Abstract
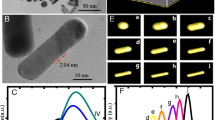
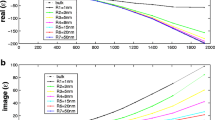
Au plasmonic hollow spherical nanostructures were synthesized by electrochemical reduction (GRR, the Galvanic Replacement Reaction) using Ag nanoparticles as templates. From UV-visible absorption spectroscopy, it was found that the surface plasmon resonance (SPR) of gold hollow spherical nanostructures first showed red shift and then blue shift. However, further addition of gold precursor (HAuCl4) resulted into a red shift of SPR peak. The morphological changes from Ag nanoparticles to Au hollow nanostructures were assessed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX)analysis. The Mie Scattering theory based simulations of SPR of Au hollow nanostructures were performed which are in good agreement with the experimental observations. Based on the experimental observations and theoretical calculations, a complete growth mechanism for Au hollow nanostructures is proposed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang X, Neretina S, El-Sayed MA (2009) Gold nanorods: from synthesis and properties to biological and biomedical applications. Adv Mater 21:4880–4910
Chen XJ, Wen R, Zhang LS, Lahiri A, Wang PJ, Fang Y (2014) Photoreduction of silver salts using Au nanoparticles to form a core-shell-type nanostructure: insight into the reaction mechanism. Plasmonics 9:945–949
Wang PJ, Liu MY, Gao GL, Zhang SP, Shi HL, Li ZP, Zhang LS, Fang Y (2012) From gold nanorods to nanodumbbells: a different way to tailor surface plasmon resonances by a chemical route. J Mate Chem 22:24006–24011
Jain PK, Huang X, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2008) Noble metals on the nanoscale: optical and photothermal properties and some applications in imaging, sensing, biology, and medicine. Acc Chem Res 41:1578–1586
Ratto F, Matteini P, Rossi F, Menabuoni L, Tiwari N, Kulkarni SK, Pini R (2009) Photothermal effects in connective tissues mediated by laser-activated gold nanorods. Nanomed-Nanotechnol 5:143–151
Xia XH, Wang Y, Ruditskiy A, Xia YN (2013) 25th anniversary article: galvanic replacement: a simple and versatile route to hollow nanostructures with tunable and well-controlled properties. Adv Mater 25:6313–6333
Sun YG, Mayers B, Xia YN (2003) Metal nanostructures with hollow interiors. Adv Mater 15:641–646
Sun Y, G Xia YN (2004) Mechanistic study on the replacement reaction between silver nanostructures and chloroauric acid in aqueous medium.J Am Chem Soc 126:3892–3901.
Sershen SR, Westcott SL, Halas NJ, West JL (2000) Temperature-sensitive polymer–nanoshell composites for photothermally modulated drug delivery. J Biomed Mater Res51:293–298.
Huang X, Jain PK, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA (2008) Plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) using gold nanoparticles. Lasers Med Sci 23:217–228
Lu LH, Sun GY, Xi SQ, Wang HS, Zhang HJ, Wang T (2003) A colloidal templating method to hollow bimetallic nanostructures. Langmuir 19:3074–3077
Lee W, Scholz R, Nielsch K, Gösele U (2005) A template-based electrochemical method for the synthesis of multisegmented metallic nanotubes. AngewChem 117:6204–6208
Gao CB, Zhang Q, Lu ZD, Yin YD (2011) Templated synthesis of metal nanorods in silica nanotubes. J Am Chem Soc 133:19706–19709
Fowler CE, Khushalani D, Mann S (2001) Interfacial synthesis of hollow microspheres of mesostructured silica. ChemCommun 19:2028–2029
Wang ZX, Chen XB, Chen M, Wu LM (2009) Facile fabrication method and characterization of hollow Ag/SiO2 double-shelled spheres. Langmuir 25:7646–7651
Bikram M, Gobin AM, Whitmire RE, West JL (2007) Temperature-sensitive hydrogels with SiO 2–Au nanoshells for controlled drug delivery. J Control Release 123:219–227
Caruso F, Lichtenfeld H, Giersig M, Möhwald HM (1998) Electrostatic self-assembly of silica nanoparticle-polyelectrolyte multilayers on polystyrene latex particles. J Am Chem Soc 120:8523–8524
Son Y, Son Y, Choi M, Ko M, Chae S, Park N, Cho J (2015) Hollow silicon nanostructures via the Kirkendall effect. Nano Lett 15:6914–6918
Knez M, Nielsch K, Niinistö L (2007) Synthesis and surface engineering of complex nanostructures by atomic layer deposition. Adv Mate 19:3425–3438
Shin H, Jeong DK, Lee J, Sung MM, Kim J (2004) Formation of TiO2 and ZrO2 nanotubes using atomic layer deposition with ultraprecise control of the wall thickness. Adv Mater 16:1197–1200
Skrabalak SE, Chen J, Sun Y, Lu X, Au L, Cobley CM, Xia Y (2008) Gold nanocages: synthesis, properties, and applications. Acc Chem Res 41:1587–1595
Lu XM, Chen J, Skrabalak SE, Xia YN (2007) Galvanic replacement reaction: a simple and powerful route to hollow and porous metal nanostructures. Pro Ins Mech Eng Part N 221:1–16
Cobley CM, Xia YN (2010) Engineering the properties of metal nanostructures via galvanic replacement reactions. Mater Sci Eng 70:44–62
Chen MH, Gao LA (2006) Synthesis and characterization of Ag nanoshells by a facile sacrificial template route through in situ replacement reaction. InorgChem 45:5145–5149
Skrabalak SE, Chen J, Sun YG, Lu XM, Au L, Cobley CM, Xia YN (2008) Gold nanocages: synthesis, properties, and applications. Acc Chem Res 41:1587–1595
Chen J, Wiley B, McLellan J, Xiong YJ, Li ZY, Xia YN (2005) Optical properties of Pd-Ag and Pt-Ag nanoboxes synthesized via galvanic replacement reactions. Nano Lett 5:2058–2062
Xu HX (2005) Multilayered metal core-shell nanostructures for inducing a large and tunable local optical field. Phys Rev B 72:073405
Lee PC, Meisel D (1982) Adsorption and surface-enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. J PhyChem 86:3391–3395
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Review B 6:4370–4379
Zhang LS, Zhao F, Li ZP, Fang Y, Wang PJ (2016) Tailoring of localized surface plasmon resonances core-shell Au@ Ag nanorods by changing the thickness of Ag shell. Plasmonics 1–7
Sun YG, Xia YN (2003) Alloying and dealloying processes involved in the preparation of metal nanoshells through a galvanic replacement reaction. Nano Lett 3:1569–1572
Dursun A, Pugh DV, Corcoran SG (2003) Dealloying of Ag-Au alloys in halide-containing electrolytes affect on critical potential and pore size. J Electro Chem Soc 15:B355–B360
Lu XM, Au L, McLellan J, Li ZY, Marquez M, Xia YN (2007) Fabrication of cubic nanocages and nanoframes by dealloying Au/Ag alloy nanoboxes with an aqueous etchant based on Fe (NO3) 3 or NH4OH. Nano Lett 7:1764–1769
Zeng HC (2007) Ostwald ripening: a synthetic approach for hollow nanomaterials. Cur Nanosci 3:177–181
Noorduin WL, Vlieg E, Kellogg RM, Kaptein B (2009) From Ostwald ripening to single chirality. AngewChemInt Ed 48:9600–9606
Sadegh Y, Josée RD, Nicolas L, George CS, Denis B, Emilie R (2016) Reversible shape and plasmon tuning in hollow AgAu nanorods. Nano Lett 16:6939–6945
Prieto G, Tüysüz H, Duyckaerts N, Knossalla J, Wang GH, Schüth F (2016) Hollow nano- and microstructures as catalysts. Chem Rev 116(22):14056–14119
Acknowledgement
This project is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21473115; No.11274004), the National Youth Foundation of China (grant no. 11204189), NCET (Grant No. NCET-13-0915), Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation (grant number 151010) and the Scientific Research Base Development Program of the Beijing Municipal Commission of Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Yang, H., Li, Z. et al. The Tunable and Well-Controlled Surface Plasmon Resonances of Au Hollow Nanostructures by a Chemical Route. Plasmonics 13, 47–53 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0482-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-016-0482-0