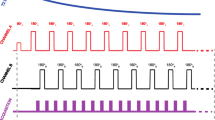
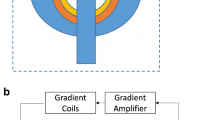
Abstract
We describe a new method for frequency down-conversion of MR signals acquired with the radio-frequency projections method for device localization. A low-amplitude, off-center RF pulse applied simultaneously with the echo signal is utilized as the reference for frequency down-conversion. Because of the low-amplitude and large offset from the Larmor frequency, the RF pulse minimally interfered with magnetic resonance of protons. We conducted an experiment with the coil placed at different positions to verify this concept. The down-converted signal was transformed into optical signal and transmitted via fiber-optic cable to a receiver unit placed outside the scanner room. The position of the coil could then be determined by the frequency analysis of this down-converted signal and superimposed on previously acquired MR images for comparison. Because of minimal positional errors (≤0.8 mm), this new device localization method may be adequate for most interventional MRI applications.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders J, Sangiorgio P, Deligianni X, Santini F, Scheer K, Boero G (2012) Integrated active tracking detector for MRI-guided interventions. Magn Reson Med 67(1):290
Bakker CJ, Hoogeveen RM, Weber J, van Vaals JJ, Viergever MA, Mali WP (1996) Visualization of dedicated catheters using fast scanning techniques with potential for MR-guided vascular interventions. Magn Reson Med 36(6):816
Bakker CJ, Smits HF, Bos C, van der Weide R, Zuiderveld KJ, van Vaals JJ, Hurtak WF, Viergever MA, Mali WP (1998) MR-guided balloon angioplasty: in vitro demonstration of the potential of MRI for guiding, monitoring, and evaluating endovascular interventions. J Magn Reson Imaging 8(1):245
Bloch F, Siegert A (1940) Magnetic resonance for nonrotating fields. Phys Rev 57:522
Bock M, Volz S, Zuehlsdorff S, Umathum R, Fink C, Hallscheidt P, Semmler W (2004) MR-guided intravascular procedures: real-time parameter control and automated slice positioning with active tracking coils. J Magn Reson Imaging 19(5):580
Bottomley PA, Kumar A, Edelstein WA, Allen JM, Karmarkar PV (2010) Designing passive MRI-safe implantable conducting leads with electrodes. Med Phys 37(7):3828
Burl M, Coutts GA, Young IR (2005) Tuned fiducial markers to identify body locations with minimal perturbation of tissue magnetization. Magn Reson Med 36(3):491
Busse H, Thormer G, Garnov N, Haase J, Kahn T, Moche M (2010) Technique for wireless position tracking of intravascular catheters: Performance evaluation in a vessel phantom. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 18:4163
Chung YC, Merkle EM, Lewin JS, Shonk JR, Duerk JL (1999) Fast T(2)-weighted imaging by PSIF at 0.2 T for interventional MRI. Magn Reson Med 42(2):335
Duerk JL, Wong EY, Lewin JS (2002) A brief review of hardware for catheter tracking in magnetic resonance imaging. MAGMA 13(3):199
Dumoulin CL, Souza SP, Darrow RD (1993) Real-time position monitoring of invasive devices using magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 29(3):411
Erhart P, Ladd ME, Steiner P, Heske N, Dumoulin CL, Debatin JF (1998) Tissue-independent MR tracking of invasive devices with an internal signal source. Magn Reson Med 39(2):279
Fandrey S, Weiss S, Müller J (2012) A novel active MR probe using a miniaturized optical link for a 1.5-T MRI scanner. Magn Reson Med 67(1):148
Fandrey S, Weiss S, Muller J (2008) Development of an active intravascular MR device with an optical transmission system. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 27(12):1723
Fritz J, U-Thainual P, Ungi T, Flammang AJ, Cho NB, Fichtinger G, Iordachita II, Carrino JA (2012) Augmented reality visualization with image overlay for MRI-guided intervention: accuracy for lumbar spinal procedures with a 1.5-T MRI system. Am J Roentgenol 198(3):W266
Guttman MA, Ozturk C, Raval AN, Raman VK, Dick AJ, DeSilva R, Karmarkar P, Lederman RJ, McVeigh ER (2007) Interventional cardiovascular procedures guided by real-time MR imaging: an interactive interface using multiple slices, adaptive projection modes and live 3D renderings. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(6):1429
Hillenbrand CM, Elgort DR, Wong EY, Reykowski A, Wacker FK, Lewin JS, Duerk JL (2004) Active device tracking and high-resolution intravascular MRI using a novel catheterbased, opposed-solenoid phased array coil. Magn Reson Med 51(4):668
Hurst GC, Hua J, Duerk JL, Cohen AM (1992) Intravascular (catheter) NMR receiver probe: Preliminary design analysis and application to canine iliofemoral imaging. Magn Reson Med 24(2):343
Kocaturk O, Saikus CE, Guttman MA, Faranesh AZ, Ratnayaka K, Ozturk C, McVeigh ER, Lederman RJ (2009) Whole shaft visibility and mechanical performance for active MR catheters using copper-nitinol braided polymer tubes. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 11:29
Kuehne T, Fahrig R, Butts K (2003) Pair of resonant fiducial markers for localization of endovascular catheters at all catheter orientations. J Magn Reson Imaging 17(5):620
Ladd ME, Zimmermann GG, McKinnon GC, von Schulthess GK, Dumoulin CL, Darrow RD, Hofmann E, Debatin JF (1998) Visualization of vascular guidewires using MR tracking. J Magn Reson Imaging 8(1):251
Lardo aC, McVeigh ER, Jumrussirikul P, Berger RD, Calkins H, Lima J, Halperin HR (2000) Visualization and temporal/spatial characterization of cardiac radiofrequency ablation lesions using magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation 102(6):698
Linte CA, Lang P, Rettmann ME, Cho DS, Holmes DR, Robb RA, Peters TM (2012) Accuracy considerations in image-guided cardiac interventions: experience and lessons learned. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 7(1):13
Nitz WR, Oppelt A, Renz W, Manke C, Lenhart M, Link J (2001) On the heating of linear conductive structures as guide wires and catheters in interventional MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(1):105
Omary RA, Unal O, Koscielski DS, Frayne R, Korosec FR, Mistretta CA, Strother CM, Grist TM (2000) Real-Time MR Imaging-guided Passive Catheter Tracking with Use of Gadolinium- filled Catheters. J Vasc Interv Radiol 11(8):1079
Ozturk C, Guttman M, McVeigh E, Lederman RJ (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging guided vascular interventions. Top Magn Reson Imaging 16(5):369
Pitsaer C, Umathum R, Homagk AK, Ozturk C, Bock M (2010) Three concepts for tuning and matching intravascular catheter coils. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 8:1852
Quick HH, Kuehl H, Kaiser G, Bosk S, Debatin JF, Ladd ME (2002) Inductively coupled stent antennas in MRI. Magn Reson Med 48(5):781
Quick HH, Zenge MO, Kuehl H, Kaiser G, Aker S, Massing S, Bosk S, Ladd ME (2005) Interventional magnetic resonance angiography with no strings attached: wireless active catheter visualization. Magn Reson Med 53(2):446
Ramsey N (1955) Resonance transitions induced by perturbations at two or more different frequencies. Phys Rev 100(4):1191
Ratnayaka K, Faranesh AZ, Guttman MA, Kocaturk O, Saikus CE, Lederman RJ (2008) Interventional cardiovascular magnetic resonance: still tantalizing. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 10:62
Razavi R, Hill DLG, Keevil SF, Miquel ME, Muthurangu V, Hegde S, Rhode K, Barnett M, van Vaals J, Hawkes DJ, Baker E (2003) Cardiac catheterisation guided by MRI in children and adults with congenital heart disease. Lancet 362(9399):1877
Sarioglu B, Aktan O, Oncu A, Mutlu S, Dundar G, Yalcinkaya AD (2012) An optically powered CMOS receiver system for intravascular magnetic resonance applications. IEEE J Emerg Sel Topics Power Electron 2(4):683
Sonmez M, Saikus CE, Bell JA, Franson DN, Halabi M, Faranesh AZ, Ozturk C, Lederman RJ, Kocaturk O (2012) MRI active guidewire with an embedded temperature probe and providing a distinct tip signal to enhance clinical safety. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 14:38
Sun N, Liu Y, Lee H, Weissleder R, Ham D (2009) CMOS RF Biosensor Utilizing Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. IEEE J Solid-State Circ 44(5):1629
Unal O, Li J, Cheng W, Yu H, Strother CM (2006) MR-visible coatings for endovascular device visualization. J Magn Reson Imaging 23(5):763
Vernickel P, Schulz V, Weiss S, Gleich B (2005) A safe transmission line for MRI. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52(6):1094
Wacker FK, Elgort D, Hillenbrand CM, Duerk JL, Lewin JS (2004) The catheter-driven MRI scanner: a new approach to intravascular catheter tracking and imaging-parameter adjustment for interventional MRI. Am J Roentgenol 183(2):391
Weiss S, Schaeffter T, Luedeke K, Leussler C, Holz D, Nehrke K, Rasche V, Sinkus R (1999) Catheter localization using a resonant fiducial marker during interactive MR fluoroscopy. Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med 12:1954
Weiss S, Vernickel P, Schaeffter T, Schulz V, Gleich B (2005) Transmission line for improved RF safety of interventional devices. Magn Reson Med 54(1):182
Yeung CJ, Atalar E (2001) A Green's function approach to local RF heating in interventional MRI. Med Phys 28(5):826
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Umut Cindemir and Berk Camli for their efforts during experiments, Mr. Francis Payne and Dr. Can Akgün for their valuable editorial support. The experiments were conducted at National Magnetic Resonance Research Center (UMRAM) at Bilkent University, Ankara and Acıbadem Kozyatağı Hospital, Istanbul. This study was supported by The Scientific and Technological Research Council Of Turkey (TUBITAK, Project 111E197) and Boğaziçi University LifeSci Center (Ministry of Development, 2009K1200520), and EU Marie Curie Actions IRSES Project 269300 (TAHITI, Improving Therapy and Intervention through Imaging).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tümer, M., Sarioglu, B., Mutlu, S. et al. Using a low-amplitude RF pulse at echo time (LARFET) for device localization in MRI. Med Biol Eng Comput 52, 885–894 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-014-1184-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-014-1184-4