Abstract
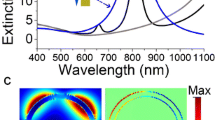
Features of the asymmetric nanocross including extinction spectrum, local electric field intensity, and temporal response of the local electric field under ultrashort laser illumination are investigated in this paper. It is found that, due to the simultaneous excitation of local electric fields in the arms that are perpendicular and parallel to the laser polarization direction of the asymmetric nanocross, extinction spectrum exhibits multiple resonant peaks and the position of the peaks can be tuned by changing the lengths of the arms. Simulation results disclose that there is a strong connection between optical response of the parallel and perpendicular arms. Moreover, temporal response of electric field in arms of the asymmetric nanocross shows that oscillations in the parallel arms start earlier than that of the perpendicular arms, and they are in phase when one of the parallel arms resonantly excited, which further reflects the relationship between the parallel and perpendicular arms. Therefore, we demonstrate that the perpendicular arm excitation is attributed to that of the nonresonant parallel arm in the asymmetric structure which cannot keep the overall electric neutrality of the nanostructure, and thus, perpendicular arms are activated to maintain this balance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schuller JA, Barnard ES, Cai W, Jun YC, White JS, Brongersma ML (2010) Plasmonics for extreme light concentration and manipulation. Nat Mater 9:193–204
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424:824–830
Atwater HA (2007) The promise of plasmonics. Sci Am 296:56–62
Rodríguez-Fortuño FJ, Martínez-Marco M, Tomás-Navarro B, Ortuño R, Martí J, Martínez A, Rodríguez-Cantó PJ (2011) Highly-sensitive chemical detection in the infrared regime using plasmonic gold nanocrosses. Appl Phys Lett 98:133118
Kinkhabwala A, Yu Z, Fan S, Avlasevich Y, Müllen K, Moerner WE (2009) Large single-molecule fluorescence enhancements produced by a bowtie nanoantenna. Nat Photonics 3:654–657
Esenturk EN, Walker ARH (2013) Gold nanostar@ iron oxide core-shell nanostructures: synthesis, characterization, and demonstrated surface-enhanced Raman scattering properties. J Nanopart Res 15:1–10
Osinkina L, Lohmuller T, Jackel F, Feldmann J (2013) Synthesis of gold nanostar arrays as reliable, large-scale, homogeneous substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering imaging and spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 117:22198–22202
Alivisatos P (2004) The use of nanocrystals in biological detection. Nat Biotechnol 22:47–52
Ye L, Yong KT, Liu L, Roy I, Hu R, Zhu J et al (2012) A pilot study in non-human primates shows no adverse response to intravenous injection of quantum dots. Nat Nanotechnol 7:453–458
Melchior P, Bayer D, Schneider C, Fischer A, Rohmer M, Pfeiffer W, Aeschlimann M (2011) Optical near-field interference in the excitation of a bowtie nanoantenna. Phys Rev B 83:235407
Hrelescu C, Sau TK, Rogach AL, Jäckel F, Laurent G, Douillard L, Charra F (2011) Selective excitation of individual plasmonic hotspots at the tips of single gold nanostars. Nano Lett 11:402–407
Yang YY, Csapó E, Zhang YL, Süßmann F, Stebbings SL, Duan XM, Kling MF et al (2012) Optimization of the field enhancement and spectral bandwidth of single and coupled bimetal core-shell nanoparticles for few-cycle laser applications. Plasmonics 7:99–106
Eustis S, El-Sayed MA (2006) Why gold nanoparticles are more precious than pretty gold: noble metal surface plasmon resonance and its enhancement of the radiative and nonradiative properties of nanocrystals of different shapes. Chem Soc Rev 35:209–217
Maier SA, Kik PG, Atwater HA, Meltzer S, Harel E, Koel BE, Requicha AA (2003) Local detection of electromagnetic energy transport below the diffraction limit in metal nanoparticle plasmon waveguides. Nat Mater 2:229–232
Krenn JR, Schider G, Rechberger W, Lamprecht B, Leitner A, Aussenegg FR, Weeber JC (2000) Design of multipolar plasmon excitations in silver nanoparticles. Appl Phys Lett 77:3379–3381
Mühlschlegel P, Eisler HJ, Martin OJF, Hecht B, Pohl DW (2005) Resonant optical antennas. Science 308:1607–1609
Kim S, Jin J, Kim YJ, Park IY, Kim Y, Kim SW (2008) High-harmonic generation by resonant plasmon field enhancement. Nature 453:757–760
Nehl CL, Liao H, Hafner JH (2006) Optical properties of star-shaped gold nanoparticles. Nano Lett 6:683–688
Hrelescu C, Sau TK, Rogach AL, Jäckel F, Feldmann J (2009) Single gold nanostars enhance Raman scattering. Appl Phys Lett 94:153113
Hao F, Nehl CL, Hafner JH, Nordlander P (2007) Plasmon resonances of a gold nanostar. Nano Lett 7:729–732
Onishi S, Matsuishi K, Oi J, Harada T, Kusaba M, Hirosawa K, Kannari F (2013) Spatiotemporal control of femtosecond plasmon using plasmon response functions measured by near-field scanning optical microscopy (NSOM). Opt Express 21:26631–26641
Pors A, Bozhevolnyi SI (2013) Plasmonic metasurfaces for efficient phase control in reflection. Opt Express 21:27438–27451
Grant J, Ma Y, Saha S, Khalid A, Cumming DR (2011) Polarization insensitive, broadband terahertz metamaterial absorber. Opt Lett 36:3476–3478
Chen S, Wang ZL, Ballato J, Foulger SH, Carroll DL (2003) Monopod, bipod, tripod, and tetrapod gold nanocrystals. J Am Chem Soc 125:16186–16187
Verellen N, Van Dorpe P, Vercruysse D, Vandenbosch GA, Moshchalkov VV (2011) Dark and bright localized surface plasmons in nanocrosses. Opt Express 19:11034–11051
Catchpole KR, Polman A (2008) Plasmonic solar cells. Opt Express 16:21793–21800
Pala RA, Liu JS, Barnard ES, Askarov D, Garnett EC, Fan S, Brongersma ML (2013) Optimization of non-periodic plasmonic light-trapping layers for thin-film solar cells. Nat Commun 4:2095
Xu Y, Munday JN (2014) Light trapping in a polymer solar cell by tailored quantum dot emission. Opt Express 22:A259–A267
Atwater HA, Polman A (2010) Plasmonics for improved photovoltaic devices. Nat Mater 9:205–213
Homola J (2008) Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem Rev 108:462–493
Chen K, Adato R, Altug H (2012) Dual-band perfect absorber for multispectral plasmon-enhanced infrared spectroscopy. ACS Nano 6:7998–8006
Adato R, Yanik AA, Altug H (2011) On chip plasmonic monopole nano-antennas and circuits. Nano Lett 11:5219–5226
FDTD solutions. http://www.lumerical.com
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370
Agio M, Alu A (2013) Optical antennas. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Maier SA (2007) Plasmonics: fundamentals and applications. Springer, New York
Crozier KB, Sundaramurthy A, Kino GS, Quate CF (2003) Optical antennas: resonators for local field enhancement. J Appl Phys 94:4632–4642
Huang JS, Voronine DV, Tuchscherer P, Brixner T, Hecht B (2009) Deterministic spatiotemporal control of optical fields in nanoantennas and plasmonic circuits. Phys Rev B 79:195441
Kubo A, Onda K, Petek H, Sun Z, Jung YS, Kim HK (2005) Femtosecond imaging of surface plasmon dynamics in a nanostructured silver film. Nano Lett 5:1123–1127
Yu N, Genevet P, Kats MA, Aieta F, Tetienne JP, Capasso F, Gaburro Z (2011) Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction. Science 334:333–337
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by 973 program (2013CB922404); National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11474040 11274053, 11474039, and 61178022; and also project 14KP007. The authors acknowledge the helpful discussion with Prof. Walter Pfeiffer at the University of Bielefeld and Prof. Zhiyuan Li at the Institute of Physics, CAS.
Funding
This study was funded by 973 program (2013CB922404); National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 11474040 11274053, 11474039, and 61178022; and also project 14KP007.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Helpful Discussion
The authors acknowledge the helpful discussion with Prof. Walter Pfeiffer at the University of Bielefeld and Prof. Zhiyuan Li at the Institute of Physics, CAS.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, B., Qin, J., Hao, Z. et al. Features of Local Electric Field Excitation in Asymmetric Nanocross Illuminated by Ultrafast Laser Pulse. Plasmonics 10, 1573–1580 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9974-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-9974-6