Abstract
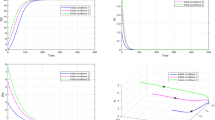
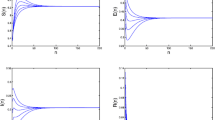
In this paper, based on SIR and SEIR epidemic models with a general nonlinear incidence rate, we incorporate time delays into the ordinary differential equation models. In particular, we consider two delay differential equation models in which delays are caused (i) by the latency of the infection in a vector, and (ii) by the latent period in an infected host. By constructing suitable Lyapunov functionals and using the Lyapunov–LaSalle invariance principle, we prove the global stability of the endemic equilibrium and the disease-free equilibrium for time delays of any length in each model. Our results show that the global properties of equilibria also only depend on the basic reproductive number and that the latent period in a vector does not affect the stability, but the latent period in an infected host plays a positive role to control disease development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beretta, E., Hara, T., Ma, W., Takeuchi, Y., 2001. Global asymptotic stability of an SIR epidemic model with distributed time delay. Nonlinear Anal. 47, 4107–4115.
Beretta, E., Takeuchi, Y., 1995. Global stability of an SIR model with time delays. J. Math. Biol. 33, 250–260.
Cooke, K.L., van den Driessche, P., 1996. Analysis of an SEIRS epidemic model with two delays. J. Math. Biol. 35, 240–260.
Cooke, K.L., van den Driessche, P., Zou, X., 1999. Interaction of maturation delay and nolinear birth in population and epidemic models. J. Math. Biol. 39, 332–352.
Derrick, W.R., van den Driessche, P., 2003. Homoclinic orbits in a disease transmission model with nonlinear incidence and nonconstant population. Discrete Continuous Dyn. Syst., Ser. B 3, 299–309.
Kermack, W.O., McKendrick, A.G., 1927. A contribution to the mathematical theory of epidemics. Proc. R. Soc. A115, 700–721.
Korobeinikov, A., Maini, P.K., 2005. Nonlinear incidence and stability of infectious disease models. Math. Med. Biol. 22, 113–128.
Korobeinikov, A., 2006. Lyapunov functions and global stability for SIR and SIRS epidemiological models with non-linear transmission. Bull. Math. Biol. 68, 615–626.
Korobeinikov, A., 2007. Global properties of infectious disease models with nonlinear incidence. Bull. Math. Biol. 69, 1871–1886.
Korobeinikov, A., 2009a. Global asymptotic properties of virus dynamics models with dose-dependent parasite reproduction and virulence, and nonlinear incidence rate. Math. Med. Biol. 26, 225–239.
Korobeinikov, A., 2009b. Stability of ecosystem: Global properties of a general prey-predator model. Math. Medic. Biol. (in print). http://imammb.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/reprint/dqp009.
Kuang, Y., 1993. Delay Differential Equations with Applications in Population Dynamics. Academic Press, San Diego.
Kyrychko, Y.N., Blyuss, K.B., 2005. Global properties of a delay SIR model with temporary immunity and nonlinear incidence rate. Nonlinear Anal. 6, 495–507.
Liu, W., Hethcote, H.W., Levin, S.A., 1987. Dynamical behavior of epidemiological models with nonlinear incidence rates. J. Math. Biol. 25, 359–380.
Ma, W., Song, M., 2004. Global stability for an SIR epidemic model with time delay. Appl. Math. Lett. 17, 1141–1145.
McCluskey, C.C., 2009a. Complete global stability for an SIR epidemic model with delay-distributed or discrete. Nonlinear Anal. doi:10.10.16/j.nonrwa.2008.10.014.
McCluskey, C.C., 2009b. Global stability for an SIER epidemiological model with varying infectivity and infinite delay. Math. Biosci. Eng. 6, 603–610.
Meng, X., Chen, L., Wu, B., 2009. A delay SIR epidemic model with pulse vaccination and incubation times. Nonlinear Anal. doi:10.1016/j.nonrwa.2008.10.041.
Rost, G., Wu, J., 2008. SEIR epidemiological model with varying infectivity and infinite delay. Math. Biosci. Eng. 5, 389–402.
Smith, H.L., 1983. Subharmonic bifurcation in an SIR epidemic model. J. Math. Biol. 17, 163–177.
van den Driessche, P., Watmough, J., 2002. Reproduction numbers and sub-threshold endemic equilibria for compartmental models of disease transmission. Math. Biosci. 180, 29–48.
Xu, R., Ma, Z., 2009. Global stability of a SIR epidemic model with nonlinear incidence rate and time delay. Nonlinear Anal. 10, 3175–3189.
Zhao, Z., Chen, L., Song, X., 2008. Impulsive vaccination of SEIR epidemic model with time delay and nonlinear incidence rate. Math. Comput. Simul. 79, 500–510.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, G., Takeuchi, Y., Ma, W. et al. Global Stability for Delay SIR and SEIR Epidemic Models with Nonlinear Incidence Rate. Bull. Math. Biol. 72, 1192–1207 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-009-9487-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11538-009-9487-6