Abstract
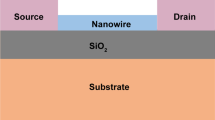
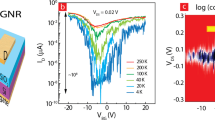
Based on the influence of edge effect and channel shape, two new graphene nanoribbon field effect transistors are presented being useful in high-voltage and highly sensitive optical applications. We fabricated and examined our devices under different conditions. It is seen that by choosing the proper channel shape, ionization rate and breakdown voltage could be improved compared to a normal rectangular device. We report nearly 11 and 19 % improvements in breakdown voltage and ionization rate of graphene nanoribbon field effect transistors (GNRFET), respectively.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novoselov KS, Geim AK, Morozov SV, Jiang D, Zhang Y, Dubonos SV et al (2004) Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306:666–669
Geim AK, Nonselov KS (2007) The rise of graphene. Nat Mater 6:183–191
Avouris P, Chen Z, Perebeinos V (2007) Carbon-based electronics. Nat Nanotechnol 2:605–615
Dragoman DDM (2008) Graphene-based quantum electronics. Prog Quantum Electron 33:165–241
Saeidmanesh M, Ghadiry MH, Khaledian M, Kiani MJ, Ismail R (2014) Carrier scattering and impact ionization in bilayer graphene. J Comput Electron 13:180–185
Rahmani M, Ismail R, Ahmadi MT, Ghadiry MH (2014) Quantum confinement effect on trilayer graphene nanoribbon carrier concentration. J Exp Nanosci 9:51–63
Abadi HKF, Ahmadi MT, Yusof R, Saeidmanesh M, Rahmani M, Kiani MJ et al (2014) Development of carbon nanotube based biosensors model for detection of single-nucleotide polymorphism. Sci Adv Mater 6:513–519
Ahmadi MT, Rahmani M, Ghadiry M, Ismail R (2012) Monolayer graphene nanoribbon homojunction characteristics. Sci Adv Mater 4:753–756
Ghadiry M, Ismail R, Naraghi B, Taheri Abed S, Kavosi D, Fotovatikhah F (2015) A new approach to model sensitivity of graphene-based gas sensors. Semicond Sci Technol 30(4):045012. doi:10.1088/0268-1242/30/4/045012
Ghadiry M, Nadi M, Mohammadi H, Bin Abd Manaf A (2012) Analysis of a novel full adder designed for implementing in carbon nanotube technology. J Circ Syst Comput 21(5):1250042
Ghadiry MH, Abd Manaf A, Ahmadi MT, Sadeghi H, Senejani MN (2011) Design and analysis of a new carbon nanotube full adder cell. J Nanomater 2011:36. doi:10.1155/2011/906237
Ghadiry MH, Manaf AA, Mousavi SM, Sadeghi H (2011) Study the effect of applied voltage on propagation delay of bilayer graphene nanoribbon transistor. In: 2011 International Semiconductor Device Research Symposium, ISDRS 2011
Rahmani M, Ahmadi MT, Ghadiry MH, Samadi J, Anwar S, Ismail R (2012) The effect of applied voltage on the carrier effective mass in ABA trilayer graphene nanoribbon. J Comput Theor Nanosci 9:1618–1621
Rahmani M, Ahmadi MT, Ismail R, Ghadiry MH (2013) Performance of bilayer graphene nanoribbon schottky diode in comparison with conventional diodes. J Comput Theor Nanosci 10:323–327
Taji S, Karimi A, Ghadiry M, Fotovatikhah F (2015) An analytical approach to calculate power and delay of carbon-based links in on-chip networks. J Comput Theor Nanosci 12:1775–1779
Zhao P, Choudhury M, Mohanram K, Guo J (2008) Computational model of edge effects in graphene nanoribbon transistors. Nano Res 1:395–402
Basu MJGD, Register LF, Banerjee SK, MacDonald AH (2008) Effect of edge roughness on electronic transport in graphene nanoribbon channel metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors. Appl Phys Lett 92:042114
Youngki Yoon JG (2007) Effect of edge roughness in graphene nanoribbon transistors. Appl Phys Lett 91:073103
Park W-D, Tanioka K (2014) Avalanche multiplication and impact ionization in amorphous selenium. Jpn J Appl Phys 53:1347–4065
Ghadiry M, Nadi M, Saiedmanesh M, Abadi HKF (2014) An analytical approach to study breakdown mechanism in graphene nanoribbon field effect transistors. J Comput Theor Nanosci 11:339–343
Ghadiry M, Ismail R, Saeidmanesh M, Khaledian M, Manaf AA (2014) Graphene nanoribbon field-effect transistor at high bias. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:1–5
Pirro L, Girdhar A, Leblebici Y, Leburton J-P (2012) Impact ionization and carrier multiplication in graphene. J Appl Phys 112(9):093707
Ghadiry M, Manaf ABA, Nadi M, Rahmani M, Ahmadi MT (2012) Theory of ionization mechanism in graphene nanoribbons. J Comput Theor Nanosci 9:2190–2192
Ghadiry M, Manaf ABA, Nadi M, Rahmani M, Ahmadi MT (2012) Ionization coefficient of monolayer graphene nanoribbon. Microelectron Reliab 52:1396–1400
Liao AD, Wu JZ, Wang X, Tahy K, Jena D, Dai H et al (2011) Thermally limited current carrying ability of graphene nanoribbons. Phys Rev Lett 106:256801
Lee K-J, Chandrakasan A, Kong J (2011) Breakdown current density of cvd-grown multilayer graphene interconnects. IEEE Electron Device Lett 32(4):557–559
Hertel S, Kisslinger F, Jobst J, Waldmann D, Krieger M, Weber HB (2011) Current annealing and electrical breakdown of epitaxial graphene. Appl Phys Lett 98:212109
Girdhar A, Leburton JP (2011) Soft carrier multiplication by hot electrons in graphene. Appl Phys Lett 99:043107
Ghadiry MH, Nadi S M, Ahmadi MT, Manaf AA (2011) A model for length of saturation velocity region in double-gate graphene nanoribbon transistors. Microelectron Reliab 51:2143–2146
Fang T, Konar A, Xing H, Jena D (2011) High-field transport in two-dimensional graphene. Phys Rev B 84:125450
Murali R, Yang Y, Brenner K, Beck T, Meindl JD (2009) Breakdown current density of graphene nanoribbons. Appl Phys Lett 94:243114
Meric I, Han MY, Young AF, Ozyilmaz B, Kim P, Shepard KL (2008) Current saturation in zero-bandgap, topgated graphene field-effect transistors. Nat Nanotechnol 3:654–659. doi:10.1038/nnano.2008.268
Ghadiry M, Nadi M, Bahadorian M, Manaf AA, Karimi H, Sadeghi H (2013) An analytical approach to calculate effective channel length in graphene nanoribbon field effect transistors. Microelectron Reliab 53:540–543
Ghadiry M, Nadi M, Rahmani M, Ahmadi M, Mahaf AA (2012) Modelling and simulation of saturation region in double gate graphene nanoribbon transistors. Semiconductors J 46(1):126–129
Rubel O, Potvin A, Laughton D (2011) Generalized lucky-drift model for impact ionization in semiconductors with disorder. J Phys Condens Matter 23(5):055802
Ferrari AC, Meyer JC, Scardaci V, Casiraghi C, Lazzeri M, Mauri F et al (2006) Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys Rev Lett 97(18):187401
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghadiry, M., Ahmad, H., Hivechi, A. et al. Exploiting Edge Effect to Control Generation Rate and Breakdown Voltage in Graphene Nanoribbon Field Effect Transistors. Plasmonics 11, 573–577 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0073-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-015-0073-5