fournier J, Stadler M (2005) Hypomiltin, a novel azaphilone from Hypoxylon hypomiltum, and chemotypes in Hypoxylon sect. Hypoxylon as inferred from analytical HPLC profiling. Mycol. Progr. 4:39–54
Hsieh HM, Ju YM, Rogers JD (2005) Molecular phylogeny of Hypoxylon and closely related genera. Mycologia 97:844–865
Ju YM, Rogers JD (1996) A revision of the genus Hypoxylon. Mycologia Memoir n° 20. APS Press, St. Paul, 365 pp
Kuhnert E, Fournier J, Persǒh D, Luangsa-ard JJ, Stadler M (2014a) New Hypoxylon species from Martinique and new evidence on the molecular phylogeny of Hypoxylon based on ITS rDNA and β-tubulin data. Fungal Divers 64:181–203
Kuhnert E, Heitkämper S, Fournier J, Surup F, Stadler M (2014b) Hypoxyvermelhotins A-C, new pigments from Hypoxylon lechatii sp. nov. Fungal Biol 118:242–252
Kuhnert E, Surup F, Sir EB, Lambert C, Hyde KD, Hladki AI, Romero AI, Stadler M (2015) Lenormandins A – G, new azaphilones from Hypoxylon lenormandii and Hypoxylon jaklitschii sp. nov., recognised by chemotaxonomic data. Fungal Divers, in press. doi: 10.1007/s13225-014-0318-1
Læssøe T, Srikitikulchai P, Fournier J, Köpcke B, Stadler M (2010) Lepraric acid derivatives as chemotaxonomic markers in Hypoxylon aeruginosum, Chlorostroma subcubisporum and C. cyaninum, sp.nov. Fungal Biol 114:481–489
Læssøe T, Srikitikulchai P, Luangsa-ard JJD, Stadler M (2013) Theissenia reconsidered, including molecular phylogeny of the type species T. pyrenocrata and a new genus Durotheca (Xylariaceae, Ascomycota). IMA Fungus 4:57–69
Mühlbauer A, Triebel D, Persǒh D, Wollweber H, Seip S, Stadler M (2002) Macrocarpones, novel metabolites from stromata of Hypoxylon macrocarpum and new evidence on the chemotaxonomiy of Hypoxylon. Mycol Prog 1:235–248
Okanya PW, Mohr KI, Gerth K, Jansen R, Müller R (2011) Marinoquinolines A - F, pyrroloquinolines from Ohtaekwangia kribbensis (Bacteroidetes). J Nat Prod 74:603–608
Pažoutová S, Follert S, Bitzer J, Keck M, Surup F, Šrůtka P, Holuša J, Stadler M (2013) A new endophytic insect-associated Daldinia species, recognised from a comparison of secondary metabolite profiles and molecular phylogeny. Fungal Divers 60:107–123
Quang DN, Hashimoto T, Stadler M, Asakawa Y (2004a) New azaphilones from the inedible mushroom Hypoxylon rubiginosum. J Nat Prod 67:1152–1155
Quang DN, Hashimoto T, Tanaka M, Stadler M, Asakawa Y (2004b) Cyclic azaphiolones daldinins E and F from the ascomycete fungus Hypoxylon fuscum (Xylariaceae). Phytochemistry 65:469–473
Quang DN, Stadler M, Fournier J, Asakawa Y (2006) Carneic acids A and B, two chemotaxonomically significant antimicrobial agents from the xylariaceous ascomycete, Hypoxylon carneum. J Nat Prod 69:1198–1202
Rayner RW (1970) A mycological colour chart. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew and British Mycological Society
Rogers JD (1981) Two new Hypoxylon species from Gabon. Can J Bot 59:1363–1364
Rogers JD (2000) Thoughts and musings on tropical Xylariaceae. Mycol Res 104:1412–1420
Singh SB, Kelly R, Guan Z, Polishook JD, Dombrowski AW, Collado J, González A, Pelaez F, Register E, Kelly TM, Bonfiglio C, Williamson JM (2006) New fungal metabolite geranyl-geranyltransferase inhibitors with antifungal activity. Nat Prod Res 19:739–747
Stadler M, Fournier J (2006) Pigment chemistry, taxonomy and phylogeny of the Hypoxyloideae (Xylariaceae). Rev Iberoam Micol 23:160–170
Stadler M, Fournier J, Læssøe T, Lechat C, Tichy HV, Piepenbring M (2008) Recognition of hypoxyloid and xylarioid Entonaema species from a comparison of holomorphic morphology, HPLC profiles, and ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycol Progr 7:53–73
Stadler M, Ju YM, Rogers JD (2004) Chemotaxonomy of Entonaema, Rhopalostroma and other Xylariaceae. Mycol Res 108:239–256
Stadler M, Kuhnert E, Persǒh D, Fournier J (2013) The Xylariaceae as model for a unified nomenclature following the “One fungus-One Name” (1F1N) concept. Mycology 4:5–21
Stadler M, Læssøe T, Fournier J, Decock C, Schmieschek B, Tichy HV, Peršoh D (2014) A polyphasic taxonomy of Daldinia (Xylariaceae). Stud Mycol 77:1–143
Stadler M, Wollweber H, Mühlbauer A, Henkel T, Wollweber H, Asakawa Y, Hashimoto T, Rogers JD, Ju YM, Wetzstein HG, Tichy HV (2001) Secondary metabolite profiles, genetic fingerprints and taxonomy of Daldinia and allies. Mycotaxon 77:379–429
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Steglich W, Klaar M, Furtner W (1974) Mitorubrin derivatives from Hypoxylon fragiforme. Phytochemistry 13:2874–2875
Surup F, Mohr KI, Jansen R, Stadler M (2013) Cohaerins G-K, azaphilone pigments from Annulohypoxylon cohaerens and absolute stereochemistry of cohaerins C-K. Phytochemistry 95:252–258
Suwannasai N, Rodtong S, Thienhirun S, Whalley AJS (2005) New species and phylogenetic relationships of Hypoxylon species found in Thailand inferred from the internal transcribed spacer regions of ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycotaxon 94:303–324
Suzuki S, Hosoe T, Nozawa K, Yaguchi T, Udagawa S, Kawai K (1999) Mitorubrin derivatives on ascomata of some Talaromyces species of ascomycetous fungi. J Nat Prod 62:1328–1329
Triebel D, Peršoh D, Wollweber H, Stadler M (2005) Phylogenetic relationships among Daldinia, Entonaema and Hypoxylon as inferred from ITS nrDNA sequences. Nova Hedw 80:25–43
Wang H, Wang Y, Wang W, Fu P, Liu P, Zhu W (2011) Anti-influenza virus polyketides from the acid-tolerant fungus Penicillium purpurogenum JS03-21. J Nat Prod 74:2014–2018
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge support from the curators of various international culture collections and herbaria, above all, BCC and MFLUCC, who provided important specimens for the present study.
The field sampling in Thailand benefited from a joint TRF-DAAD PPP academic exchange grant by the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) and the Thai Royal Golden Ph.D. Jubilee-Industry program (RGJ) to Kevin D. Hyde, Eric Kuhnert, and Marc Stadler. The DAAD and the Argentina Ministerio de Ciencia, Tecnología e Innovación Productiva are also gratefully acknowledged for an academic exchange grant involving Eric Kuhnert, Esteban Benjamin Sir and Marc Stadler.
We thank Simone Heitkämper for her excellent assistance in the molecular work and Benjarong Thongbai for help with the fieldwork. Furthermore, we are grateful to various colleagues at the HZI: Kathrin I. Mohr and Wera Collisi for conducting the bioassays and Christel Kakoschke for recording NMR spectra. Manfred Rohde is thanked for SEM recordings. For measurements of the HPLC–HRMS data we are grateful to Aileen Teichmann. We also thank Philine Wotsch for technical assistance in culture maintenance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sir, E.B., Kuhnert, E., Surup, F. et al. Discovery of new mitorubrin derivatives from Hypoxylon fulvo-sulphureum sp. nov. (Ascomycota, Xylariales). Mycol Progress 14, 28 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-015-1043-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-015-1043-1