Abstract
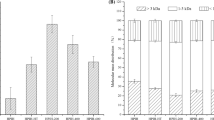
Ultrasound pretreatment of protein could improve the angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of hydrolysates and by alerting the structure of enzyme substrates. In this research the effects on ACE inhibitory activity and enzymolysis efficiency were explored under the optimum counter flow ultrasound (CFU) pretreatment conditions which obtained from our previous studies. The mechanism was studied by microstructure, nano-mechanical properties and secondary structures of wheat gluten (WG), which measured by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and flourier transform infrared spectrum (FTIR). The results showed that the CFU pretreatment resulted in significantly (P < 0.05) higher value compared with control, the ACE inhibitory activity was increased by 29.8 % and the value of IC50 was decreased by 36.92 %. CFU pretreatment increased the initial reaction rate by 9.58–20.27 % at a substrate concentration of 10–50 g/L, the KA was increased by 2.90 % and KM was decreased by 15.83 % compared to control. The microstructure revealed that the meshwork structure of WG was loosened and the surface roughness values of R a and R q were increased by CFU pretreatment. The nano-mechanical analyses showed that CFU pretreatment redistributed the adhesion map and decreased the stiffness. The secondary structures were less ordered by CFU pretreatment. Intermolecular β-sheet of protein aggregation and random coil were increased, Intramolecular β-sheet, α-helix and β-turn were decreased. It was concluded that CFU pretreatment can remarkably improve the ACE inhibitory activity of hydrolysate and enzymolysis efficiency of WG confirmed by the changes of microstructure, nano-mechanical properties, and secondary structures.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.G. Dadzie, H. Ma, E.E. Abano, Optimization of process conditions for production of Angiotensin IConverting Enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from vital wheat gluten using response surface methodology. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 22, 1531 (2013)
P. Park, J. Je, S. Kim, Angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity of hetero-chitooligosaccharides prepared from partially different deacetylated chitosans. J Agric. Food Chem. 51, 4930 (2003)
D.D. Kitts, K. Weiler, Bioactive proteins and peptides from food sources. Applications of bioprocesses used in isolation and recovery. Curr. Pharm. Des. 9, 1309 (2003)
H. Motoi, T. Kodama, Isolation and characterization of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from wheat gliadin hydrolysate. Food Nahrung 47, 354 (2003)
W. Qu, H. Ma, J. Jia, Enzymolysis kinetics and activities of ACE inhibitory peptides from wheat germ protein prepared with SFP ultrasound-assisted processing. Ultrason. Sonochem. 19, 1021 (2012)
J. Jia, H. Ma, W. Zhao, The use of ultrasound for enzymatic preparation of ACE-inhibitory peptides from wheat germ protein. Food Chem. 119, 336 (2010)
X. Ren, H. Ma, S. Mao, Effects of sweeping frequency ultrasound treatment on enzymatic preparations of ACE-inhibitory peptides from zein.Eur. Food Res. Technol. 238, 435 (2014)
C. Zhou, H. Ma, X. Yu, Pretreatment of defatted wheat germ proteins (by-products of flour mill industry) using ultrasonic horn and bath reactors: Effect on structure and preparation of ACE-inhibitory peptides. Ultrason. Sonochem. 20, 1390 (2013)
X.Y. Zhou, Enzyme Technology. (Petroleum Industry Press, Beijing, 1995), p. 284
S. Maruyama, E. Cantu III, C. DeMartino, Interaction of baboon anti-α-galactosyl antibody with pig tissues. Am. J. Pathol. 155, 1635 (1999)
A.P. Williams, Enzymic hydrolysis of food proteins: By J. Adler-Nissen. Elsevier Applied Science Publishers, London. 1986. Food Chem. 26, 81 (1987)
S. Jian, T. Wenyi, C. Wuyong, Ultrasound-accelerated enzymatic hydrolysis of solid leather waste. J. Clean. Prod. 16, 591 (2008)
A. Mendez-Vilas, J.M. Bruque, M.L. González-Martín. Sensitivity of surface roughness parameters to changes in the density of scanning points in multi-scale AFM studies. Application to a biomaterial surface. Ultramicroscopy. 107(8), 615 (2007)
T.J. Young, M.A. Monclus, T.L. Burnett, The use of the PeakForceTM quantitative nanomechanical mapping AFM-based method for high-resolution Young’s modulus measurement of polymers. Meas. Sci. Technol. 22, 125703 (2011)
L. Liao, M. Zhao, J. Ren, Effect of acetic acid deamidation induced modification on functional and nutritional properties and conformation of wheat gluten. J. Sci. Food Agric. 90, 409 (2010)
B. Wang, G.G. Atungulu, R. Khir, Ultrasonic treatment effect on enzymolysis kinetics and activities of ACE-inhibitory peptides from oat-isolated protein. Food Biophys. doi:10.1007/s11483-014-9375-y (2014)
J. Jin, H. Ma, K. Wang, Effects of multi-frequency power ultrasound on the enzymolysis and structural characteristics of corn gluten meal. Ultrason. Sonochem. 24, 55 (2015)
A. Shanmugam, J. Chandrapala, M. Ashokkumar, The effect of ultrasound on the physical and functional properties of skim milk. Innovative Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 16, 251 (2012)
C.L.M.A. Galvão, G.A. Pinto, C.D.F. Jesus, Producing a phenylalanine-free pool of peptides after tailored enzymatic hydrolyses of cheese whey. J. Food Eng. 91, 109 (2009)
L. Paniwnyk, H. Cai, S. Albu, The enhancement and scale up of the extraction of anti-oxidants from Rosmarinus officinalis using ultrasound. Ultrason. Sonochem. 16, 287 (2009)
R.A. Torres, C.P. Trier, E. Combet, Ultrasonic cavitation applied to the treatment of bisphenol A. Effect of sonochemical parameters and analysis of BPA by-products. Ultrason. Sonochem. 15, 605 (2008)
D.L. Miller, Ultrasonic detection of resonant cavitation bubbles in a flow tube by their second-harmonic emissions. Ultrasonics 19, 217 (1981)
J.C. Zheng, J.H. Chen, General Biochemistry (Higher Education Press, Beijing, 2006)
Q. Huang, L. Li, X. Fu, Ultrasound effects on the structure and chemical reactivity of cornstarch granules. Starch 59, 371 (2007)
L. Lin, H. Cui, R. He, Effect of ultrasonic treatment on the morphology of casein particles. Ultrason. Sonochem. 21, 513 (2014)
M.G. Donoso, A. Mendez-Vilas, J.M. Bruque, On the relationship between common amplitude surface roughness parameters and surface area: implications for the study of cell-Cmaterial interactions. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. 59, 245 (2007)
E. Chichti, M. George, J. Delenne, Nano-mechanical properties of starch and gluten biopolymers from atomic force microscopy. Eur. Polym. J. 49, 3788 (2013)
V. Kontogiorgos, Microstructure of hydrated gluten network. Food Res. Int. 44, 2582 (2011)
J. Cleaver, L. Looi, AFM study of adhesion between polystyrene particles: the influence of relative humidity and applied load. Powder Technol. 174, 34 (2007)
P.I. Haris, F. Severcan, FTIR spectroscopic characterization of protein structure in aqueous and non-aqueous media. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 7, 207 (1999)
L. Liao, Q. Wang, M. Zhao, Functional, conformational and topographical changes of succinic acid deamidated wheat gluten upon freeze-and spray-drying: a comparative study. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 50, 177 (2013)
M. Severcan, P.I. Haris, F. Severcan, Using artificially generated spectral data to improve protein secondary structure prediction from fourier transform infrared spectra of proteins. Anal. Biochem. 332, 238 (2004)
S. GuoSheng, H. Juan, S. Xin, Effects of ultrasound-assisted freeze on secondary structure of gluten protein. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 25, 860 (2009)
R. Khurana, A.L. Fink, Do parallel α-helix proteins have a unique fourier transform infrared spectrum. Biophys. J. 78, 994 (2000)
A.S. Tatham, L. Hayes, P.R. Shewry, Wheat seed proteins exhibit a complex mechanism of protein elasticity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1548, 187 (2001)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from National High Technology Research and Development Program 863 (No.2013AA102203), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No.31471698), (No.31301423), Jiangsu provincial science and technology support program---part of agriculture (No.BE2013408), The Jiangsu provincial major project on natural science for universities (No.12KJA550001), National publicsector (Agriculture) special science and technology (201303071) and the Research-Innovation Program of postgraduate in General Universities of Jiangsu, China (KYLX_1071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Ma, H., Wang, B. et al. Effects of Ultrasound Pretreatment on the Enzymolysis and Structural Characterization of Wheat Gluten. Food Biophysics 10, 385–395 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-015-9393-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-015-9393-4