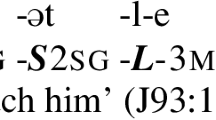Abstract
The interplay of the main factors affecting affix order in inflection (semantic scope, phonology, and morphological templates) can be accounted for in an inferential-realizational Optimality-Theoretic model of morphology, which we present here. Within this model, phonological form is spelled out by means of individual-language-particular realization constraints that associate abstract morphosyntactic feature values with phonological forms and that are ordered among more general constraints governing factors like scope and feature splitting. The data used to exemplify the application of our theory to affix order are drawn from Haspelmath’s (A grammar of Lezgian, Mouton de Gruyter, Berlin, 1993) grammar of Lezgian, a language of the Northeast Caucasian family spoken largely in Dagestan (Russia) and Azerbaijan.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aissen J. (1999) Markedness and subject choice in Optimality Theory. Natural Language and Linguistic Theory 17: 673–711
Aissen, J. (2003a). Differential coding, partial blocking, and Bidirectional OT. In P. Nowak & C. Yoquelet (Eds.), Proceedings of Berkeley Linguistic Society (Vol. 29, pp. 1–16).
Aissen J. (2003) Differential object marking: Iconicity vs. economy. Natural Language and Linguistic Theory 21: 435–483
Anderson S.R. (1992) A-morphous morphology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Anderson S.R. (2004) Morphological universals and diachrony. Yearbook of Morphology 2004: 1–17
Aronoff M. (1976) Word formation in generative grammar. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Aronoff M. (1994) Morphology by itself: Stems and inflectional classes. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Baerman M. (2004) Directionality and (un)natural classes in syncretism. Language 80: 807–827
Baker M. (1985) The mirror principle and morphosyntactic explanation. Linguistic Inquiry 16: 373–415
Benua L. (1995) Identity effects in morphological truncation. In: Beckman J.N., Dickey L.W., Urbanczyk S. (eds) Papers in Optimality Theory (University of Massachusetts Occasional Papers 18). Amherst, UMass, GLSA, pp 77–136
Blevins J.P. (2006) Word-based morphology. Journal of Linguistics 42: 531–573
Bonet, E. (2004). Morph insertion and allomorphy in Optimality Theory. In P. Boersma & J. A. Cutillas (Eds.), Advances in Optimality Theory, special issue of International Journal of English Studies, 4, 74–104.
Booij G. (2005) Compounding and derivation: Evidence for construction morphology. In: Dressler W.U., Rainer F., Kastovsky D., Pfeiffer O. (eds) Morphology and its demarcations. John Benjamins, Amsterdam, pp 109–132
Booij G. (2007) Construction morphology and the lexicon. In: Montermini F., Boyé G., Hatbout N. (eds) Selected proceedings of the 5th Décembrettes: Morphology in Toulouse. Cascadilla Press, Somerville, MA, pp 34–44
Booij, G. (2008). Construction morphology and compounding. In R. Lieber & P. Štekauer (Eds.), The Oxford handbook of compounding (pp. 201–216). Oxford: Oxford University Press. M. Aronoff, Z. Xu
Booij, G. (2009). Constructions and lexical units: An analysis of Dutch numerals. Linguistische Berichte 19(Sonderheft), 1–14.
Bybee J.L. (1985) Morphology: A study of the relation between meaning and form. John Benjamins, Amsterdam
Cole P. (1982) Imbabura Quechua (Lingua Descriptive Series 5). North Holland, Amsterdam
Comrie B. (1975) Causatives and universal grammar. Transactions of the Philological Society 1974: 1–32
Comrie, B. (1976). The syntax of causative constructions: Cross-language similarities and divergences. In M. Shibatani (Ed.), The grammar of causative constructions (Syntax and semantics) (Vol. 6, pp. 261–312). New York: Academic Press.
Dimmendaal G.J. (1983) The Turkana language. Foris, Dordrecht
Embick D., Marantz A. (2008) Architecture and blocking. Linguistic Inquiry 39: 1–53
Embick D., Noyer R. (2001) Movement operations after syntax. Linguistic Inquiry 32: 555–595
Good, J. (2003). Strong linearity: Three case studies towards a theory of morphosyntactic templatic constructions. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Berkeley.
Greenberg J. (1963) Some universals of grammar with particular reference to the order of meaningful elements. In: Greenberg J. (eds) Universals of language. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 73–113
Grimshaw J. (1986) A morphosyntactic explanation for the mirror principle. Linguistic Inquiry 17: 745–749
Grimshaw J. (1997) Projection, heads, and optimality. Linguistic Inquiry 28: 373–422
Grimshaw J. (1997) The best clitic: Constraint conflict in morphosyntax. In: Haegeman L. (eds) Elements of grammar. Kluwer, Dortrecht, pp 169–196
Grimshaw J. (2001) Optimal clitic positions and the lexicon in Romance clitic systems. In: Legendre G., Grimshaw J., Vikner S. (eds) Optimality-Theoretic syntax. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 205–240
Halle M., Marantz A. (1993) Distributed morphology and the pieces of inflection. In: Hale K., Keyser S.J. (eds) The view from building 20: Essays in linguistics in honor of Sylvain Bromberger. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 111–176
Haspelmath M. (1993) A grammar of Lezgian. Mouton de Gruyter, Berlin
Hyman L.M. (2003) Suffix ordering in Bantu: A morphocentric approach. Yearbook of Morphology 2002: 245–281
Julien, M. (2000). Syntactic heads and word-formation: A study of verbal inflection. Ph.D. thesis, University of Tromsø.
Kager R. (1996) On affix allomorphy and syllable counting. In: Kleinheiz U. (eds) Interfaces in phonology. Akademie Verlag, Berlin, pp 155–171
Kager R. (1999) Optimality Theory. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Kenstowicz M. (1994) Phonology in generative grammar. Blackwell, Cambridge, MA
Kenstowicz M. (1997) Base identity and uniform exponence: Alternatives to cyclicity. In: Durand J., Laks B. (eds) Current trends in phonology: Models and methods. University of Salford, Salford, pp 363–394
Kiparsky P. (1982) Lexical phonology and morphology. In: Yang I.-S. (eds) Linguistics in the morning calm. Seoul, Hanshin
Kiparsky P. (2005) Blocking and periphrasis in inflectional paradigms. Yearbook of Morphology 2004: 113–135
Lakämper R., Wunderlich D. (1998) Person marking in Quechua: A constraint-based minimalist analysis. Lingua 105: 113–148
MacBride, A. I. (2004). A constraint-based approach to morphology. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Los Angeles.
Magometov A.A. (1965) Tabasaranskij jazyk. Tbilisi, Mecniereba
Magometov A.A. (1970) Agul’skij jazyk. Tbilisi, Mecniereba
Mascaró J. (2007) External allomorphy and lexical representation. Linguistic Inquiry 38: 715–735
Matthews P.H. (1972) Inflectional morphology: A theoretical study based on aspects of Latin verb conjugation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Matthews P.H. (1974) Morphology: An introduction to the theory of word-structure. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Matthews P.H. (1991) Morphology (2nd ed). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
McCarthy, J. J. (2011). Pausal phonology and morpheme realization. in T. Borowsky, S. Kawahara, T. Shinya & M. Sugahara (Eds.), Prosody matters: Essays in honor of Lisa Selkirk. http://www.equinoxpub.com/books/showbook.asp?bkid=417.
McCarthy J.J., Prince A. (1993) Generalized alignment. Yearbook of Morphology 1993a: 79–153
McCarthy, J. J., & Prince, A. (1993b). Prosodic morphology I: Constraint interaction and satisfaction. Rutgers Optimality Archive, ROA-482.
McCarthy, J. J., & Prince, A. (1994). The emergence of the unmarked: Optimality in prosodic morphology. In M. Gonzàlez (Ed.), Proceedings of NELS 24 (pp. 333–379). Amherst: University of Massachusetts, GLSA.
McCarthy, J. J., & Prince, A. (1995). Faithfulness and reduplicative identity. In J. N. Beckman, L. W. Dickey, & S. Urbanczyk (Eds.), Papers in Optimality Theory (University of Massachusetts Occasional Papers 18) (pp. 249–384). Amherst: University of Massachusetts, GLSA.
Mohanan, K. P., & Mohanan, T. (2003). Universal and language-particular constraints in OT-LFG. In M. Butt & T. H. King (Eds.), Proceedings of the LFG03 conference. Stanford: CSLI.
Moor M. (1985) Studien zum lesgischen Verb. Otto Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden
Noyer R. (1998) Impoverishment theory and morphosyntactic markedness. In: Lapointe S.G., Brentari D.K., Farrell P.M. (eds) Morphology and its relation to phonology and syntax. CSLI Publications, Stanford, CA, pp 264–285
Palmer F.R. (2001) Mood and modality (2nd Ed). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Paster M. (2005) Pulaar verbal extensions and phonologically driven affix order. Yearbook of Morphology 2005: 155–199
Paster, M. (2006). Phonological conditions on affixation. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, Berkeley.
Paster, M. (2009). Phonologically conditioned affix order as an illusory phenomenon. Paper presented at the workshop on division of labor between morphology and phonology. Amsterdam.
Rice K. (2000) Morpheme order and semantic scope: Word formation in the Athapaskan verb. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rice, K. (2008). Forming the Athapaskan verb: What role for phonological factors? Paper presented at the Berkeley workshop on affix ordering.
Rosenthall S. (1997) The distribution of prevocalic vowels. Natural Language and Linguistic Theory 15: 139–180
Russell, K. (1995). Morphemes and candidates in Optimality Theory. Rutgers Optimality Archive, ROA-44.
Russell K. (1997) Optimality Theory and morphology. In: Archangeli D., Langendoen D.T. (eds) Optimality Theory: An overview. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 102–133
Sapir E. (1921) Language: An introduction to the study of speech. Harcourt Brace & Company, New York
Spencer A. (2003) Putting some order into morphology: Reflections on Rice (2000) and Stump (2001). Journal of Linguistics 39: 621–646
Stiebels, B. (2000). Linker inventories, linking splits and lexical economy. In B. Stiebels & D. Wunderlich (Eds.), Lexicon in focus (Studia Grammatica) (Vol. 45, pp. 211–245). Berlin: Akademie Verlag.
Stiebels B. (2003) Transparent, restricted and opaque affix orders. In: Junghanns U., Szucsich L. (eds) Syntactic structures and morphological information. Mouton de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 283–315
Stump G.T. (1993) On rules of referral. Language 69: 449–479
Stump G.T. (2001) Inflectional morphology: A theory of paradigm structure. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Stump, G. T. (2009). The typology of ordinal formation and its implications for a theory of derivational morphology. Paper presented at the conference “Universals and typology in word-formation”, P. J. Šafárik University, KoŠice, Slovakia.
Trommer, J. (2001). A hybrid account of affix order. In M. Andronis, C. Ball, H. Elston, & S. Neuvel (Eds.), Proceedings of Chicago Linguistic Society (Vol. 37, pp. 469–480).
Trommer J. (2003) The interaction of morphology and syntax in affix order. Yearbook of Morphology 2002: 283–324
Uslar, P. K. (1896). Étnografija Kavkaza. Jazykoznanie. VI. Kjurinskij jazyk [Ethnography of the Caucasus. Linguistics. VI. The Küre language]. Tiflis.
Wolf, M. A. (2008). Optimal interleaving: Serial phonology–morphology interaction in a constraintbased model. Ph.D. thesis, University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
Woolford E. (2001) Case patterns. In: Legendre G., Grimshaw J., Vikner S. (eds) Optimality-Theoretic syntax. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, pp 509–543
Wunderlich D. (1997) Cause and the structure of verbs. Linguistic Inquiry 28: 27–68
Wunderlich D. (2001) A correspondence-theoretic analysis of Dalabon transitive paradigms. Yearbook of Morphology 2000: 233–252
Wunderlich, D. (2006). Syntax: Optimality Theory. In K. Brown (Ed.), Encyclopedia of language and linguistics (2nd ed., Vol. 12, pp. 408–418). Elsevier: Oxford.
Wunderlich D., Fabri R. (1996) Minimalist morphology: An approach to inflection. Zeitschrift für Sprachwissenschaft, 1995 14(2): 236–294
Wurzel W.U. (1989) Inflectional morphology and naturalness. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Xu, Z. (2007a). An Optimality-Theoretic account of full and partial identity of forms. In Proceedings of the thirtieth annual Penn Linguistics Colloquium (PLC-30). Penn Working Papers in Linguistics (Vol. 13, Issue 1, pp. 421–434).
Xu, Z. (2007b). Inflectional morphology in Optimality Theory. Ph.D. thesis, Stony Brook University.
Xu, Z., & Aronoff, M. (2008). A realization Optimality-Theoretic approach to blocking and extended morphological exponence. Paper presented at the 2008 annual meeting of the Linguistic Society of America.
Yip M. (1998) Identity avoidance in phonology and morphology. In: Lapointe S.G., Brentari D.K., Farrell P.M. (eds) Morphology and its relation to phonology and syntax. Stanford, CSLI, pp 216–246
Zwicky, A. (1985). How to describe inflection. In M. Niepokuj, M. van Clay, V. Nikiforidou, & D. Feder (Eds.), Proceedings of Berkekey Linguistic Society (Vol. 11, pp. 372–386). Berkeley: University of California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aronoff, M., Xu, Z. A Realization Optimality-Theoretic approach to affix order. Morphology 20, 381–411 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11525-010-9181-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11525-010-9181-2