Abstract
Purpose
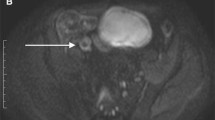
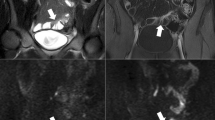
This study was undertaken to determine the diagnostic capabilities of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DWI) in detecting ileal inflammation in Crohn’s disease (CD), and to verify the correlation between the DWI sequences and the Harvey-Bradshaw index (HBI).
Materials and methods
Twenty patients with an endoscopic-histological diagnosis of CD of the terminal ileum and MR enterography with DWI sequences and HBI were retrospectively selected. Disease activity was visually evaluated on the DWI sequences. In quantitative analysis, the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) of the terminal ileum was compared with that of normal ileal loops. Pearson’s r was used to verify the correlation between the DWI findings and the HBI.
Results
On visual assessment, the accuracy, sensitivity and positive predictive value of DWI for the detection of inflammation were 100 %. In the quantitative assessment, the ADC value of the disease-active terminal ileum was significantly lower (p < 0.00001) than that of normal ileal loops. A correlation was found between visual assessment of the terminal ileum with the DWI sequences and HBI; no correlation was found between ADC of the terminal ileum and HBI.
Conclusion
DWI sequences may be useful in differentiating actively inflamed small bowel segments from normal small bowel in CD. Though partial, the correlation between DWI sequences and HBI confirms the utility of this technique in the study of patients with CD.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Laghi A, Paolantonio P, Iafrate F et al (2002) Oral contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging of the bowel. Top Magn Reson Imaging 13(6):389–396
Laghi A, Paolantonio P, Passariello R (2005) Small bowel. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 13(2):331–348
Rechichi G, Galimberti S, Signorelli M et al (2010) Myometrial invasion in endometrial cancer: diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR imaging at 1.5-T. Eur Radiol 20(3):754–762
Lin G, Ng KK, Chang CJ et al (2009) Myometrial invasion in endometrial cancer: diagnostic accuracy of diffusion-weighted 3.0-T MR imaging–initial experience. Radiology 250(3):784–792
Rizzo L, Crasto SG, Moruno PG et al (2009) Role of diffusion- and perfusion-weighted MR imaging for brain tumour characterisation. Radiol Med 114(4):645–659
Tondo F, Saponaro A, Stecco A et al (2011) Role of diffusion-weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant lesions of the chest-mediastinum. Radiol Med 116(5):720–733
Colagrande S, Carbone SF, Carusi LM et al (2006) Magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging: extraneurological applications. Radiol Med 111(3):392–419
Manenti G, Di Roma M, Mancino S et al (2008) Malignant renal neoplasms: correlation between ADC values and cellularity in diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging at 3 T. Radiol Med 113(2):199–213
Rizzo S, Summers P, Raimondi S et al (2011) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in assessing cervical tumour response to nonsurgical therapy. Radiol Med 116(5):766–780
Kiroglu Y, Calli C, Yunten N et al (2006) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of viral encephalitis. Neuroradiology 48:875–880
Verswijvel G, Vandecaveye V, Gelin G et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the evaluation of renal infection: preliminary results. JBR-BTR 85:100–103
Taouli B, Chouli M, Martin AJ et al (2008) Chronic hepatitis: role of diffusion-weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging for the diagnosis of liver fibrosis and inflammation. J Magn Reson Imaging 28:89–95
Palmucci S, Mauro LA, Failla G et al (2012) Magnetic resonance with diffusion-weighted imaging in the evaluation of transplanted kidneys: updating results in 35 patients. Transplant Proc 44:1884–1888
Oto A, Zhu F, Kulkarni K et al (2009) Evaluation of diffusion-weighted MR imaging for detection of bowel inflammation in patients with Crohn’s disease. Acad Radiol 16:597–603
Kiryu S, Dodanuki K, Takao H et al (2009) Free-breathing diffusionweighted imaging for the assessment of inflammatory activity in Crohn’s disease. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:880–886
Oto A, Kayhan A, Williams Jt et al (2011) Active Crohn’s disease in the small bowel: evaluation by diffusion weighted imaging and quantitative dynamic contrast enhanced MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 33(3):615–624
Best WR (2006) Predicting the Crohn’s disease activity index from the Harvey-Bradshaw index. Inflamm Bowel Dis 12(4):304–310
Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM (1980) A simple index of Crohn’s-disease activity. Lancet 1(8167):514
Laghi A, Paolantonio P, Iafrate F et al (2003) MR of the small bowel with a biphasic oral contrast agent (polyethylene glycol): technical aspects and findings in patients affected by Crohn’s disease. Radiol Med 106(1–2):18–27
Stange EF, Travis SP, Vermeire S et al (2006) European evidence based consensus on the diagnosis and management of Crohn’s disease: definitions and diagnosis. Gut 55(Suppl 1):i1–i15
Paolantonio P, Ferrari R, Vecchietti F et al (2009) Current status of MR imaging in the evaluation of IBD in a pediatric population of patients. Eur J Radiol 69(3):418–424
Laghi A, Borrelli O, Paolantonio P (2003) Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of the terminal ileum in children with Crohn’s disease. Gut 52(3):393–397
Ream JM, Dillman JR, Adler J et al (2013) MRI diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in pediatric small bowel Crohn disease: correlation with MRI findings of active bowel wall inflammation. Pediatr Radiol. 43(9):1077–1085
Maccioni F, Viscido A, Broglia L et al (2000) Evaluation of Crohn disease activity with magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom Imaging 25(3):219–228
Malagò R, D’Onofrio M, Mantovani W et al (2012) Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (CEUS) vs. MRI of the small bowel in the evaluation of Crohn’s disease activity. Radiol Med 117(2):268–281
Oussalah A, Laurent V, Bruot O et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance without bowel preparation for detecting colonic inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut 59(8):1056–1065
Rimola J, Ordás I, Rodriguez S et al (2011) Magnetic resonance imaging for evaluation of Crohn’s disease: validation of parameters of severity and quantitative index of activity. Inflamm Bowel Dis 17(8):1759–1768
Buisson A, Joubert A, Montoriol PF et al (2013) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for detecting and assessing ileal inflammation in Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 37(5):537–545
Hordonneau C, Buisson A, Scanzi J et al (2014) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in ileocolonic Crohn’s disease: validation of quantitative index of activity. Am J Gastroenterol 109(1):89–98
Shen SH, Chiou YY, Wang JH et al (2008) Diffusion-weighted single-shot echo-planar imaging with parallel technique in assessment of endometrial cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:481–488
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foti, P.V., Farina, R., Coronella, M. et al. Crohn’s disease of the small bowel: evaluation of ileal inflammation by diffusion-weighted MR imaging and correlation with the Harvey-Bradshaw index. Radiol med 120, 585–594 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-015-0502-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-015-0502-8