Abstract
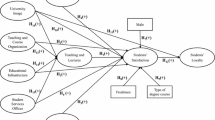
The quality of academic life (QAL) is concerned with all the general feelings of satisfaction of a student who experiences university. For universities, academic staff, public managers and policy makers, the fundamental question is how the measures and management of this construct can be improved in order to render a better service to students. Based on a sample of 726 students from all Portuguese State universities, we test a structural model that allows us to evaluate the impact of QAL on students’ academic performance (SAP) along with loyalty and willingness to recommend the university. In the analysis of all groups, the results reveal that QAL has a positive and significant, although not robust, influence on SAP. That positive influence is ratified, however, in the multi-group analysis for the 2nd and 3rd Study Cycles, through obtaining significant and robust empirical evidence. The results also show that QAL is a good predictor of loyalty and university recommendation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida, L., & Soares, A. P. (2004). Os estudantes universitários: sucesso escolar e desenvolvimento psicossocial. In E. Mercuri & S. A. J. Polydoro (Eds.), Estudante universitário: características e experiências de formação (Universida., pp. 15–40). Cabral Editora e Livraria Universitária
Almeida, L. S., Soares, A. C. P., Vasconcelos, R. M., Capela, J. V., Vasconcelos, J. B., Corais, J. M., & Fernandes, Á. (2000). Envolvimento extracurricular e ajustamento académico: Um estudo sobre as vivências dos estudantes universitários com e sem funções associativas. In A. paula Soares, A. Osório, J. V. Capela, L. S. Almeida, R. M. Vasconcelos, & S. M. Caires (Eds.), Transição para o ensino superior (Universida., pp. 167–187). Braga
Anderson, J., & Gerbing, D. (1988). Structural equation modeling in practice: A review and recommended two-step approach. Psychological Bulletin, 103(3), 411–423.
Arrington, L., & Cheek, J. (1990). SAE scope and student achievement in agribusiness and natural resources education. Journal of Agricultural Education, 31(2), 55–61.
Bagozzi, R., & Yi, Y. (1988). On the evaluation of structural equation models. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 16(1), 74–94.
Barclay, D., Thompson, R., & Higgins, C. (1995). The partial least squares (PLS) approaches to causal modeling: Personal computer adoption and use as an illustration. Technology Studies, 2(2), 285–309.
Barros, M. (2002). A relevância e a qualidade da vivência académica: um percurso de formação ativa. In A. S. Pouzada, L. S. Almeida, & R. Vasconcelos (Eds.), Contextos e dinâmicas da vida académica (Universida., pp. 99–106).
Bhattacharya, C., & Sen, S. (2003). Consumer-company identification: A framework for understanding consumers’ relationships with companies. Journal of Marketing, 67, 76–88.
Billups, F. (2008). Measuring college student satisfaction: a multi-year study of the factors leading to persistence. In NERA Conference Proceedings (paper 14) (pp. 1–17).
Bollen, K. (1989). Structural equations with latent variables. John Wiley & Sons
Braxton, J., & Hirschy, A. (2004). Reconceptualizing antecedents of social integration in student departure. In M. Yorke & B. Longden (Eds.), Retention and student success in higher education (pp. 89–102). Maidenhead: Open University Press.
Bryant, J. (2006). Assessing expectations and perceptions of the campus experience: The Noel-•Levitz student satisfaction inventory. New Directions for Community Colleges, 134, 25–35.
Cardador, M., & Pratt, M. (2006). Identification management and its bases: Bridging management and marketing perspectives through a focus on affiliation dimensions. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 34(2), 174–184.
Cha, K.-H. (2003). Subjective Well-Being Among College Students. Social Indicators Research, 62/63(1–3), 455–477.
Cheung, L., & Kan, A. (2002). Evaluation of factors related to student performance in a distance-learning business communication course. Journal of Education for Business, (May/June), 257–264.
Chin, W. W. (1998a). Issues and opinion on structural equation modeling. MIS Quarterly, 22(1), vii–xvi. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org/stable/10.2307/249674
Chin, W. W. (1998b). The Partial Least Squares Approach to Structural Equation Modeling, in Marcoulides. In G. A. (Ed.), Modern Methods for Business Research (Laurence E., pp. 295–336).
Chow, H. P. H. (2005). Life satisfaction among university students in a canadian prairie city: A multivariate analysis. Social Indicators Research, 70(2), 139–150.
Dick, A., & Basu, K. (1994). Customer loyalty: Toward an integrated conceptual framework. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 22(2), 99–113.
Diener, E., Smith, H., & Fujita, F. (1995). The personality structure of affect. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 69(1), 130–141.
Douglas, J., & Douglas, A. (2006). Evaluating teaching quality. Quality in Higher Education, 12(1), 3–13.
El Hassan, K. (2011). Quality of college life (QCL): Validation of a measure of student well-being in the Middle East. The International Journal of Educational and Psychological Assessment, 8(1), 12–22.
Elliott, K., & Healy, M. (2001). Key factors influencing student satisfaction related to recruitment and retention. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 10(4), 1–11.
Elliott, K., & Shin, D. (2002). Student satisfaction: An alternative approach to assessing this important concept. Journal of Higher Education Policy and Management, 24(2), 197–209.
Ferreira, I. M. E. da S. (2009). Adaptação e desenvolvimento psicossocial dos estudantes do ensino superior: fatores familiares e sociodemográficos (Fundação C., pp. 55–93).
Ferriss, A. L. (2006). A theory of social structure and the quality of life. Applied Research in Quality of Life, 1(1), 117–123. doi:10.1007/s11482-006-9003-1.
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50.
Garkaz, M., Banimahd, B., & Esmaeili, H. (2011). Factors affecting accounting students’ performance: The case of students at the Islamic Azad university. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 29, 122–128.
Guney, Y. (2009). Exogenous and endogenous factors influencing students’ performance in undergraduate accounting modules. Accounting Education, 18(1), 51–73.
Gustafsson, A., Johnson, M., & Roos, I. (2005). The effects of customer satisfaction, relationship commitment dimensions, and triggers on customer retention. Journal of Marketing, 69(october 2005), 210–218.
Hair, J. F. J., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Black, W. C. (1998). Multivariate Data Analysis (5a ed.). Englewood Cliffs, N. J: Prentice-Hall.
Hair, J. F., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2011). PLS-SEM: Indeed a silver bullet. The Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 19(2), 139–152. doi:10.2753/MTP1069-6679190202.
Helgesen, O., & Nesset, E. (2007). What accounts for students’ loyalty? some field study evidence. International Journal of Educational Management, 21(2), 126–143.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Langer, M. F., & Hansen, U. (2001). Modeling and managing student loyalty: An approach based on the concept of relationship quality. Journal of Service Research, 3(4), 331–344.
Henseler, J., & Sarstedt, M. (2012). Goodness-of-fit indices for partial least squares path modeling. Computational Statistics, (March).
Hill, M. M., & Hill, A. (2000). Investigação por questionário (1a Edição.). Edições Sílabo, Lda.
Hulland, J. (1999). Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: a review of four recent studies. Strategic Management Journal, 20, 195–204.
Keil, M., Tan, B. C., Wei, K.-K., Saarinen, T., Tuunainen, V., & Wassenaar, A. (2000). A cross-cultural study on escalation of commitment behavior in software projects. MIS Quarterly, 24(2), 299–325.
King, L., & Kotrlid, J. W. (1995). Reference of the general education, core curriculum to career goals of college of agriculture student. Journal of Agricultural Education, 30(3), 26–33.
Koh, M., & Koh, H. (1999). The determinants of performance in an accountancy degree programme. Accounting Education: An Internacional Journal, 8(1), 13–29.
Mavondo, F., Tsarenko, Y., & Gabbott, M. (2004). International and local student satisfaction: Resources and capabilities perspective. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 14(1), 41–60.
Miller, R. (2003). Student satisfaction and institutional success. May, 2003. In Paper presented at the 43rd annual AIR Forum, Tampa, FL, May 2003
Mize, M. G. (2007). Retention and student success in higher education, edited by Mantz Yorke and Bernard Longden. Interchange, 38(1), 93–95.
Noxel, S., & Cheek, J. (1988). Relationship of supervised occupational experience program scope to student achievement in ornamental horticulture. Journal of the American Association of Teacher Educators on Agriculture, 29(4), 24–31.
Oliver, R. L. (1999). Whence consumer loyalty? Journal of Marketing, 63, 33–34.
Pilcher, J. (1998). Affective and daily event predictors of life satisfaction in college students. Social Indicators Research, 43(1985), 291–306.
Posadzki, P., Musonda, P., Debska, G., & Polczyk, R. (2009). Psychosocial conditions of quality of life among undergraduate students: A cross sectional survey. Applied Research in Quality of Life, 4(3), 239–258.
Reichheld, F. F. (2003). The one number you need to crow. Harvard Business Review, 81(12), 46–54.
Richardson, J. T. E. (2005). Instruments for obtaining student feedback: a review of the literature. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 30(4), 387–415.
Ringle, C. M., & Sven/Will, A. (2005). SmartPLS. SmartPLS. Retrieved from http://www.smartpls.de
Russell-Bennett, R., McColl-Kennedy, J. R., & Coote, L. V. (2007). Involvement, satisfaction, and brand loyalty in a small business services setting. Journal of Business Research, 60(12), 1253–1260.
Salgueira, A. P., & Almeida, L. S. (2000). Vivências Académicas e rendimento escolar em estudantes do ensino superior: Estudo longitudinal na Universidade do Minho. In A. paula Soares, A. Osório, J. V. Capela, L. S. Almeida, R. M. Vasconcelos, & S. M. Caires (Eds.), Transição para o ensino superior (Universida., pp. 193–202). Braga
Sam, D. (2001). Satisfaction with life among international students: An exploratory study. Social indicators research, 53, 315–337.
Santos, L., & Almeida, L. S. (2000). Vivências e Rendimentos Académicos: A integração dos Alunos na Universidade. In A. P. Soares, A. Osório, J. V. Capela, L. S. Almeida, R. M. Vasconcelos, & S. M. Caires (Eds.), Transição para o ensino superior (Universida., pp. 175–191). Braga
Sarkar, M., Echambadi, R., Cavusgil, S. T., & Aulakh, P. S. (2001). The influence of complementarity, compatibility, and relationship capital on alliance performance. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 29(4), 358–373.
Sarstedt, M., & Ringle, C. M. (2010). Treating unobserved heterogeneity in PLS path modeling: a comparison of FIMIX-PLS with different data analysis strategies. Journal of Applied Statistics, 37(8), 1299–1318. doi:10.1080/02664760903030213.
Schertzer, C., & Schertzer, S. (2004). Student satisfaction and retention: A conceptual model. Journal of Marketing for Higher Education, 14(1), 79–91.
Sirgy, M. J., Grzeskowiak, S., & Rahtz, D. (2006). Quality of college Life (QCL) of students: Developing and validating a measure of well-being. Social Indicators Research, 80(2), 343–360.
Sirgy, M. J., Grzeskowiak, S., & Rahtz, D. (2007). Quality of college Life (QCL) of students: Developing and validating a measure of well-being. Social Indicators Research, 80(2), 343–360.
Sirgy, M. J., Lee, D.-J., Grzeskowiak, S., Yu, G. B., Webb, D., El-Hasan, K., & Kuruuzum, A. (2010). Quality of college life (QCL) of students: Further validation of a measure of well-being. Social Indicators Research, 99(3), 375–390.
Suh, E., Diener, E., & Fujita, F. (1996). Events and subjective well-being: Only recent events matter. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 70(5), 1091–102.
Thomas, L. (2002). Student retention in higher education: The role of institutional habitus. Journal of Education Policy, 17(4), 423–442.
Tinto, V., & Cullen, J. (1973). Dropout in higher education: A review and theoretical synthesis of recent research. Office of Education (DHEW), D.C. Offiice of Planning, Budgeting, and Evaluation, 30, 1–100.
Verhoef, P. (2002). The effect of relational constructs on customer referrals and number of services purchased from a multiservice provider: Does age of relationship matter? Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 30(3), 202–216.
Wiers-Jenssen, J., Stensaker, B., & Grogaard, J. B. (2002). Student satisfaction: Towards an empirical deconstruction of the concept. Quality in Higher Education, 8(2), 183–195.
Yu, G. B., & Kim, J.-H. (2008). Testing the mediating effect of the quality of college life in the student satisfaction and student loyalty relationship. Applied Research in Quality of Life, 3(1), 1–21.
Yu, G., & Lee, D.-J. (2008). A model of quality of college life (QCL) of students in Korea. Social Indicators Research, 87(2), 269–285.
Acknowledgment
We gratefully acknowledge the editor and the anonymous reviewers for providing very constructive and useful comments that enabled us to make additional efforts to improve the clarity and quality of our research and correct some inaccuracies present in the previous version of our manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedro, E., Leitão, J. & Alves, H. Does the Quality of Academic Life Matter for Students’ Performance, Loyalty and University Recommendation?. Applied Research Quality Life 11, 293–316 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-014-9367-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-014-9367-6