Abstract
Purpose
We evaluated the experience with and efficacy of stent-grafting for iatrogenic peripheral arterial ruptures.
Materials and methods
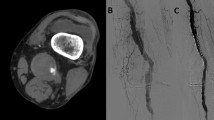
From 2005 to 2009 we performed stent-grafting on four male patients (age 38–67 years) with iatrogenic peripheral arterial ruptures. In patient 1, grointissue necrosis followed a subcutaneous injection and led to femoral arterial rupture. Pseudoaneurysms ruptured in patients 2 and 3 who were undergoing femoral arteriotomy. Patient 1 experienced a ruptured carotid artery during neck surgery. Shock occurred in three of the four patients. Four patients underwent self-expanding stent-grafting (8 mm×60 mm or 8 mm×80 mm) under local anaesthesia.
Results
Haemorrhages were controlled in all patients. No procedure-related complications occurred. Patient 1 died of lung metastases 13 months after stent-grafting. Follow-up examinations showed that the stent-graft remained patent in patients 1, 2 and 4, whereas stent occlusion occurred after 15 months in patient 3; in this case, a pseudoaneurysm proximal to the stent was identified, and although repeat stent-grafting successfully stopped the bleeding, the patient died of multiple organ failure 1 week later.
Conclusions
Emergency stent-grafting is a technically feasible and therapeutically effective modality for treating high-risk patients who experience iatrogenic peripheral arterial ruptures. The efficient treatment of hypotension and early endovascular intervention will improve the prognosis.
Riassunto
Obiettivo
Scopo del presente lavoro è valutare la nostra esperienza nell’utilizzo di endoprotesi e la loro efficacia nel trattamento delle rotture iatrogene delle arterie periferiche.
Materiali e metodi
Dal 2005 al 2009 abbiamo posizionato quattro endoprotesi in altrettanti pazienti (età 38–67 anni) con rottura iatrogena delle arterie periferiche. Nel paziente 1, la necrosi dei tessuti molli inguinali, sviluppatasi in seguito ad una iniezione sottocutanea, ha portato alla rottura dell’arteria femorale. Nei pazienti 2 e 3, che sono stati sottoposti ad arteriotomia femorale, si è verificata la rottura di pseudoaneurisma. Il paziente 4 ha subito la rottura della carotide durante un intervento chirurgico al collo. Tre su quattro pazienti sono entrati in stato di shock. A tutti i pazienti è stata posizionata un’endoprotesi autoespandente (8 mm×60 mm or 8 mm×80 mm) in anestesia locale.
Risultati
In tutti i casi si è avuto un arresto dell’emorragia. Non ci sono state complicanze correlate alle procedure. Il paziente 1 è morto per metastasi polmonari 13 mesi dopo il posizionamento dell’endoprotesi. Gli esami di follow-up hanno dimostrato che le endoprotesi nei pazienti 1, 2 e 4 sono rimaste pervie, mentre nel paziente 3 si è occlusa dopo 15 mesi; in quest’ultimo caso, è stato individuato uno pseudoaneurisma prossimale allo stent e, nonostante il posizionamento di una nuova endoprotesi abbia bloccato l’emorragia, il paziente è morto per insufficienza multiorgano una settimana dopo.
Conclusioni
Il posizionamento in emergenza di endoprotesi è una modalità tecnicamente realizzabile e terapeuticamente efficace nel trattamento di pazienti ad alto rischio che hanno subito la rottura iatrogena di un’arteria periferica. Un efficiente trattamento ipotensivo e un precoce intervento endovascolare migliorano la prognosi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References/Bibliografia
Morgan R, Belli AM (2003) Current treatment methods for postcatheterization pseudoaneurysms. J Vasc Interv Radiol 14:697–710
Tsetis D (2010) Endovascular treatment of complications of femoral arterial access. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 33:457–468
Parodi JC, Palmaz JC, Barone HD (1991) Transfemoral intraluminal graft implantation for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Ann Vase Surg 5:491–499
Gasparini D, Lovaria A, Saccheri S et al (1997) Percutaneous treatment of iliac aneurysms and pseudoaneurysms with Cragg Endopro System 1 stent-grafts. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 20:348–352
Baltacioǧlu F, Cimşt NC, Cil B et al (2003) Endovascular stent-graft applications in iatrogenic vascular injuries. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 26:434–439
Adovasio R, Mucelli FP, Lubrano G et al (2003) Endovascular treatment of external iliac artery injuries after hip arthroplasty. J Endovasc Ther 10:672–675
Fellmeth BD, Roberts AC, Bookstein JJ et al (1991) Postangiographic femoral artery injuries: nonsurgical repair with US guided compression. Radiology 178:671–675
Vlachou PA, Karkos CD, Bains S et al (2011) Percutaneous ultrasoundguided thrombin injection for the treatment of iatrogenic femoral artery pseudoaneurysms. Eur J Radiol 77:172–174
Franco CD, Goldsmith J, Veith FJ et al (1993) Management of arterial injuries produced by percutaneous femoral procedures. Surgery 113:419–425
Onal B, Kosar S, Gumus T et al (2004) Postcatheterization femoral arteriovenous fistulas: endovascular treatment with stent-grafts. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 27: 453–458
Hussain FM, Kopchok G, Heilbron M et al (1998) Wallgraft endoprosthesis: initial canine evaluation. Am Surg 64:1002–1006
Bates MC, AbuRahma AF, Crotty B (2005) Successful urgent endovascular surgery for symptomatic subclavian artery aneurysmal compression of the trachea. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 64: 291–295
Gandini R, Pipitone V, Konda D et al (2005) Endovascular treatment of a giant superior mesenteric artery pseudoaneurysm using a nitinol stentgraft. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 28: 102–106
Jahnke T, Schaefer PJ, Heller M et al (2008) Interventional management of massive hemothorax due to inadvertent puncture of an aberrant right subclavian artery. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 31:S124–S127
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, L., Shen, J. & Tong, J.J. Emergency stent-graft implantation for iatrogenic peripheral arterial rupture. Radiol med 118, 152–157 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-012-0826-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11547-012-0826-6