Abstract
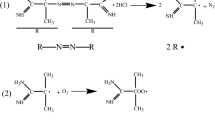
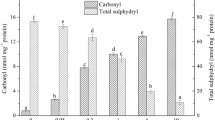
Oxidation extent of myofibrillar protein (MP) from silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) was affected by the content and type of lipid peroxidation (LPO) products. Oxidized linoleic acid (OLA) was selected as a main representative of lipid peroxidation to investigate the effects of oxidative modification of LPO products on MP structure. Structural changes of the oxidized myofibrillar protein were evaluated by the contents of carbonyl and total sulfhydryls, surface hydrophobicity, SDS-PAGE and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Heating procedure was also applied for further evaluation of gelling properties. The results from SDS-PAGE indicated that aggregation and denaturation of myosin occurred in the oxidized system. The presence of OLA intensified oxidation-initiated loss of a-helix conformation as well as tertiary structure of MP. With the addition of OLA concentration less than 3 mM, a remarkably enhanced gelling capacity of MP was observed. While the excessive covalent bond (OLA > 5 mM) could lead to the breakage of protein-protein bonds, causing the collapse of the gel structure. The gelation procedure induced by OLA involved simultaneous protein oxidation and internal cross-linking.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Qiu, W. Xia, Q. Jiang, Pressure-induced changes of silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) myofibrillar protein structure. Eur Food Res and Technol. 238, 753–761 (2014)
G. K. Tanaji, B. Soottawat, Combining effect of microbial transglutaminase and bambara groundnut protein isolate on gel properties of surimi from sardine (Sardinella albella). Food Biophys. 51, 146–155 (2015)
H.-H. Chen, Thermal gelation behaviors of surimi protein mixed with Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose. Fisheries Sci. 72, 679–685 (2006)
D. Sun X., A. Holley R., Factors influencing gel formation by myofibrillar proteins in muscle foods. Compr Rev Food Sci. 10, 33–51 (2011)
D. Park, Y. L. Xiong, A. L. Alderton, T. Ooizumi, Biochemical changes in myofibrillar protein isolates exposed to three oxidizing systems. J. Agric. Food Chem 12, 4445–4451 (2006)
M. N. Lund, M. Heinonen, C. P. Baron, M. Estévez, Protein oxidation in muscle foods: A review. Molecular Nutri & Food Res. 55, 83–95 (2011)
Y. L. Xiong, D. Park, T. Ooizumi, Variation in the cross-linking pattern of porcine myofibrillar protein exposed to three oxidative environments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 153–159 (2008)
C. Li, Y. L. Xiong, J. Chen, Protein oxidation at different salt concentrations affects the cross-linking and gelation of pork myofibrillar protein catalyzed by microbial transglutaminase. J. Food Sci 78, C823–C831 (2013)
W. Sun, F. Zhou, D.-W. Sun, M. Zhao, Effect of oxidation on the emulsifying properties of myofibrillar proteins. Food Bioprocess Tech. 6, 1703–1712 (2012)
M. N. Lund, M. Heinonen, C. P. Baron, M. Estévez, Protein oxidation in muscle foods: A review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res 55, 83–95 (2011)
M. Estevez, Protein carbonyls in meat systems: a review. Meat Sci. 89, 259–279 (2011)
H. Esterbauer, R. J. Schaur, H. Zollner, Chemistry and biochemistry of 4-hydroxynonenal, malonaldehyde and related aldehydes. Free Radical Biology. Med 11, 81–128 (1991)
V. A. Tironi, M. C. Tomas, M. C. Anon, Structural and functional changes in myofibrillar proteins of sea salmon (Pseudopercis semifasciata) by interaction with malonaldehyde (RI). J. Food Sci. 67, 930–935 (2002)
V. Fuentes, M. Estevez, J. Ventanas, S. Ventanas, Impact of lipid content and composition on lipid oxidation and protein carbonylation in experimental fermented sausages. Food Chem. 147, 70–77 (2014)
R. L. Levine, D. Garland, C. N. Oliver, A. Amici, I. Clement, A. G. Lenz, B. W. Ahn, S. Shaltiel, E. R. Stadtman, Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186, 464–542 (1990)
I. Chelh, P. Gatellier, V. Santé-Lhoutellier, Technical note: A simplified procedure for myofibril hydrophobicity determination. Meat Sci. 4, 681–683 (2006)
X. Xia, B. Kong, Y. Xiong, Y. Ren, Decreased gelling and emulsifying properties of myofibrillar protein from repeatedly frozen-thawed porcine longissimus muscle are due to protein denaturation and susceptibility to aggregation. Meat Sci. 85, 481–486 (2010)
M. Flores, J. M. Barat, M. C. Aristoy, M. M. Peris, R. Grau, F. Toldra, Accelerated processing of dry-cured ham. Part 2. Influence of brine thawing/salting operation on proteolysis and sensory acceptability. Meat Sci 72, 766–772 (2006)
W. Sun, F. Zhou, D.-W. Sun, M. Zhao, Effect of Oxidation on the Emulsifying Properties of Myofibrillar Proteins. Food Bioprocess Tech. 6, 1703–1712 (2012)
F. Zhou, M. Zhao, G. Su, C. Cui, W. Sun, Gelation of salted myofibrillar protein under malondialdehyde-induced oxidative stress. Food Hydrocoll. 40, 153–162 (2014)
E. R. Stadtman, Protein oxidation and aging. Free Radical Res. 40, 1250–1258 (2006)
J. Kanner, Oxidative processes in meat and meat products: Quality implications*1. Meat Sci. 1, 169–189 (1994)
V. Sante-Lhoutellier, T. Astruc, Marinova. P, Greve. E, Gatellier P, Effect of meat cooking on physicochemical state and in vitro digestibility of myofibrillar proteins. J. Agric. Food Chem. 56, 1488–1494 (2008)
K. J. Davies, Degradation of oxidized proteins by the 20S proteasome. Biochimie. 83, 301–310 (2001)
C. Li, Y. L. Xiong, J. Chen, Oxidation-induced unfolding facilitates myosin cross-linking in myofibrillar protein by microbial transglutaminase. J. Agric. Food Chem 60, 8020–8027 (2012)
A. Promeyrat, P. Gatellier, B. Lebret, K. Kajak-Siemaszko, L. Aubry, V. Santé-Lhoutellier, Evaluation of protein aggregation in cooked meat. Food Chem. 121, 412–417 (2010)
Y. Cao, Y. L. Xiong, Chlorogenic acid-mediated gel formation of oxidatively stressed myofibrillar protein. Food Chem 180, 235–243 (2015)
S. Traore, L. Aubry, P. Gatellier, W. Przybylski, D. Jaworska, K. Kajak-Siemaszko, Effect of heat treatment on protein oxidation in pig meat. Meat Sci. 91, 14–21 (2012)
E. Saguer, P. Alvarez, J. Sedman, A. Ismail, Study of the denaturation/ aggregation behaviour of whole porcine plasma and its protein fractions during heating under acidic pH by variable-temperature FTIR spectroscopy. Food Hydrocoll. 33, 402–414 (2013)
U. Böcker, R. Ofstad, H. C. Bertram, B. Egelandsdal, A. Kohler, Saltinduced changes in pork myofibrillar tissue investigated by FT-IR microspectroscopy and light microscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem 54, 6733–6740 (2006)
Z. Y. Ju, A. Kilara, Gelation of pH-aggregated whey protein isolate solution induced by heat, protease, calcium salt, and acidulant. J. Agric. Food Chem. 46, 1830–1835 (1998)
H. C. Bertram, A. Kohler, U. Böcker, R. Ofstad, H. J. Andersen, Heatinduced changes in myofibrillar protein structures and myowater of two pork qualities. A combined FT-IR spectroscopy and low-field NMR relaxometry study. J. Agric. Food Chem 54, 1740–1746 (2006)
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support by Jiangsu Province (China) “Collaborative Innovation Center for Food Safety and Quality Control”Industry Development Program, and Jiangsu Province (China) Infrastructure Project (Contract No. BM2014051) which have enabled us to carry out this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zhang, M., Fang, Z. et al. Influence of Linoleic Acid-Induced Oxidative Modification on Gel Properties of Myofibrillar Protein from Silver Carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) Muscle. Food Biophysics 11, 266–274 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-016-9438-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-016-9438-3