Abstract
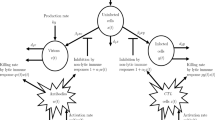
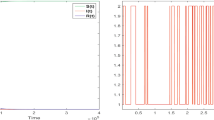
Stable periodic oscillations have been shown to exist in mathematical models for the CTL response to HTLV-I infection. These periodic oscillations can be the result of mitosis of infected target CD4+ cells, of a general form of response function, or of time delays in the CTL response. In this study, we show through a simple mathematical model that time delays in the CTL response process to HTLV-I infection can lead to the coexistence of multiple stable periodic solutions, which differ in amplitude and period, with their own basins of attraction. Our results imply that the dynamic interactions between the CTL immune response and HTLV-I infection are very complex, and that multi-stability in CTL response dynamics can exist in the form of coexisting stable oscillations instead of stable equilibria. Biologically, our findings imply that different routes or initial dosages of the viral infection may lead to quantitatively and qualitatively different outcomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asquith, B., & Bangham, C. R. M. (2007). Quantifying HTLV-I dynamics. Immunol. Cell Biol., 85, 280–286.
Bangham, C. R. (2000). The immune response to HTLV-I. Curr. Opin. Immunol., 12, 397–402.
Bangham, C. R. M. (2003). The immune control and cell-to-cell spread of human T-lymphotropic virus type 1. J. Gen. Virol., 84, 3177–3189.
Beretta, E., Carletti, M. et al. (2006). Stability analysis of a mathematical model of the immune response with delays. In Y. Iwasa, K. Sato, & Y. Takeuchi (Eds.), Mathematics for life science and medicine (pp. 179–208). Berlin: Springer.
Beretta, E., & Kuang, Y. (2002). Geometric stability switch criteria in delay differential systems with delay dependent parameters. SIAM J. Math. Anal., 33, 1144–1165.
Beretta, E., & Tang, Y. (2003). Extension of a geometric stability switch criterion. Funkcial. Ekvac., 46, 337–361.
Burić, N., Mudrinic, M., & Vasović, N. (2001). Time delay in a basic model of the immune response. Chaos Solitons Fractals, 12, 483–489.
Carletti, M., & Beretta, E. (2007). Numerical detection of instability regions for delay models with delay-dependent parameters. J. Comput. Appl. Math., 205, 835–848.
Clark, L. H., Schlosser, P. M., & Selgrade, J. F. (2003). Multiple stable periodic solutions in a model for hormonal control of the menstrual cycle. Bull. Math. Biol., 65, 157–173.
Crauste, F. (2009). Delay model of hematopoietic stem cell dynamics: asymptotic stability and stability switch. Math. Model. Nat. Phenom., 4, 28–47.
Freedman, H. I., Tang, M. X., & Ruan, S. G. (1994). Uniform persistence and flows near a closed positively invariant set. J. Dyn. Differ. Equ., 6, 583–600.
Gallo, R. C. (2005). History of the discoveries of the first human retroviruses: HTLV-1 and HTLV-2. Oncogene, 24, 5926–5930.
Gomez-Acevedo, H., & Li, M. Y. (2002). Global dynamics of a mathematical model for HTLV-I infection of T cells. Can. Appl. Math. Q., 10, 71–86.
Gomez-Acevedo, H., Li, M. Y., & Jacobson, S. (2010). Multi-stability in a model for CTL response to HTLV-I infection and its consequences in HAM/TSP development and prevention. Bull. Math. Biol., 72, 681–696.
Gyllenberg, M., & Yan, P. (2009). Four limit cycles for a three-dimensional competitive Lotka–Volterra system with a heteroclinic cycle. Comput. Math. Appl., 58, 649–669.
Hale, J. K., & Lunel, S. V. (1993). Introduction to functional differential equations. New York: Springer.
Hofbauer, J., & So, J. W. (1990). Multiple limit cycles for predator–prey models. Math. Biosci., 99, 71–75.
Hofbauer, J., & So, J. W. (1994). Multiple limit cycles for three-dimensional Lotka–Volterra equations. Appl. Math. Lett., 7, 65–70.
Hollsberg, P., & Hafler, D. A. (1993). Pathogenesis of diseases induced by human lymphotropic virus type I infection. N. Engl. J. Med., 328, 1173–1182.
Jacobson, S. (2002). Immunopathogenesis of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I associated neurologic disease. J. Infect. Dis., 186, S187–S192.
Koup, R. A., Safrit, J. T., et al. (1994). Temporal association of cellular immune responses with the initial control of viremia in primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 syndrome. J. Virol., 68, 4650–4655.
Kubota, R., Osame, M., & Jacobson, S. (2000). Retrovirus: human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I associated diseases and immune dysfunction. In M. W. Cunningham & R. S. Fujinami (Eds.), Effects of microbes on the immune system (pp. 349–371). Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Lang, J., & Li, M. Y. (2010). Stable and transient periodic oscillations in a mathematical model for CTL response to HTLV-I infection. Preprint.
LaSalle, J., & Lefschetz, S. (1961). Stability by Liapunov’s direct method. New York: Academic Press.
Li, M. Y., & Shu, H. (2010). Global dynamics of a mathematical model for HTLV-I infection of CD4+ T cells with delayed CTL response. Preprint.
Nowak, M. A., & May, R. M. (2000). Virus dynamics: mathematical principles of immunology and virology. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Osame, M., Janssen, R., et al. (1990). Nationwide survey of HTLV-I-associated myelopathy in Japan: association with blood transfusion. Ann. Neurol., 28, 50–56.
Perelson, A. S., & Nelson, P. W. (1999). Mathematical analysis of HIV-I dynamics in vivo. SIAM Rev., 41, 3–44.
Pilyugin, S. S., & Waltman, P. (2003). Multiple limit cycles in the chemostat with variable yield. Math. Biosci., 132, 151–166.
Seto, K., Abe, M. et al. (1995). A rat model of HTLV-I infection: development of chronic progressive myeloneuropathy in seropositive WKAH rats and related apoptosis. Acta Neuropathol., 89, 483–490.
Tang, Y., & Zhou, L. (2007). Stability switch and Hopf bifurcation for a diffusive prey–predator system with delay. J. Math. Anal. Appl., 334, 1290–1307.
Wang, K., Wang, W., Pang, H., & Liu, X. (2007). Complex dynamic behavior in a viral model with delayed immune response. Physica D, 226, 197–208.
Wodarz, D., & Bangham, C. R. M. (2000). Evolutionary dynamics of HTLV-I. J. Mol. Evol., 50, 448–455.
Wodarz, D., Nowak, M. A., & Bangham, C. R. M. (1999). The dynamics of HTLV-I and the CTL response. Immunol. Today, 20, 220–227.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, M.Y., Shu, H. Multiple Stable Periodic Oscillations in a Mathematical Model of CTL Response to HTLV-I Infection. Bull Math Biol 73, 1774–1793 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-010-9591-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-010-9591-7