Abstract
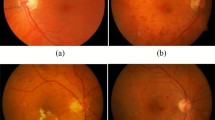
Diabetic macular edema (DME) is one of the most common causes of visual loss among diabetes mellitus patients. Early detection and successive treatment may improve the visual acuity. DME is mainly graded into non-clinically significant macular edema (NCSME) and clinically significant macular edema according to the location of hard exudates in the macula region. DME can be identified by manual examination of fundus images. It is laborious and resource intensive. Hence, in this work, automated grading of DME is proposed using higher-order spectra (HOS) of Radon transform projections of the fundus images. We have used third-order cumulants and bispectrum magnitude, in this work, as features, and compared their performance. They can capture subtle changes in the fundus image. Spectral regression discriminant analysis (SRDA) reduces feature dimension, and minimum redundancy maximum relevance method is used to rank the significant SRDA components. Ranked features are fed to various supervised classifiers, viz. Naive Bayes, AdaBoost and support vector machine, to discriminate No DME, NCSME and clinically significant macular edema classes. The performance of our system is evaluated using the publicly available MESSIDOR dataset (300 images) and also verified with a local dataset (300 images). Our results show that HOS cumulants and bispectrum magnitude obtained an average accuracy of 95.56 and 94.39 % for MESSIDOR dataset and 95.93 and 93.33 % for local dataset, respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adarsh P (2013) A novel approach for diagnosis and severity grading of diabetic maculopathy. In: 2013 international conference on advances in computing, communications and informatics (ICACCI), pp 1230–1235
Ahmad Fadzil MH, Izhar LI, Nugroho H, Nugroho HA (2011) Analysis of retinal fundus images for grading of diabetic retinopathy severity. Med Biol Eng Comput 49(6):693–700
Akram MU, Akhtar M, Javed MY (2012) An automated system for the grading of diabetic maculopathy in fundus images. In: Huang T, Zeng Z, Li C, Leung CS (eds) Neural information processing. Springer, pp 36–43
Ang MH, Acharya UR, Sree SV, Lim T-C, Suri JS (2011) Computer-based identification of diabetic maculopathy stages using fundus images. In: Multi modality state-of-the-art medical image segmentation and registration methodologies. Springer, pp 377–399
Bock R, Meier J, Nyúl LG, Hornegger J, Michelson G (2010) Glaucoma risk index: automated glaucoma detection from color fundus images. Med Image Anal 14(3):471–481
Cai D, He X, Han J (2008) Srda: an efficient algorithm for large-scale discriminant analysis. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 20(1):1–12
Chandran V, Elgar SL (1992) Position, rotation, and scale invariant recognition of images using higher-order spectra. In: IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing (ICASSP92). 5:213
Chandran V, Elgar SL (1993) Pattern recognition using invariants defined from higher order spectra-one-dimensional inputs. IEEE Trans Signal Proces 41(1):205–212
Chandran V, Steve E (1991) Shape discrimination using invariants defined from higher-order spectra. In: International conference on acoustics, speech, and signal processing ICASSP91, pp 3105–3108
Chandran V, Carswell B, Boashash B, Elgar S (1997) Pattern recognition using invariants defined from higher order spectra: 2-d image inputs. IEEE Trans Image Proces 6(5):703–712
Chowriappa P, Dua S, Acharya UR, Mookiah MRK (2013) Ensemble selection for feature-based classification of diabetic maculopathy images. Comput Biol Med 43(12):2156–2162
Chua KC, Chandran V, Acharya UR, Ng EYK, Caroline C, Manjunath G, Lim CM, Yan JMT, Gracielynne F, Suri JS (2008a) Computer-based detection of diabetes maculopathy stages. In: Acharya UR, Ng EYK, Suri JS (eds) Image modelling of the human eye. Artech House Inc, Norwood
Chua KC, Chandran V, Acharya UR, Lim CM (2008b) Cardiac state diagnosis using higher order spectra of heart rate variability. J Med Eng Technol 32(2):145–155
Chua KC, Chandran V, Acharya UR, Lim CM (2009) Analysis of epileptic eeg signals using higher order spectra. J Med Eng Technol 33(1):42–50
Chua KC, Chandran V, Acharya UR, Lim CM (2011) Application of higher order spectra to identify epileptic EEG. J Med Syst 35(6):1563–1571
Chua CK, Mookiah MRK, Koh JEW, Acharya UR, Lim CM, Laude A, Ng EYK et al (2013) Automated diagnosis of maculopathy stages using texture features. Int J Integr Care 13:1–2
Deepak KS, Sivaswamy J (2012) Automatic assessment of macular edema from color retinal images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(3):766–776
Diep TM, Tsui I (2013) Risk factors associated with diabetic macular edema. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 100(3):298–305
Duda RO, Hart PE, Stork DG (2012) Pattern classification. Wiley, New York
Fleming AD, Goatman KA, Philip S, Prescott GJ, Sharp PF, Olson JA (2010) Automated grading for diabetic retinopathy: a large-scale audit using arbitration by clinical experts. Br J Ophthalmol 94(12):1606–1610
Foracchia M, Ruggeri A (2004) Automatic estimation of endothelium cell density in donor corneas by means of fourier analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 42(5):725–731
Freund Y, Schapire RE (1997) A decision-theoretic generalization of on-line learning and an application to boosting. J Comput Syst Sci 55(1):119–139
Geoff D, Johnson MJ, Wiers MD (2010) Measurement of retinal vascular tortuosity and its application to retinal pathologies. Med Biol Eng Comput 48(1):87–95
Gun AM, Gupta MK, Dasgupta B (2008) Fundamentals of statistics (Vol I & II), 4th edn. World Press Private Ltd, Kolkata
Harney F (2006) Diabetic retinopathy. Medicine 34(3):95–98. ISSN 1357–3039
Hunter A, Lowell JA, Ryder B, Basu A, Steel D (2011) Automated diagnosis of referable maculopathy in diabetic retinopathy screening. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBC, 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE, pp. 3375–3378
International Diabetes Federation (2013) Idf diabetes atlas. http://www.idf.org/sites/default/files/EN_6E_Atlas_Full_0.pdf. Accessed 31 Sep 2014
Khademi A, Krishnan S (2007) Shift-invariant discrete wavelet transform analysis for retinal image classification. Med Biol Eng Comput 45(12):1211–1222
Khushaba RN, Sarath K, Sara L, Gamini D (2011) Driver drowsiness classification using fuzzy wavelet-packet-based feature-extraction algorithm. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(1):121–131
Kiire CA, Porta M, Chong V (2013) Medical management for the prevention and treatment of diabetic macular edema. Surv Ophthalmol 58(5):459–465
Li H, Chutatape O (2004) Automated feature extraction in color retinal images by a model based approach. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51(2):246–254
Lim ST, Zaki WMDW, Hussain A, Lim SL, Kusalavan S (2011) Automatic classification of diabetic macular edema in digital fundus images. In: 2011 IEEE colloquium on humanities, science and engineering (CHUSER), pp. 265–269
Luca G, Fabrice M, Karnowski TP, Li Y, Garg S, Tobin KW, Chaum E (2012) Exudate-based diabetic macular edema detection in fundus images using publicly available datasets. Med Image Anal 16(1):216–226
Mendel JM (1991) Tutorial on higher-order statistics (spectra) in signal processing and system theory: theoretical results and some applications. Proceed IEEE 79(3):278–305
Mookiah MRK, Oliver F (2013) Automated glaucoma detection using hybrid feature extraction in retinal fundus images. J Mech Med Biol 13(01):1350011(1)–1350011(21)
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Chua CK, Lim CM, Ng EYK, Laude A (2013a) Computer-aided diagnosis of diabetic retinopathy: a review. Comput Biol Med 43(12):2136–2155
Mookiah MRK, Acharya UR, Martis RJ, Chua CK, Lim CM, Ng EYK, Laude A (2013b) Evolutionary algorithm based classifier parameter tuning for automatic diabetic retinopathy grading: a hybrid feature extraction approach. Knowl Based Syst 39:9–22
Nayak J, Bhat PS, Acharya UR (2009) Automatic identification of diabetic maculopathy stages using fundus images. J Med Eng Technol 33(2):119–129
Neelakshi B, Grigorian RA, Tutela A, Zarbin MA (2009) Diabetic macular edema: pathogenesis and treatment. Survey Ophthalmol 54(1):1–32
Nikias CL, Mendel JM (1993) Signal processing with higher-order spectra. IEEE Signal Proces Mag 10(3):10–37
Noronha KP, Acharya UR, Nayak KP, Martis RJ, Bhandary SV (2014) Automated classification of glaucoma stages using higher order cumulant features. Biomed Signal Proces Control 10:174–183
Peng H, Long F, Ding C (2005) Feature selection based on mutual information criteria of max-dependency, max-relevance, and min-redundancy. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(8):1226–1238. ISSN 0162–8828
Pisano ED, Zong S, Hemminger BM, DeLuca M, Johnston RE, Muller K, Braeuning MP, Pizer SM (1998) Contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization image processing to improve the detection of simulated spiculations in dense mammograms. J Digital Imaging 11(4):193–200
Radon J (1986) On the determination of functions from their integral values along certain manifolds. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 5(4):170–176
Siddalingaswamy PC, Gopalakrishna PK (2010) Automatic grading of diabetic maculopathy severity levels. In: 2010 International conference on systems in medicine and biology (ICSMB), pp 331–334
Swami A, Mendel JM, Nikias CLM (1998) Higher-order spectral analysis toolbox: for use with MATLAB: user’s guide, vol 2. Mathworks Inc., pp 1–258
Tariq A, Akram MU, Shaukat A, Khan SA (2013) Automated detection and grading of diabetic maculopathy in digital retinal images. J Digit Imaging 26(4):803–812
ter Haar F (2005) Automatic localization of the optic disc in digital colour images of the human retina. PhD thesis, Citeseer
Vapnik V (2000) The nature of statistical learning theory. Springer, Berlin
Yau JWY, Rogers SL, Kawasaki R, Lamoureux EL, Kowalski JW, Bek T, Chen S-J, Dekker JM, Fletcher A, Grauslund J et al (2012) Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 35(3):556–564
Zhuo Z, Keong KC, Jiang L, Lui CCY, Tin A, Tien W (2012) Automatic glaucoma diagnosis with mRMR based feature selection. J Biom Biostat S7:1–8
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Social Innovation Research Fund (Project ID: T1202), Singapore, for providing grant for this research. Also authors would like to thank National Medical Research Council (NMRC/CSA/045/2012) and National Healthcare Group Clinician Scientist Career Scheme/12006 grant. We express our sincere thanks to Mr. Kevin Noronha, Manipal University, Manipal, India, for sharing the images for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have any related conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mookiah, M.R.K., Acharya, U.R., Chandran, V. et al. Application of higher-order spectra for automated grading of diabetic maculopathy. Med Biol Eng Comput 53, 1319–1331 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1278-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1278-7