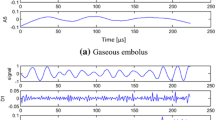
Abstract
This paper addresses the detection of emboli in transcranial Doppler ultrasound data acquired from an original portable device. The challenge is the removal of several artifacts (motion and voice) intrinsically related to long-duration (up to 1 h 40 mn per patient) outpatient signals monitoring from this device, as well as high intensities due to the stochastic nature of blood flow. This paper proposes an adapted removal procedure. This firstly consists of reducing the background noise and detecting the blood flow in the time–frequency domain using a likelihood method for contour detection. Then, a hierarchical extraction of features from magnitude and bounding boxes is achieved for the discrimination of emboli and artifacts. After processing of the long-duration outpatient signals, the number of artifacts predicted as emboli is considerably reduced (by 92% for some parameter values) between the first and the last step of our algorithm.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour S, Fallah A (2014) Removing ecg artifact from the surface emg signal using adaptive subtraction technique. J Biomed Phys Eng 4(1):33
Aydin N, Marvasti F, Markus H (2004) Embolic doppler ultrasound signal detection using discrete wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Inf Tech Biomed 8(2):182–190
Biard M, Kouamé D, Girault JM, Patat F (2003) Discrimination between emboli and artifacts during transcranial doppler. In: Proceedings of the world congress on ultrasonics, société française d’acoustique, WCU. pp 1101–1104
Biard M, Kouamé D, Girault J, Souchon G, Guibert B (2004) Casc : caractrisation du sang circulant. ITBM-RBM 25(5):283–288
Caruana R, Niculescu-Mizil A (2006) An empirical comparison of supervised learning algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 23rd international conference on machine learning, ICML ’06. ACM, New York, pp 161–168
Chan T, Vese L (2001) Active contours without edges. IEEE Trans Image Process 10(2):266–277
Chen Y, Wang Y (2008) Doppler embolic signal detection using the adaptive wavelet packet basis and neurofuzzy classification. Pattern Recogn Lett 29(10):1589–1595
Chung G, Jeong J, Kwak H, Hwang S (2015) Associations between cerebral embolism and carotid intraplaque hemorrhage during protected carotid artery stenting. Am J Neuroradiol 37(4):686–691
Gencer M, Bilgin G, Aydin N (2013) Embolic doppler ultrasound signal detection via fractional fourier transform. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 35th annual international conference of the IEEE. pp 3050–3053
Girault JM, Zhao Z (2014) Synchronous detector as a new paradigm for automatic microembolus detection. Int J Biomed Eng Technol 14(1):60–70
Huang YM, xin Du S (2005) Weighted support vector machine for classification with uneven training class sizes. In: Proceedings of 2005 international conference on machine learning and cybernetics, vol 7. pp 4365–4369
Karahoca A, Tunga MA (2015) A polynomial based algorithm for detection of embolism. Soft Comput 19(1):167–177
Karahoca A, Kucur T, Aydin N (2007) Data mining usage in emboli detection. In: ECSIS symposium on bio-inspired, learning, and intelligent systems for security, BLISS 2007. pp 159–162
Krongold BS, Sayeed AM, Moehring M, Ritcey J, Spencer MP, Jones DL (1999) Time-scale detection of microemboli in flowing blood with doppler ultrasound. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 46(9):1081–1089
Marvasti S, Gillies D, Marvasti F, Markus HS (2004) Online automated detection of cerebral embolic signals using a wavelet-based system. Ultrasound Med Biol 30(5):647–653
Menigot S, Dreibine L, Meziati N, Girault J (2009) Automatic detection of microemboli by means of a synchronous linear prediction technique. In: Ultrasonics symposium (IUS), 2009 IEEE International. pp 2371–2374
Mercer J (1909) Functions of positive and negative type, and their connection with the theory of integral equations. Philos Trans R Soc Lond 209:415–446
Millioz F, Martin N (2010) Estimation of a white Gaussian noise in the short time Fourier transform based on the spectral kurtosis of the minimal statistics: application to underwater noise. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics speech and signal processing (ICASSP). pp 5638–5641
Millioz F, Martin N (2011) Circularity of the stft and spectral kurtosis for time-frequency segmentation in Gaussian environment. IEEE Trans Signal Process 59(2):515–524
Otsu N (1975) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. Automatica 11(285–296):23–27
Parzen E (1962) On estimation of a probability density function and mode. Ann Math Stat 33(3):1065–1076
Paschoal FM, de Almeida Lins Ronconi K, de Lima Oliveira M, Nogueira RdC, Paschoal EHA, Teixeira MJ, Figueiredo EG, Bor-Seng-Shu E (2015) Embolic signals during routine transcranial doppler ultrasonography in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. BioMed research international 2015
Sarti A, Corsi C, Mazzini E, Lamberti C (2005) Maximum likelihood segmentation of ultrasound images with rayleigh distribution. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control 52(6):947–960
Sciolla B, Ceccato P, Dambry T, Guibert B, Delachartre P (2015) A comparison of non-parametric segmentation methods. In: GRETSI, Lyon. https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01307318
Serbes G, Aydin N (2014) Denoising performance of modified dual-tree complex wavelet transform for processing quadrature embolic doppler signals. Med Biol Eng Comput 52(1):29–43
Smith J, Evans D, Fan L, Bell P, Naylor A (1996) Differentiation between emboli and artefacts using dual-gated transcranial doppler ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 22(8):1031–1036
Sweeney KT, Ayaz H, Ward TE, Izzetoglu M, McLoone SF, Onaral B (2012) A methodology for validating artifact removal techniques for physiological signals. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 16(5):918–926
Wallace S, Døhlen G, Holmstrøm H, Lund C, Russell D (2015) Cerebral microemboli detection and differentiation during transcatheter closure of atrial septal defect in a paediatric population. Cardiol Young 25:237–244
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the ANR-13-LAB3-0006-01 LabCom AtysCrea and was supported by the LABEX CELYA (ANR-10-LABX-0060) and PRIMES (ANR-11-LABX-0063) of Université de Lyon, within the program “Investissements d’Avenir” (ANR-11-IDEX-0007) operated by the French National Research Agency (ANR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guépié, B.K., Sciolla, B., Millioz, F. et al. Discrimination between emboli and artifacts for outpatient transcranial Doppler ultrasound data. Med Biol Eng Comput 55, 1787–1797 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1624-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1624-z