Abstract
Purpose
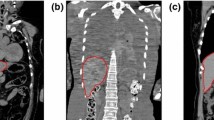
Modeling the postmortem liver for autopsy imaging is a challenging problem owing to the variation in organ deformation found in cadavers and limited availability of postmortem liver CT scans. An algorithm was developed to construct a statistical shape model (SSM) for the adult postmortem liver in autopsy imaging.
Methods
First, we investigated the relationship between SSMs obtained from in vivo liver CT scans and those from postmortem cases. Liver shapes were embedded in level set functions and statistically modeled using a spatially weighted principal components analysis. The performance of the SSMs was evaluated in terms of generalization and specificity. Several algorithms for the transformation from in vivo livers to postmortem livers were proposed to enhance the performance of an SSM for a postmortem liver, followed by a comparative study on SSMs. Specifically, five SSMs for a postmortem liver were constructed and evaluated using 32 postmortem liver labels, and postmortem liver labels synthesized from 144 in vivo liver labels were constructed using the proposed transformation algorithms. We also compared the proposed SSMs with three conventional SSMs trained from postmortem liver labels and/or in vivo liver labels.
Results
The investigation showed that the performance of an SSM constructed using in vivo liver labels suffered when describing postmortem liver shapes. Two of the five proposed SSMs trained using synthesized postmortem livers showed the best performance with no significant differences between them, and they statistically outperformed all conventional SSMs tested.
Conclusions
The performance of conventional SSMs can be improved by using both postmortem liver shape labels and artificial shape labels synthesized from in vivo liver shape labels.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ezawa H, Yoneyama R, Kandatsu S (2003) Introduction of autopsy imaging redefines the concept of autopsy: 27 cases of clinical experience. Pathol Int 53:865–873. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1827.2003.01573.x
Ezawa E, Shiotani S, Uchigasaki S (2007) Autopsy imaging in Japan. Rechtsmedizin 17:19–20. doi:10.1007/s00194-006-0409-8
Heimann T, Meinzer HP (2009) Statistical shape models for 3D medical image segmentation: a review. Med Image Anal 13:543–563. doi:10.1016/j.media.2009.05.004
Kainmüller D, Lange T, Lamecker H (2007) Shape constrained automatic segmentation of the liver based on a heuristic intensity model. In: Proceedings of MICCAI workshop 3D segmentation in the clinic: a grand challenge
Okada T, Shimada R, Hori M, Nakamoto M, Chen YW, Nakamura H, Sato Y (2008) Automated segmentation of the liver from 3D CT images using probabilistic atlas and multilevel statistical shape model. Acad Radiol 15:1390–1403. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2008.07.008
Nakagomi K, Shimizu A, Kobatake H, Yakami M, Fujimoto K, Togashi K (2012) Multi-shape graph cuts with neighbor prior constraints and its application to lung segmentation from a chest CT volume. Med Image Anal 17:62–77. doi:10.1016/j.media.2012.08.002
De Bruijne M, Lund MT, Tanko LB, Pettersen PC, Nielsen M (2007) Quantitative vertebral morphometry using neighbor-conditional shape models. Med Image Anal 11:503–512. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2007.07.004
Baka N, De Bruijne M, Reiber JHC, Niessen W, Lelieveldt BPF (2010) Confidence of model based shape reconstruction from sparse data. In: Proceedings of ISBI 1077–1080. doi:10.1109/ISBI.2010.5490179
Syrkina E, Blanc R, Székely G (2011) Propagating uncertainties in statistical model based shape prediction. In: Proceedings of SPIE 796240. doi:10.1117/12.877960
Tomoshige S, Oost E, Shimizu A, Watanabe H, Kobatake H, Nawano S (2012) Relaxed conditional statistical shape models and their application to non-contrast liver segmentation. Med Image Anal 7601:126–136. doi:10.1016/j.media.2012.02.001
Tsai A, Wells W, Tempany C, Grimson E, Willsky A (2004) Mutual information in coupled multi-shape model for medical image segmentation. Med Image Anal 8:429–445. doi:10.1016/j.media.2004.01.003
Yang J, Staib LH, Duncan JS (2004) Neighbor-constrained segmentation with level set based 3-d deformable models. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23:940–948. doi:10.1109/TMI.2004.830802
Pohl KM, Fisher J, Shenton ME, McCarley RW, Grimson WEL, Kikinis R, Wells WM (2006) Logarithm odds maps for shape representation. Proc MICCAI 4191:955–963. doi:10.1007/11866763_117
Malcolm JG, Rathi Y, Shenton ME, Tannenbaum A (2008) Label space: a coupled multi-shape representation. Proc MICCAI 5242:416–424. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-85990-1_50
Changizi N, Hamarneh G (2010) Probabilistic multi-shape representation using an isometric log-ratio mapping. Proc MICCAI 6363:563–570. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-15711-0_70
Okada T, Linguraru MG, Yoshida Y, Hori M, Summers RM, Chen Y, Tomiyama N, Sato Y (2011) Abdominal multi-organ segmentation of CT images based on hierarchical spatial modeling of organ interrelations. 7029:173–180. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-28557-8_22
Linguraru MG, Pura JA, Pamulapati V, Summers RM (2012) Statistical 4D graphs for multi-organ abdominal segmentation from multiphase CT. Med Image Anal 16:904–914. doi:10.1016/j.media.2012.02.001
Murase H, Nayar SK (1996) Learning by a generation approach to appearance-based object recognition. Int Conf Pattern Recognit 1:25–29. doi:10.1109/ICPR.1996.545985
Gavrila DM, Giebel J (2001) Virtual sample generation for template-based shape matching. Proc IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 1:676–681. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2001.990540
Ishida H, Takahashi H, Ide I, Mekada Y, Murase H (2007) Generation of training data by degradation models for traffic sign symbol recognition. IEICE Trans Inf Syst E90–D:1134–1141. doi:10.1093/ietisy/e90-d.8.1134
Leventon M, Grimson WEL, Faugeras O (2000) Statistical shape influence in geodesic active contours. Proc IEEE Comput Soc Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 1:316–323. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2000.855835
Uchida Y, Shimizu A, Kobatake H, Nawano S, Shinozaki K (2010) A comparative study of statistical shape models of the pancreas. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 5(suppl 1):S385–S387. doi:10.1007/s11548-010-0469-9
Jeong JY (2009) Estimation of probability distribution on multiple anatomical objects and evaluation of statistical shape models. PhD thesis, Department of Computer Science, University of North Carolina
Styner MA, Rajamani KT, Nolte L-P, Zsemlye G, Székely G, Taylor CJ, Davies RH (2003) Evaluation of 3D correspondence methods for model building. Inf Process Med Imaging 2732:63–75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-45087-0_6
Lagarias JC, Reeds JA, Wright MH, Wright PE (1998) Convergence properties of the Nelder-Mead simplex method in low dimensions. SIAM J Optim 9:112–147. doi:10.1137/S1052623496303470
Acknowledgments
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology, Japan.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, A., Shimizu, A., Watanabe, H. et al. Statistical shape model of a liver for autopsy imaging. Int J CARS 9, 269–281 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0923-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0923-6