Abstract
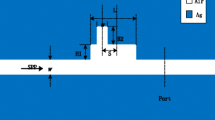
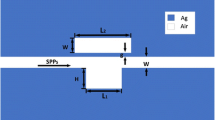
A plasmonic nano-sensor is proposed by means of Fano resonance in a metal-insulator-metal (MIM) waveguide structure, which consists of two identical slot cavities placed nearby two symmetrical grooves in a MIM bus waveguide. Due to the interaction of the broad bright mode and the narrow dark mode caused by the grooves and the side-coupled slot cavities, respectively, the transmission spectrum possesses a sharp asymmetrical profile. The spectral line shape can be manipulated by changing the length of the grooves, and the wavelength of the resonance peak has a linear relationship with the length of the slot cavity. These characteristics offer flexibility to design the device. This nano-sensor yields a sensitivity of ~903 nm/RIU and a figure of merit (FOM) of ~3.1 × 105. Besides, dual Fano resonance peaks are also achieved by shifting the slot cavities away from the center of the grooves, resulting in a FOM as high as 4.6 × 105. The proposed structure may find important applications in the on-chip nano-sensing area.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luk’yanchuk B, Zheludev N, Maier S, Halas N, Nordlander P, Giessen H, Chong C (2010) The Fano resonance in plasmonic nanostructures and metamaterials. Nat Mater 9(9):707–715
Miroshnichenko E, Flach S, Kivshar YS (2010) Fano resonances in nanoscale structures. Rev Mod Phys 82(3):2257–2298
Verellen N, Sonnefraud Y, Sobhani H, Hao F, Moshchalkov VV, Van Dorpe P, Nordlander P, Maier SA (2009) Fano resonances in individual coherent plasmonic nanocavities. Nano Lett 9(9):1663–1667
Chen JJ, Li Z, Zhang X, Xiao JH, Gong QH (2013) Submicron bidirectional all-optical plasmonic switches. Sci Rep 3:1451
Barnes WL, Dereux A, Ebbesen TW (2003) Surface plasmon subwavelength optics. Nature 424(6950):824–830
Liu N, Hentschel M, Weiss T, Alivisatos AP, Giessen H (2011) Three-dimensional plasmon rulers. Science 332(6036):1407–1410
Fan JA, Wu C, Bao K, Bao J, Bardhan R, Halas NJ, Manoharan VN, Nordlander P, Shvets G, Capasso F (2010) Self-assembled plasmonic nanoparticle clusters. Science 328(5982):1135–1138
Artar A, Yanik AA, Altug H (2011) Directional double Fano resonances in plasmonic hetero-oligomers. Nano Lett 11(9):3694–3700
Hu Y, Noelck SJ, Drezek RA (2010) Symmetry breaking in gold-silica-gold multilayer nanoshells. ACS Nano 4(3):1521–1528
Wang JQ, Fan CZ, He JN, Ding P, Liang EJ, Xue QZ (2013) Double Fano resonances due to interplay of electric and magnetic plasmon modes in planar plasmonic structure with high sensing sensitivity. Opt Express 21(2):2236–2244
Zhang ZS, Yang ZJ, Li JB, Hao ZH, Wang QQ (2011) Plasmonic interferences in two-dimensional stacked double-disk array. Appl Phys Lett 98(17):173111
Fang ZY, Cai J, Yan Z, Nordlander P, Halas NJ, Zhu X (2011) Removing a wedge from a metallic nanodisk reveals a Fano resonance. Nano Lett 11(10):4475–4479
Zhang S, Bao K, Halas NJ, Xu H, Nordlander P (2011) Substrate-induced Fano resonances of a plasmonic nanocube: a route to increased-sensitivity localized surface plasmon resonance sensors revealed. Nano Lett 11(4):1657–1663
Chen J, Li Z, Zou Y, Deng Z, Xiao J, Gong Q (2013) Coupled-resonator-induced fano resonances for plasmonic sensing with ultra-high figure of merits. Plasmonics 8(4):1627–1631
Piao X, Yu S, Koo S, Lee K, Park N (2011) Fano-type spectral asymmetry and its control for plasmonic metal-insulator-metal stub structures. Opt Express 19(11):10907–10912
Qi J, Chen Z, Chen J, Li Y, Qiang W, Xu J, Sun Q (2014) Independently tunable double Fano resonances in asymmetric MIM waveguide structure. Opt Express 22(12):14688–14695
Wen KH, Yan LS, Pan W, Luo B, Guo Z, Guo YH, Luo XG (2014) Electromagnetically induced transparency-like transmission in a compact side-coupled T-shaped resonator. J Lightwave Technol 32(9):1701–1707
Wen KH, Yan LS, Hu YH, Chen L, Lei L (2014) A plasmonic wavelength-selected intersection structure. Plasmonics 9(3):685–690
Song G, Yu L, Wu C, Duan G, Wang L, Xiao J (2013) Polarization splitter with optical bistability in metal gap waveguide nanocavities. Plasmonics 8(2):943–947
Liu Y, Zhou F, Yao B, Cao J, Mao Q (2013) High-extinction-ratio and low-insertion-loss plasmonic filter with coherent coupled nano-cavity array in a MIM waveguide. Plasmonics 8(2):1035–1041
Dionne JA, Sweatlock LA, Atwater HA (2006) Plasmon slot waveguides: towards chip-scale propagation with subwavelength-scale localization. Phys Rev B 73:035407
Lin XS, Huang XG (2008) Tooth-shaped plasmonic waveguide filters with nanometeric sizes. Opt Lett 33(23):2874–2876
Ma FS, Lee C (2013) Optical nanofilters based on meta-atom side-coupled plasmonics metal-insulator-metal waveguides. J Lightwave Technol 31(17):2876–2880
Wen KH, Yan LS, Pan W, Luo B, Guo Z, Guo YH, Luo XG (2013) Design of plasmonic comb-like filters using loop-based resonators. Plasmonics 8(2):1017–1022
Becker J, Trügler A, Jakab A, Hohenester U, Sönnichsen C (2010) The optimal aspect ratio of gold nanorods for plasmonic bio-sensing. Plasmonics 5(2):161–167
Lu H, Liu X, Mao D, Wang G (2012) Plasmonic nanosensor based on Fano resonance in waveguide-coupled resonators. Opt Lett 37(18):3780–3782
Johnson PB, Christy RW (1972) Optical constants of the noble metals. Phys Rev B 6:4370–4379
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2014 M552173), the Open Research Fund of State Key Lab of Optical Technologies for Micro-Engineering and Nano-Fabrication of China, and the Research Fund of Guangdong University of Technology (No. 13ZK0387).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, K., Hu, Y., Chen, L. et al. Fano Resonance with Ultra-High Figure of Merits Based on Plasmonic Metal-Insulator-Metal Waveguide. Plasmonics 10, 27–32 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9772-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11468-014-9772-6