Abstract
Purpose
Radiochemotherapy (RCT) is the standard adjuvant treatment for patients affected by glioblastoma (GBM). As there is no evidence in elderly patients with GBM, combined, single modality or best supportive care is used. The aim of this retrospective study was to evaluate acute toxicity and outcome of elderly patients with GBM treated with RCT with temozolomide (TMZ).
Materials and methods
Patients >65 years with newly diagnosed GBM who underwent surgery or biopsy and RCT were evaluated. Recursive Partitioning Analysis (RPA) class and National Cancer Institute — Common Toxicity Criteria (NCI-CTC) version 3 were used to classify patients and evaluate acute toxicity, respectively.
Results
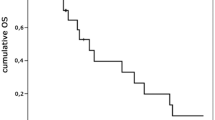
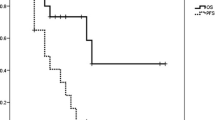
From April 2005 to January 2011, 35 patients (18 women and 17 men) with GBM were treated at our institution. Only 31.43% of cases underwent complete resection. Median progression-free survival (PFS) was 8 months and median overall survival (OS) 13 months. At univariate and multivariate analysis, only RPA class correlated with OS (p=0.01, p=0.03, respectively). During RCT, toxicity was mild (thrombocytopaenia G3–4, 11.43%; neurological toxicity, G3–4, 8.57%).
Conclusions
Our data suggest that RCT with TMZ seems to produce a better outcome with a mild toxicity profile in elderly patients affected by GBM.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
La radiochemioterapia (RTCHT) è il trattamento standard nei pazienti affetti da glioblastoma (GBM), ma a causa della mancanza di evidenze nei pazienti anziani, la radioterapia e la chemioterapia possono essere utilizzate singolarmente o integrate. Il nostro studio retrospettivo valuta la tossicità acuta e l’outcome della RTCHT con temozolomide (TMZ) nei pazienti anziani affetti da GBM.
Materiali e metodi
Sono stati valutati pazienti con età superiore a 65anni affetti da GBM sottoposti a chirurgia o biopsia e RTCHT. I pazienti sono stati suddivisi secondo le classi prognostiche del radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG)- recursive partitioning analysis (RPA). La tossicità acuta durante RTCHT è stata valutata secondo la scala National Cancer Institute-Common Toxicity Criteria (NCICTC) vers.3.
Risultati
Da aprile 2005 a gennaio 2011, 35 pazienti (18 donne e 17 uomini) sono stati trattati presso la nostra divisione. Solo 11 pazienti (31,43%) sono stati sottoposti a resezione completa. La sopravvivenza libera da progressione e la sopravvivenza mediane sono state di 8 e 13 mesi, rispettivamente. All’analisi univariata e multivariata solo la classe RPA ha mostrato influenzare la sopravvivenza (p=0,01; p=0,03). La tossicità acuta, durante RTCHT, è stata accettabile (11,43% di trombocitopenia G3–4; 8,57% di tossicità neurologica G3–4).
Conclusioni
I nostri dati suggeriscono che nei pazienti anziani l’associazione di radioterapia e temozolomide sembra essere efficace e sicura.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
DeAngelis LM (2001) Brain tumors. N Engl J Med 344:114–123
Fisher JL, Schwartzbaum JA, Wrensch M, Wiemels JL (2007) Epidemiology of brain tumors. Neurol Clin 25:867–890 vii
Curran WJ Jr, Scott CB, Horton J et al (1993) Recursive partitioning analysis of prognostic factors in three radiation therapy oncology group malignant glioma trials. J Natl Cancer Inst 85:704–710
Simpson JR, Horton J, Scott C et al (2003) Influence of location and extent of surgical resection on survival of patients with glioblastoma multiforme: results of three consecutive Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) clinical trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 26:239–244
Stupp R, Mason W, Van der Bent M et al (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant Temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996
Athanassiou H, Sinodinou M, Maragoudakis E et al (2005) Randomized phase II study of temozolomide and radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol 23:2372–2377
Iwamoto FM, Cooper AR, Reiner AS et al (2009) Glioblastoma in eldery: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center experience (1997–2007) Cancer 16:3758–3766
Scott J, Tsai YY, Chinnaiyan P, Yu HH (2011) Effectiveness of Radiotherapy for elderly patients with glioblastoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:206–210
Mohan DS, Suh JH, Phan JL et al (1998) Outcome in elderly patients undergoing definitive surgery and radiation therapy for supratentorial glioblastoma multiforme at a tertiary care institution. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 42:981–987
Balducci M, Apicella G, Manfrida S et al (2010) Single-arm phase II study of conformal radiation therapy and temozolomide plus fractionated stereotactic conformal boost in high grade gliomas. Strahlenther Onkol 186:558–564
Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA et al (2000) New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst 92:205–216
Chaichana KL, Garzon-Muvdi T, Parker S et al (2011) Supratentorial Glioblastoma Multiforme: The role of Surgical Resection Versus Biopsy Among Older Patients. Ann Surg Oncol 18:239–245
Mangiola A, Maira G, De Bonis P et al (2006) Glioblastoma Multiforme in elderly: a therapeutic challenge. J Neurooncol 76:159–163
Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP et al (2009) Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomized phase III study: 5-years analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol 10:459–466
Kocher M, Frommolt P, Borberg SK et al (2008) Randomized study of postoperative radiotherapy and simultaneous temozolomide without adjuvant chemotherapy for glioblastoma. Strahlenther Onkol 184:572–579
Sridhar T, Gore A, Boiangiu I, Machin D, Symonds RP (2009) Concomitant (without adjuvant) temozolomide and radiation to treat glioblastoma: a retrospective study. Clin Oncol (R Coll) 21:19–22
Mrugala MM, Chamberlain MC (2008) Mechanisms of disease: temozolomide and glioblastoma-look to the future. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 5:476–486
Kocher M, Kunze S, Eich HT et al (2005) Efficacy and toxicity of postoperative temozolomide radiochemotherapy in malignant glioma. Strahlenther Onkol 181:157–163
Balducci, M, D’Agostino GR, Manfrida S et al (2010) Radiotherapy and concomitant temozolomide during the first and last weeks in high grade gliomas: long-term analysis of a phase II study. J Neurooncol 97:95–100
Rubino G, Sacco P, Cerase A et al (2004) Radiotherapy of malignant gliomas: results from conventional treatment methods and the prospects of advanced techniques. Radiol Med 107:128–135
Dirier A, Abacioglu MU, Okkan S et al (2010) Radiotherapy with or without temozolomide in elderly glioblastoma patients: Treatment results and prognostic factor. J Clin Oncol 28:15s
Minniti G, De Sanctis V, Muni R et al (2008) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma in elderly patiets. J Neurooncol 88:97–103
Fiorentino A, Chiesa S, De Bonis P et al (2010) Impact of temozolomide and radiation therapy in elderly patients affected by glioblastoma: a pooled analysis of three prospectic phase II trials. J Clin Oncol 28:7s
Fiorica F, Berretta M, Colosimo C et al (2010) Glioblastoma in elderly patients: Safety and efficacy of adjuvant radiotherapy with concomitant temozolomide. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 51:277–282
Combs SE, Wagner J, Bischof M et al (2008) Postoperative treatment of primary gioblastoma multiforme with radiation and concomitant temozolomide in elderly patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:987–992
Brandes AA, Franceschi E, Tosoni A et al (2009) Temozolomide concomitant and adjuvant to radiotherapy in elderly patients with glioblastoma: correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. Cancer 115:3512–3518
Gerstein J, Franz K, Steinbach JP et al (2010) Postoperative radiotherapy and concomitant Temozolomide for elderly patients with glioblastoma. Radiother Oncol 97:382–386
Keim-Guibert F, Chinot O, Taillandier L et al (2007)Radiotherapy for glioblastoma in elderly. N Eng J Med 356:1527–1535
Roa W, Brasher PM, Bauman G et al (2004) Abbreviated course of radiation therapy in older patients with glioblastoma multiforme: a prospective randomized clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 22:1593–1598
Chamberlain MC, Chalmers L (2007) A pilot study of primary temozolomide chemotherapy and deferred radiotherapy in elderly patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 82:207–209
Laigle-Donadey F, Figarella-Branger D, Chinot O et al (2010) Up-front temozolomide in elderly patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 99:89–94
Glantz M, Chamberlain M, Liu Q et al (2003) Temozolomide as an alternative to irradiation for elderly patients with new diagnosed malignant gliomas. Cancer 97:2262–2266
Chinot OL, Barrie M, Barrie M et al (2004) Phase II study of temozolomide without radiotherapy in newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme in an elderly population. Cancer 100:2208–2214
Wick W, Engel C, Combs SE et al (2010) NOA-08 randomized phase III trial of 1-week-on/1-week-off temozolomide versus involved field radiotherapy in elderly (older than 65) patients with newly diagnosed anaplastic astrocytoma or glioblastoma (Methusalem) J Clin Oncol 28(Suppl):18s
Malmstrom A, Grønberg BH, Stupp R et al (2010) Glioblastoma (GBM) in elderly patients: a randomized phase III trial comparing survival in patients treated with 6-week radiotherapy (RT) versus hypofractionated RT over 2 weeks versus temozolomide single agent chemotherapy (TMZ) J Clin Oncol 28(Suppl):18s
Yovino S, Grossman SA (2011) Treatment of glioblastoma in “elderly” patients. Cur Treat Opin Oncol 12:253–262
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiorentino, A., Chiumento, C., Caivano, R. et al. Adjuvant radiochemotherapy in the elderly affected by glioblastoma: single-institution experience and literature review. Radiol med 118, 870–881 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-012-0906-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-012-0906-7