Abstract
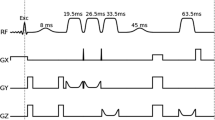
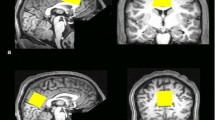
The aim of this work is to quantify individual and regional differences in the relative concentration of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in human brain with in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Spectral editing Mescher–Garwood point resolved spectroscopy (MEGA-PRESS) sequence and GABA analysis toolkit (Gannet) were used to detect and quantify GABA in anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and occipital cortex (OCC) of healthy volunteers. Residual bootstrap, a model-based statistical analysis technique, was applied to resample the fitting residuals of GABA from the Gaussian fitting model (referred to as GABA+ thereafter) in both individual and group data of ACC and OCC. The inter-subject coefficient of variation (CV) of GABA+ in OCC (20.66 %) and ACC (12.55 %) with residual bootstrap was lower than that of a standard Gaussian model analysis (21.58 % and 16.73 % for OCC and ACC, respectively). The intra-subject uncertainty and CV of OCC were lower than that of ACC in both analyses. The residual bootstrap analysis thus provides a more robust uncertainty estimation of individual and group GABA+ detection in different brain regions, which may be useful in our understanding of GABA biochemistry in brain and its use for the diagnosis of related neuropsychiatric diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1:307–310
Bogner W, Gruber S, Doelken M, Stadlbauer A, Ganslandt O, Boettcher U, Trattnig S, Doerfler A, Stefan H, Hammen T (2010) In vivo quantification of intracerebral GABA by single-voxel (1)H-MRS—How reproducible are the results? Eur J Radiol 73(3):526–531
Bolan PJ, Auffermann WF, Henry PG, Garwood M (2004) Feasibility of computer-intensive methods for estimating the variance of spectral fitting parameters. In: Proceedings of the 12th annual meeting ISMRM (abstract 304), Kyoto
Bolliger CS, Boesch C, Kreis R (2013) On the use of Cramer–Rao minimum variance bounds for the design of magnetic resonance spectroscopy experiments. Neuroimage 83:1031–1040
Bush G, Luu P, Posner MI (2000) Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cogn Sci 4(6):215–222
Choi IY, Lee SP, Merkle H, Shen J (2004) Single-shot two-echo technique for simultaneous measurement of GABA and creatine in the human brain in vivo. Magn Reson Med 51(6):1115–1121
Chung S, Lu Y, Henry RG (2006) Comparison of bootstrap approaches for estimation of uncertainties of DTI parameters. Neuroimage 33(2):531–541
Dobbe JG, Pre KJ, Kloen P, Blankevoort L, Streekstra GJ (2011) Computer-assisted and patient-specific 3-D planning and evaluation of a single-cut rotational osteotomy for complex long-bone deformities. Med Biol Eng Comput 49:1363–1370
Edden RA, Puts NA, Harris AD, Barker PB, Evans CJ (2014) Gannet: a batch-processing tool for the quantitative analysis of gamma-aminobutyric acid-edited MR spectroscopy spectra. J Magn Reson Imaging 40(6):1445–1452
Evans CJ, Puts NA, Robson SE, Boy F, McGonigle DJ, Sumner P, Singh KD, Edden RA (2013) Subtraction artifacts and frequency (mis-)alignment in J-difference GABA editing. J Magn Reson Imaging 38(4):970–975
Gao F, Edden RA, Li M, Puts NA, Wang G, Liu C, Zhao B, Wang H, Bai X, Zhao C, Wang X, Barker PB (2013) Edited magnetic resonance spectroscopy detects an age-related decline in brain GABA levels. Neuroimage 78:75–82
Harris AD, Puts NAJ, Barker PB, Edden RAE (2015) Spectral-editing measurements of GABA in the human brain with and without macromolecule suppression. Magn Reson Med 74:1523–1529
Haroon HA, Morris DM, Embleton KV, Alexander DC, Parker GJM (2009) Using the model-based residual bootstrap to quantify uncertainty in fiber orientations from Q-Ball analysis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(4):535–550
Johnson RW (2001) An introduction to the bootstrap. Teach Stat 23(2):49–54
Mescher M, Merkle H, Kirsch J, Garwood M, Gruetter R (1998) Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression. NMR Biomed 11:466–472
Mullins PG, McGonigle DJ, O’Gorman RL, Puts NAJ, Vidyasagar R, Evans CJ, Cardiff Symposium on MRS of GABA, Edden RAE (2014) Current practice in the use of MEGA-PRESS spectroscopy for the detection of GABA. Neuroimage 86:43–52
Near J, Ho YC, Sandberg K, Kumaragamage C, Blicher JU (2014) Long-term reproducibility of GABA magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Neuroimage 99:191–196
Polders DL, Leemans A, Luijten PR, Hoogduin H (2012) Uncertainty estimations for quantitative in vivo MRI T1 mapping. J Magn Reson 224:53–60
Provencher SW (2001) Automatic quantitation of localized in vivo 1H spectra with LCModel. NMR Biomed 14(4):260–264
Puts NA, Edden RA (2012) In vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy of GABA: a methodological review. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 60:29–41
Rothman DL, Petroff OAC, Behar KL, Mattson RH (1993) Localized 1H NMR measurements of γ-aminobutyric acid in human. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5662–5666
Rugelj D, Hrastnik A, Sevsek F, Vauhnik R (2015) Reliability of modified sensory interaction test as measured with force platform. Med Biol Eng Comput 53:525–534
Stephenson MC, Gunner F, Napolitano A, Greenhaff PL, Macdonald IA, Saeed N, Vennart W, Francis ST, Morris PG (2011) Applications of multi-nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 7T. World J Radiol 3:105–113
Terpstra M, Ugurbil K, Gruetter R (2002) Direct in vivo measurement of human cerebral GABA concentration using MEGA-editing at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 47(5):1009–1012
van der Veen JW, Shen J (2013) Regional difference in GABA levels between medial prefrontal and occipital cortices. J Magn Reson Imaging 38:745–750
Zhu T, Hu R, Qiu X, Taylor M, Tso Y, Yiannoutsos C, Navia B, Mori S, Ekholm S, Schifitto G, Zhong J (2011) Quantification of accuracy and precision of multi-center DTI measurements: a diffusion phantom and human brain study. Neuroimage 56(3):1398–1411
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant 2013QNA5004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Liao, C., Chen, S. et al. Uncertainty assessment of gamma-aminobutyric acid concentration of different brain regions in individual and group using residual bootstrap analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 55, 1051–1059 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1579-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-016-1579-5