Abstract
Objectives
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a disorder progressing to end-stage kidney failure. Early diagnosis and treatment are important for medical care. The aim of this prospective study was to define the strain index (SI) and resistivity index (RI) values in the same CKD group for each kidney separately at the same time, and also to compare the efficacy of SI and RI in the differentiation of normal population and CKD patients.
Materials and methods
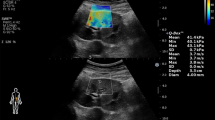
Toshiba Aplio 500 USG device and 3.5–5 MHz convex probe were used for USG, CDUSG, and USG elastography examinations. The patients were referred to radiology clinique from nephrology and endocrinology cliniques after GFR calculation. Patients with renal cyst, tumor, or obstructive renal disease were excluded. Healthy volunteers according to laboratory and clinical examinations were selected from non-kidney disease patients.
Results
A total of 121 CKD (68 men, 53 women) and 40 healthy volunteers (19 men, 21 women) were participated. The mean SI and RI values of CKD were significantly higher than the normal healthy volunteers (p < 0.05). The SI and RI values of right and left kidney did not show any difference in CKD patients (p values were 0.381 for SI and 0.821 for RI). The sensitivity and the specificity of the SI were higher than RI.
Conclusion
The RI and SI values of kidneys in CKD patients were significantly higher than those of apparently normal kidneys. SI was more sensitive than RI in our study. Determining cut-off SI and RI values between normal and damaged renal parenchyma can help in the diagnosis and follow up of CKD patients.
Advances in knowledge
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study comparing RI and SI in CKD patients, and SI is found to be more sensitive than RI for the evaluation of CKD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
El Nahas AM, Bello AK (2005) Chronic kidney disease: the global challenge. Lancet 365(9456):331–340
Hanamura K, Tojo A, Kinugasa S, Asaba K, Fujita T (2012) The resistive index is a marker of renal function, pathology, prognosis, and responsiveness to steroid therapy in chronic kidney disease patients. Int J Nephrol 2012:139565
Jenderka KV, Delorme S (2015) Principles of Doppler sonography. Radiologe 55(7):593–609
Kimura N, Kimura H, Takahashi N, Hamada T, Maegawa H, Mori M, et al (2015) Renal resistive index correlates with peritubular capillary loss and arteriosclerosis in biopsy tissues from patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 19(6):1114–1119
Carrol LE (2006) The stages of chronic kidney disease and the estimated glomerular filtration rate. J Lanc Gener Hosp 1(2):64–69
Ophir J, Cespedes I, Ponnekanti H, Yazdi Y, Li X (1991) Elastography: a quantitative method for imaging the elasticity of biological tissues. Ultrason Imaging 13(2):111–134
Onur MR, Göya C (2013) Ultrasound elastography: abdominal applications. Türkiye Klinikleri j Radiology-Special Topics 6(3):59–69
Bamber J, Cosgrove D, Dietrich CF, Fromageau J, Bojunga J, Calliada F et al (2013) EFSUMB guidelines and recommendations on the clinical use of ultrasound elastography. Part 1: basic principles and technology. Ultraschall Med 34(2):169–184
Shimizu Y, Itoh T, Hougaku H, Nagai Y, Hashimoto H, Sakaguchi M et al (2001) Clinical usefulness of duplex ultrasonography for the assessment of renal arteriosclerosis in essential hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 24(1):13–17
Florczak E, Januszewicz M, Januszewicz A, Prejbisz A, Kaczmarska M, Michalowska I et al (2009) Relationship between renal resistive index and early target organ damage in patients with never-treated essential hypertension. Blood Press 18(1–2):55–61
Menzilcioglu MS, Duymus M, Citil S, Avcu S, Gungor G, Sahin T et al (2015) Strain wave elastography for evaluation of renal parenchyma in chronic kidney disease. Br J Radiol 88:20140714
Ozkan F, Yavuz YC, Inci MF, Altunoluk B, Ozcan N, Yuksel M et al (2013) Interobserver variability of ultrasound elastography in transplant kidneys: correlations with clinical-Doppler parameters. Ultrasound Med Biol 39(1):4–9
Havre RF, Waage JR, Gilja OH, Odegaard S, Nesje LB (2011) Real-time elastography: strain ratio measurements are influenced by the position of the reference area. Ultraschall in der Medizin. [Epub ahead of print]
Guo LH, Xu HX, Fu HJ, Peng A, Zhang YF, Liu LN (2013) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for noninvasive evaluation of renal parenchyma elasticity: preliminary findings. PLoS One 8(7):e68925
Goya C, Kilinc F, Hamidi C, Yavuz A, Yildirim Y, Cetincakmak MG et al (2015) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for evaluation of renal parenchyma elasticity in diabetic nephropathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 204(2):324–329
Krumme B (2006) Renal Doppler sonography–update in clinical nephrology. Nephron Clin Pract 103(2):c24–c28
Sugiura T, Wada A (2009) Resistive index predicts renal prognosis in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transpl 24(9):2780–2785
Viazzi F, Leoncini G, Derchi LE et al (2014) Ultrasound Doppler renal resistive index: a useful tool for the management of the hypertensive patient. J Hypertens 32(1):149–153
Winther SO, Thiesson HC, Poulsen LN, Chehri M, Agerskov H, Tepel M (2012) The renal arterial resistive index and stage of chronic kidney disease in patients with renal allograft. PLoS One 7(12):e51772
Havre RF, Elde E, Gilja OH, Odegaard S, Eide GE, Matre K et al (2008) Freehand real-time elastography: impact of scanning parameters on image quality and in vitro intra- and interobserver validations. Ultrasound Med Biol 34(10):1638–1650
Göya C, Hamidi C, Ece A, Okur MH, Taşdemir B, Çetinçakmak MG et al (2015) Acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography for detection of renal damage in children. Pediatr Radiol 45:55–61
Mostbeck GH, Kain R, Mallek R, Derfler K, Walter R, Havelec L et al (1991) Duplex Doppler sonography in renal parenchymal disease. Histopathologic correlation. J Ultrasound Med 10(4):189–194
Bige N, Levy PP, Callard P, Faintuch JM, Chigot V, Jousselin V et al (2012) Renal arterial resistive index is associated with severe histological changes and poor renal outcome during chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol 13:139
Ikee R, Kobayashi S, Hemmi N, Imakiire T, Kikuchi Y, Moriya H et al (2005) Correlation between the resistive index by Doppler ultrasound and kidney function and histology. Am J Kidney Dis 46(4):603–609
Acknowledgments
None of the authors involved in this study received financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menzilcioglu, M.S., Duymus, M., Citil, S. et al. The comparison of resistivity index and strain index values in the ultrasonographic evaluation of chronic kidney disease. Radiol med 121, 681–687 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-016-0652-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-016-0652-3