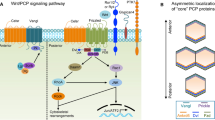
Abstract
Members of the Wnt family of secreted signaling proteins influence many aspects of neural development and function. Wnts are required from neural induction and axis formation to axon guidance and synapse development, and even help modulate synapse activity. Wnt proteins activate a variety of downstream signaling pathways and can induce a similar variety of cellular responses, including gene transcription changes and cytoskeletal rearrangements. This review provides an introduction to Wnt signaling pathways and discusses current research on their roles in vertebrate neural development and function.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad-Annuar A, Ciani L, Simeonidis I, Herreros J, Fredj NB, Rosso SB, Hall A, Brickley S, Salinas PC (2006) Signaling across the synapse: a role for Wnt and Dishevelled in presynaptic assembly and neurotransmitter release. J Cell Biol 174:127–139
Alves dos Santos MT, Smidt MP (2011) En1 and Wnt signaling in midbrain dopaminergic neuronal development. Neural Dev 6:23
Bamji SX, Shimazu K, Kimes N, Huelsken J, Birchmeier W, Lu B, Reichardt LF (2003) Role of beta-catenin in synaptic vesicle localization and presynaptic assembly. Neuron 40:719–731
Bang AG, Papalopulu N, Goulding MD, Kintner C (1999) Expression of Pax-3 in the lateral neural plate is dependent on a Wnt-mediated signal from posterior nonaxial mesoderm. Dev Biol 212:366–380
Bilic J, Huang YL, Davidson G, Zimmermann T, Cruciat CM, Bienz M, Niehrs C (2007) Wnt induces LRP6 signalosomes and promotes dishevelled-dependent LRP6 phosphorylation. Science 316:1619–1622
Brault V, Moore R, Kutsch S, Ishibashi M, Rowitch DH, McMahon AP, Sommer L, Boussadia O, Kemler R (2001) Inactivation of the beta-catenin gene by Wnt1-Cre-mediated deletion results in dramatic brain malformation and failure of craniofacial development. Development 128:1253–1264
Budnik V, Salinas PC (2011) Wnt signaling during synaptic development and plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21:151–159
Callahan CA, Muralidhar MG, Lundgren SE, Scully AL, Thomas JB (1995) Control of neuronal pathway selection by a Drosophila receptor protein-tyrosine kinase family member. Nature 376:171–174
Carmon KS, Lin Q, Gong X, Thomas A, Liu Q (2011) LGR5 interacts and cointernalizes with Wnt receptors to modulate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol 32:2054–2064
Carter M, Chen X, Slowinska B, Minnerath S, Glickstein S, Shi L, Campagne F, Weinstein H, Ross ME (2005) Crooked tail (Cd) model of human folate-responsive neural tube defects is mutated in Wnt coreceptor lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102:12843–12848
Castelo-Branco G, Arenas E (2006) Function of Wnts in dopaminergic neuron development. Neurodegener Dis 3:5–11
Castelo-Branco G, Andersson ER, Minina E, Sousa KM, Ribeiro D, Kokubu C, Imai K, Prakash N, Wurst W, Arenas E (2010) Delayed dopaminergic neuron differentiation in Lrp6 mutant mice. Dev Dyn 239:211–221
Cerpa W, Godoy JA, Alfaro I, Farias GG, Metcalfe MJ, Fuentealba R, Bonansco C, Inestrosa NC (2008) Wnt-7a modulates the synaptic vesicle cycle and synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 283:5918–5927
Cerpa W, Gambrill A, Inestrosa NC, Barria A (2011) Regulation of NMDA-receptor synaptic transmission by Wnt signaling. J Neurosci 31:9466–9471
Chen J, Park CS, Tang SJ (2006) Activity-dependent synaptic Wnt release regulates hippocampal long term potentiation. J Biol Chem 281:11910–11916
Chenn A, Walsh CA (2002) Regulation of cerebral cortical size by control of cell cycle exit in neural precursors. Science 297:365–369
Chenn A, Walsh CA (2003) Increased neuronal production, enlarged forebrains and cytoarchitectural distortions in beta-catenin overexpressing transgenic mice. Cereb Cortex 13:599–606
Cheyette BN (2004) Ryk: another heretical Wnt receptor defies the canon. Sci STKE pe54
Chilov D, Sinjushina N, Rita H, Taketo MM, Makela TP, Partanen J (2011) Phosphorylated beta-catenin localizes to centrosomes of neuronal progenitors and is required for cell polarity and neurogenesis in developing midbrain. Dev Biol 357:259–268
Ciani L, Salinas PC (2005) WNTs in the vertebrate nervous system: from patterning to neuronal connectivity. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:351–362
Ciani L, Krylova O, Smalley MJ, Dale TC, Salinas PC (2004) A divergent canonical WNT-signaling pathway regulates microtubule dynamics: dishevelled signals locally to stabilize microtubules. J Cell Biol 164:243–253
Ciani L, Boyle KA, Dickins E, Sahores M, Anane D, Lopes DM, Gibb AJ, Salinas PC (2011) Wnt7a signaling promotes dendritic spine growth and synaptic strength through Ca(2)(+)/Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:10732–10737
Clark CE, Nourse CC, Cooper HM (2012) The tangled web of non-canonical Wnt signalling in neural migration. Neurosignals 20:202–220
Cuitino L, Godoy JA, Farias GG, Couve A, Bonansco C, Fuenzalida M, Inestrosa NC (2010) Wnt-5a modulates recycling of functional GABAA receptors on hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 30:8411–8420
Curtin JA, Quint E, Tsipouri V, Arkell RM, Cattanach B, Copp AJ, Henderson DJ, Spurr N, Stanier P, Fisher EM et al (2003) Mutation of Celsr1 disrupts planar polarity of inner ear hair cells and causes severe neural tube defects in the mouse. Curr Biol 13:1129–1133
Danesin C, Peres JN, Johansson M, Snowden V, Cording A, Papalopulu N, Houart C (2009) Integration of telencephalic Wnt and hedgehog signaling center activities by Foxg1. Dev Cell 16:576–587
Dehner M, Hadjihannas M, Weiske J, Huber O, Behrens J (2008) Wnt signaling inhibits Forkhead box O3a-induced transcription and apoptosis through up-regulation of serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1. J Biol Chem 283:19201–19210
Dickinson ME, Krumlauf R, McMahon AP (1994) Evidence for a mitogenic effect of Wnt-1 in the developing mammalian central nervous system. Development 120:1453–1471
Elkouby YM, Elias S, Casey ES, Blythe SA, Tsabar N, Klein PS, Root H, Liu KJ, Frank D (2010) Mesodermal Wnt signaling organizes the neural plate via Meis3. Development 137:1531–1541
Esteve P, Morcillo J, Bovolenta P (2000) Early and dynamic expression of cSfrp1 during chick embryo development. Mech Dev 97:217–221
Farias GG, Alfaro IE, Cerpa W, Grabowski CP, Godoy JA, Bonansco C, Inestrosa NC (2009) Wnt-5a/JNK signaling promotes the clustering of PSD-95 in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 284:15857–15866
Fiedler M, Mendoza-Topaz C, Rutherford TJ, Mieszczanek J, Bienz M (2011) Dishevelled interacts with the DIX domain polymerization interface of Axin to interfere with its function in down-regulating beta-catenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:1937–1942
Fotaki V, Price DJ, Mason JO (2011) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling is disrupted in the extra-toes (Gli3(Xt/Xt)) mutant from early stages of forebrain development, concomitant with anterior neural plate patterning defects. J Comp Neurol 519:1640–1657
Galjart N (2005) CLIPs and CLASPs and cellular dynamics. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:487–498
Glinka A, Wu W, Delius H, Monaghan AP, Blumenstock C, Niehrs C (1998) Dickkopf-1 is a member of a new family of secreted proteins and functions in head induction. Nature 391:357–362
Glinka A, Dolde C, Kirsch N, Huang YL, Kazanskaya O, Ingelfinger D, Boutros M, Cruciat CM, Niehrs C (2011) LGR4 and LGR5 are R-spondin receptors mediating Wnt/beta-catenin and Wnt/PCP signalling. EMBO Rep 12:1055–1061
Gong X, Carmon KS, Lin Q, Thomas A, Yi J, Liu Q (2012) LGR6 is a high affinity receptor of R-spondins and potentially functions as a tumor suppressor. PLoS One 7:e37137
Grove EA, Tole S, Limon J, Yip L, Ragsdale CW (1998) The hem of the embryonic cerebral cortex is defined by the expression of multiple Wnt genes and is compromised in Gli3-deficient mice. Development 125:2315–2325
Guan KL, Rao Y (2003) Signalling mechanisms mediating neuronal responses to guidance cues. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:941–956
Gulacsi AA, Anderson SA (2008) Beta-catenin-mediated Wnt signaling regulates neurogenesis in the ventral telencephalon. Nat Neurosci 11:1383–1391
Gunhaga L, Marklund M, Sjodal M, Hsieh JC, Jessell TM, Edlund T (2003) Specification of dorsal telencephalic character by sequential Wnt and FGF signaling. Nat Neurosci 6:701–707
Hall AC, Lucas FR, Salinas PC (2000) Axonal remodeling and synaptic differentiation in the cerebellum is regulated by WNT-7a signaling. Cell 100:525–535
Hamblet NS, Lijam N, Ruiz-Lozano P, Wang J, Yang Y, Luo Z, Mei L, Chien KR, Sussman DJ, Wynshaw-Boris A (2002) Dishevelled 2 is essential for cardiac outflow tract development, somite segmentation and neural tube closure. Development 129:5827–5838
Henriquez JP, Webb A, Bence M, Bildsoe H, Sahores M, Hughes SM, Salinas PC (2008) Wnt signaling promotes AChR aggregation at the neuromuscular synapse in collaboration with agrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:18812–18817
Hirabayashi Y, Itoh Y, Tabata H, Nakajima K, Akiyama T, Masuyama N, Gotoh Y (2004) The Wnt/beta-catenin pathway directs neuronal differentiation of cortical neural precursor cells. Development 131:2791–2801
Houart C, Caneparo L, Heisenberg C, Barth K, Take-Uchi M, Wilson S (2002) Establishment of the telencephalon during gastrulation by local antagonism of Wnt signaling. Neuron 35:255–265
Hovens CM, Stacker SA, Andres AC, Harpur AG, Ziemiecki A, Wilks AF (1992) RYK, a receptor tyrosine kinase-related molecule with unusual kinase domain motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:11818–11822
Hur EM, Zhou FQ (2010) GSK3 signalling in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:539–551
Hutchins BI, Li L, Kalil K (2011) Wnt/calcium signaling mediates axon growth and guidance in the developing corpus callosum. Dev Neurobiol 71:269–283
Hutchins BI, Li L, Kalil K (2012) Wnt-induced calcium signaling mediates axon growth and guidance in the developing corpus callosum. Sci Signal 5:pt1
Ikeya M, Lee SM, Johnson JE, McMahon AP, Takada S (1997) Wnt signalling required for expansion of neural crest and CNS progenitors. Nature 389:966–970
Inestrosa NC, Arenas E (2010) Emerging roles of Wnts in the adult nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci 11:77–86
Janda CY, Waghray D, Levin AM, Thomas C, Garcia KC (2012) Structural basis of Wnt recognition by Frizzled. Science 337:59–64
Kazanskaya O, Glinka A, Niehrs C (2000) The role of Xenopus dickkopf1 in prechordal plate specification and neural patterning. Development 127:4981–4992
Keeble TR, Halford MM, Seaman C, Kee N, Macheda M, Anderson RB, Stacker SA, Cooper HM (2006) The Wnt receptor Ryk is required for Wnt5a-mediated axon guidance on the contralateral side of the corpus callosum. J Neurosci 26:5840–5848
Kestler HA, Kuhl M (2008) From individual Wnt pathways towards a Wnt signalling network. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:1333–1347
Kibar Z, Salem S, Bosoi CM, Pauwels E, De Marco P, Merello E, Bassuk AG, Capra V, Gros P (2011) Contribution of VANGL2 mutations to isolated neural tube defects. Clin Genet 80:76–82
Kiecker C, Niehrs C (2001) A morphogen gradient of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling regulates anteroposterior neural patterning in Xenopus. Development 128:4189–4201
Kim CH, Oda T, Itoh M, Jiang D, Artinger KB, Chandrasekharappa SC, Driever W, Chitnis AB (2000) Repressor activity of Headless/Tcf3 is essential for vertebrate head formation. Nature 407:913–916
Kimura-Yoshida C, Nakano H, Okamura D, Nakao K, Yonemura S, Belo JA, Aizawa S, Matsui Y, Matsuo I (2005) Canonical Wnt signaling and its antagonist regulate anterior-posterior axis polarization by guiding cell migration in mouse visceral endoderm. Dev Cell 9:639–650
Kokubu C, Heinzmann U, Kokubu T, Sakai N, Kubota T, Kawai M, Wahl MB, Galceran J, Grosschedl R, Ozono K et al (2004) Skeletal defects in ringelschwanz mutant mice reveal that Lrp6 is required for proper somitogenesis and osteogenesis. Development 131:5469–5480
Krylova O, Herreros J, Cleverley KE, Ehler E, Henriquez JP, Hughes SM, Salinas PC (2002) WNT-3, expressed by motoneurons, regulates terminal arborization of neurotrophin-3-responsive spinal sensory neurons. Neuron 35:1043–1056
Kuhl M, Sheldahl LC, Malbon CC, Moon RT (2000a) Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is stimulated by Wnt and Frizzled homologs and promotes ventral cell fates in Xenopus. J Biol Chem 275:12701–12711
Kuhl M, Sheldahl LC, Park M, Miller JR, Moon RT (2000b) The Wnt/Ca2+ pathway: a new vertebrate Wnt signaling pathway takes shape. Trends Genet 16:279–283
Kuwahara A, Hirabayashi Y, Knoepfler PS, Taketo MM, Sakai J, Kodama T, Gotoh Y (2010) Wnt signaling and its downstream target N-myc regulate basal progenitors in the developing neocortex. Development 137:1035–1044
Lee SM, Tole S, Grove E, McMahon AP (2000) A local Wnt-3a signal is required for development of the mammalian hippocampus. Development 127:457–467
Li L, Hutchins BI, Kalil K (2009) Wnt5a induces simultaneous cortical axon outgrowth and repulsive axon guidance through distinct signaling mechanisms. J Neurosci 29:5873–5883
Liu Y, Shi J, Lu CC, Wang ZB, Lyuksyutova AI, Song XJ, Zou Y (2005) Ryk-mediated Wnt repulsion regulates posterior-directed growth of corticospinal tract. Nat Neurosci 8:1151–1159
Logan CY, Nusse R (2004) The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 20:781–810
Lopez-Rios J, Esteve P, Ruiz JM, Bovolenta P (2008) The netrin-related domain of Sfrp1 interacts with Wnt ligands and antagonizes their activity in the anterior neural plate. Neural Dev 3:19
Lucas FR, Salinas PC (1997) WNT-7a induces axonal remodeling and increases synapsin I levels in cerebellar neurons. Dev Biol 192:31–44
Lucas FR, Goold RG, Gordon-Weeks PR, Salinas PC (1998) Inhibition of GSK-3beta leading to the loss of phosphorylated MAP-1B is an early event in axonal remodelling induced by WNT-7a or lithium. J Cell Sci 111(Pt 10):1351–1361
Lyuksyutova AI, Lu CC, Milanesio N, King LA, Guo N, Wang Y, Nathans J, Tessier-Lavigne M, Zou Y (2003) Anterior-posterior guidance of commissural axons by Wnt-frizzled signaling. Science 302:1984–1988
Mangale VS, Hirokawa KE, Satyaki PR, Gokulchandran N, Chikbire S, Subramanian L, Shetty AS, Martynoga B, Paul J, Mai MV et al (2008) Lhx2 selector activity specifies cortical identity and suppresses hippocampal organizer fate. Science 319:304–309
Manoranjan B, Venugopal C, McFarlane N, Doble BW, Dunn SE, Scheinemann K, Singh SK (2012) Medulloblastoma stem cells: where development and cancer cross pathways. Pediatr Res 71:516–522
Maretto S, Cordenonsi M, Dupont S, Braghetta P, Broccoli V, Hassan AB, Volpin D, Bressan GM, Piccolo S (2003) Mapping Wnt/beta-catenin signaling during mouse development and in colorectal tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:3299–3304
Mathew D, Ataman B, Chen J, Zhang Y, Cumberledge S, Budnik V (2005) Wingless signaling at synapses is through cleavage and nuclear import of receptor DFrizzled2. Science 310:1344–1347
Mattes B, Weber S, Peres J, Chen Q, Davidson G, Houart C, Scholpp S (2012) Wnt3 and Wnt3a are required for induction of the mid-diencephalic organizer in the caudal forebrain. Neural Dev 7:12
McGrew LL, Lai CJ, Moon RT (1995) Specification of the anteroposterior neural axis through synergistic interaction of the Wnt signaling cascade with noggin and follistatin. Dev Biol 172:337–342
McGrew LL, Hoppler S, Moon RT (1997) Wnt and FGF pathways cooperatively pattern anteroposterior neural ectoderm in Xenopus. Mech Dev 69:105–114
McMahon AP, Bradley A (1990) The Wnt-1 (int-1) proto-oncogene is required for development of a large region of the mouse brain. Cell 62:1073–1085
Megason SG, McMahon AP (2002) A mitogen gradient of dorsal midline Wnts organizes growth in the CNS. Development 129:2087–2098
Mikels AJ, Nusse R (2006) Purified Wnt5a protein activates or inhibits beta-catenin-TCF signaling depending on receptor context. PLoS Biol 4:e115
Mosca TJ, Schwarz TL (2010) The nuclear import of Frizzled2-C by Importins-beta11 and alpha2 promotes postsynaptic development. Nat Neurosci 13:935–943
Murdoch JN, Henderson DJ, Doudney K, Gaston-Massuet C, Phillips HM, Paternotte C, Arkell R, Stanier P, Copp AJ (2003) Disruption of scribble (Scrb1) causes severe neural tube defects in the circletail mouse. Hum Mol Genet 12:87–98
Oishi I, Suzuki H, Onishi N, Takada R, Kani S, Ohkawara B, Koshida I, Suzuki K, Yamada G, Schwabe GC et al (2003) The receptor tyrosine kinase Ror2 is involved in non-canonical Wnt5a/JNK signalling pathway. Genes Cells 8:645–654
Okerlund ND, Cheyette BN (2011) Synaptic Wnt signaling-a contributor to major psychiatric disorders? J Neurodev Disord 3:162–174
Okerlund ND, Kivimae S, Tong CK, Peng IF, Ullian EM, Cheyette BN (2010) Dact1 is a postsynaptic protein required for dendrite, spine, and excitatory synapse development in the mouse forebrain. J Neurosci 30:4362–4368
Oosterwegel M, van de Wetering M, Timmerman J, Kruisbeek A, Destree O, Meijlink F, Clevers H (1993) Differential expression of the HMG box factors TCF-1 and LEF-1 during murine embryogenesis. Development 118:439–448
Packard M, Koo ES, Gorczyca M, Sharpe J, Cumberledge S, Budnik V (2002) The Drosophila Wnt, wingless, provides an essential signal for pre- and postsynaptic differentiation. Cell 111:319–330
Paganoni S, Bernstein J, Ferreira A (2010) Ror1-Ror2 complexes modulate synapse formation in hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 165:1261–1274
Parr BA, Shea MJ, Vassileva G, McMahon AP (1993) Mouse Wnt genes exhibit discrete domains of expression in the early embryonic CNS and limb buds. Development 119:247–261
Pei Y, Brun SN, Markant SL, Lento W, Gibson P, Taketo MM, Giovannini M, Gilbertson RJ, Wechsler-Reya RJ (2012) WNT signaling increases proliferation and impairs differentiation of stem cells in the developing cerebellum. Development 139:1724–1733
Perea-Gomez A, Lawson KA, Rhinn M, Zakin L, Brulet P, Mazan S, Ang SL (2001) Otx2 is required for visceral endoderm movement and for the restriction of posterior signals in the epiblast of the mouse embryo. Development 128:753–765
Perry WL 3rd, Vasicek TJ, Lee JJ, Rossi JM, Zeng L, Zhang T, Tilghman SM, Costantini F (1995) Phenotypic and molecular analysis of a transgenic insertional allele of the mouse Fused locus. Genetics 141:321–332
Peukert D, Weber S, Lumsden A, Scholpp S (2011) Lhx2 and Lhx9 determine neuronal differentiation and compartition in the caudal forebrain by regulating Wnt signaling. PLoS Biol 9:e1001218
Pinson KI, Brennan J, Monkley S, Avery BJ, Skarnes WC (2000) An LDL-receptor-related protein mediates Wnt signalling in mice. Nature 407:535–538
Popperl H, Schmidt C, Wilson V, Hume CR, Dodd J, Krumlauf R, Beddington RS (1997) Misexpression of Cwnt8C in the mouse induces an ectopic embryonic axis and causes a truncation of the anterior neuroectoderm. Development 124:2997–3005
Purro SA, Ciani L, Hoyos-Flight M, Stamatakou E, Siomou E, Salinas PC (2008) Wnt regulates axon behavior through changes in microtubule growth directionality: a new role for adenomatous polyposis coli. J Neurosci 28:8644–8654
Rhinn M, Lun K, Luz M, Werner M, Brand M (2005) Positioning of the midbrain-hindbrain boundary organizer through global posteriorization of the neuroectoderm mediated by Wnt8 signaling. Development 132:1261–1272
Robinson A, Escuin S, Doudney K, Vekemans M, Stevenson RE, Greene ND, Copp AJ, Stanier P (2012) Mutations in the planar cell polarity genes CELSR1 and SCRIB are associated with the severe neural tube defect craniorachischisis. Hum Mutat 33:440–447
Rosso SB, Sussman D, Wynshaw-Boris A, Salinas PC (2005) Wnt signaling through Dishevelled, Rac and JNK regulates dendritic development. Nat Neurosci 8:34–42
Schambony A, Wedlich D (2007) Wnt-5A/Ror2 regulate expression of XPAPC through an alternative noncanonical signaling pathway. Dev Cell 12:779–792
Selvadurai HJ, Mason JO (2011) Wnt/beta-catenin signalling is active in a highly dynamic pattern during development of the mouse cerebellum. PLoS One 6:e23012
Shafer B, Onishi K, Lo C, Colakoglu G, Zou Y (2011) Vangl2 promotes Wnt/planar cell polarity-like signaling by antagonizing Dvl1-mediated feedback inhibition in growth cone guidance. Dev Cell 20:177–191
Shimogori T, Banuchi V, Ng HY, Strauss JB, Grove EA (2004) Embryonic signaling centers expressing BMP, WNT and FGF proteins interact to pattern the cerebral cortex. Development 131:5639–5647
Singh KK, Ge X, Mao Y, Drane L, Meletis K, Samuels BA, Tsai LH (2010) Dixdc1 is a critical regulator of DISC1 and embryonic cortical development. Neuron 67:33–48
Speese SD, Budnik V (2007) Wnts: up-and-coming at the synapse. Trends Neurosci 30:268–275
Stuebner S, Faus-Kessler T, Fischer T, Wurst W, Prakash N (2010) Fzd3 and Fzd6 deficiency results in a severe midbrain morphogenesis defect. Dev Dyn 239:246–260
Subramanian L, Tole S (2009) Mechanisms underlying the specification, positional regulation, and function of the cortical hem. Cereb Cortex 19(Suppl 1):i90–i95
Suriben R, Kivimae S, Fisher DA, Moon RT, Cheyette BN (2009) Posterior malformations in Dact1 mutant mice arise through misregulated Vangl2 at the primitive streak. Nat Genet 41:977–985
Tang M, Villaescusa JC, Luo SX, Guitarte C, Lei S, Miyamoto Y, Taketo MM, Arenas E, Huang EJ (2010) Interactions of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and sonic hedgehog regulate the neurogenesis of ventral midbrain dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 30:9280–9291
Theil T, Aydin S, Koch S, Grotewold L, Ruther U (2002) Wnt and Bmp signalling cooperatively regulate graded Emx2 expression in the dorsal telencephalon. Development 129:3045–3054
Thomas KR, Capecchi MR (1990) Targeted disruption of the murine int-1 proto-oncogene resulting in severe abnormalities in midbrain and cerebellar development. Nature 346:847–850
Thomas KR, Musci TS, Neumann PE, Capecchi MR (1991) Swaying is a mutant allele of the proto-oncogene Wnt-1. Cell 67:969–976
Torban E, Patenaude AM, Leclerc S, Rakowiecki S, Gauthier S, Andelfinger G, Epstein DJ, Gros P (2008) Genetic interaction between members of the Vangl family causes neural tube defects in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:3449–3454
Valvezan AJ, Klein PS (2012) GSK-3 and Wnt signaling in neurogenesis and bipolar disorder. Front Mol Neurosci 5:1
van Amerongen R, Nusse R (2009) Towards an integrated view of Wnt signaling in development. Development 136:3205–3214
Varela-Nallar L, Alfaro IE, Serrano FG, Parodi J, Inestrosa NC (2010) Wingless-type family member 5A (Wnt-5a) stimulates synaptic differentiation and function of glutamatergic synapses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:21164–21169
Varela-Nallar L, Parodi J, Farias GG, Inestrosa NC (2012) Wnt-5a is a synaptogenic factor with neuroprotective properties against Abeta toxicity. Neurodegener Dis 10:23–26
Vivancos V, Chen P, Spassky N, Qian D, Dabdoub A, Kelley M, Studer M, Guthrie S (2009) Wnt activity guides facial branchiomotor neuron migration, and involves the PCP pathway and JNK and ROCK kinases. Neural Dev 4:7
Wang J, Ruan NJ, Qian L, Lei WL, Chen F, Luo ZG (2008) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling suppresses Rapsyn expression and inhibits acetylcholine receptor clustering at the neuromuscular junction. J Biol Chem 283:21668–21675
Wayman GA, Impey S, Marks D, Saneyoshi T, Grant WF, Derkach V, Soderling TR (2006) Activity-dependent dendritic arborization mediated by CaM-kinase I activation and enhanced CREB-dependent transcription of Wnt-2. Neuron 50:897–909
Wen S, Zhu H, Lu W, Mitchell LE, Shaw GM, Lammer EJ, Finnell RH (2010) Planar cell polarity pathway genes and risk for spina bifida. Am J Med Genet A 152A:299–304
Woodhead GJ, Mutch CA, Olson EC, Chenn A (2006) Cell-autonomous beta-catenin signaling regulates cortical precursor proliferation. J Neurosci 26:12620–12630
Wrobel CN, Mutch CA, Swaminathan S, Taketo MM, Chenn A (2007) Persistent expression of stabilized beta-catenin delays maturation of radial glial cells into intermediate progenitors. Dev Biol 309:285–297
Wu CI, Hoffman JA, Shy BR, Ford EM, Fuchs E, Nguyen H, Merrill BJ (2012) Function of Wnt/beta-catenin in counteracting Tcf3 repression through the Tcf3-beta-catenin interaction. Development 139:2118–2129
Yu X, Malenka RC (2003) Beta-catenin is critical for dendritic morphogenesis. Nat Neurosci 6:1169–1177
Zakin L, Reversade B, Virlon B, Rusniok C, Glaser P, Elalouf JM, Brulet P (2000) Gene expression profiles in normal and Otx2-/- early gastrulating mouse embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:14388–14393
Zechner D, Fujita Y, Hulsken J, Muller T, Walther I, Taketo MM, Crenshaw EB 3rd, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C (2003) beta-Catenin signals regulate cell growth and the balance between progenitor cell expansion and differentiation in the nervous system. Dev Biol 258:406–418
Zechner D, Muller T, Wende H, Walther I, Taketo MM, Crenshaw EB 3rd, Treier M, Birchmeier W, Birchmeier C (2007) Bmp and Wnt/beta-catenin signals control expression of the transcription factor Olig3 and the specification of spinal cord neurons. Dev Biol 303:181–190
Zhou CJ, Pinson KI, Pleasure SJ (2004a) Severe defects in dorsal thalamic development in low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein-6 mutants. J Neurosci 24:7632–7639
Zhou CJ, Zhao C, Pleasure SJ (2004b) Wnt signaling mutants have decreased dentate granule cell production and radial glial scaffolding abnormalities. J Neurosci 24:121–126
Funding
This work was supported by NIMH (T32 MH089920) and by The Center for Neurobiology and Psychiatry at the University of California, San Francisco.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mulligan, K.A., Cheyette, B.N.R. Wnt Signaling in Vertebrate Neural Development and Function. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 7, 774–787 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-012-9404-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-012-9404-x