Abstract
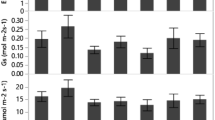
The growth and water metabolism of three common shrubs on the Loess Plateau were studied under soil with different water contents. Results showed that water consumption of those species decreased with the increase in drought stress, and water consumptions of these shrubs were different: Forsythia suspensa was the greatest, and Syringa oblata was the lowest. The growth rate of new branches and leaf area of three species were the fastest under adequate soil water conditions, and were the lowest under severe drought. Under the same water conditions, the growth of F. suspensa was the fastest while that of S. oblata was the slowest. The water content, proline and chlorophyll content of different species changed with the increase in soil water stress. The leaf water content of Periploca sepium and F. suspensa was obviously higher than that of S. oblata, while the leaf proline content of F. suspensa and S. oblata was lower than that of P. sepium. The ratio leaf chlorophyll a: b of F. suspensa and S. oblata decreased with the decrease in soil water content. Although these three shrubs had different mechanisms in response to drought stress, they all had higher drought resistance and could adapt to the drought condition on the Loess Plateau. This paper provided some bases for choosing tree species on the Loess Plateau.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ding C, Yang Q H, Li F S (2006). Effect of cold stress on the content of free-proline in leaf of Snccharum spontaneum L. and Sderostachya. J Anhui Agric Sci, 34(5): 846–849 (in Chinese)
Fu K J (2000). Flora Loess Plateaus Sinicae. Science Press (in Chinese)
Gao J F (1999). Experimental Technology of Plant Physiology. Xi’an: World Publishing Corporation (in Chinese)
Han R L, Jing W J, Hou Q C (2003). Research advance of artificial preparation and drought-resistant afforestation on Loess Plateau. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 23(8): 1,331–1,335 (in Chinese)
Han R L, Liang Z S, Hou Q C (1994). Water consumption properties of adaptable nursery stocks on Loess Plateau. Chin J Appl Ecol, 5(2): 210–213 (in Chinese)
Hou Q C, Han R L, Li H P (2000). On problems of vegetation reconstruction in Yan’an experimental area. Res Soil Water Conserv, 7(2): 119–123 (in Chinese)
Huang Z B, Shan L (1998). Research progression on water use efficiency and its physio-ecological mechanism. Eco-agricult Agric Res, 6(4): 19–23 (in Chinese)
Li Y Y, Shao M A (2004). The change of plant diversity during natural recovery process of vegetation in Ziwuling area. Acta Ecol Sin, 24(2): 252–260 (in Chinese)
Ren A Z, Gao Y B, Liu S (2000). Effects of Cr, Cd and Pb on free proline content etc in leaves of Brassica chinensis L. Chin J Appl Environ Biol, 6(4): 112–116 (in Chinese)
Ren X W (1997). Trees. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House (in Chinese)
Ru W M, Qu X X, Hou J Q (2004). Study on the characteristics of Forsythia suspense community in Taiyue wood district. Acta Bot Boreal-Occident Sin, 24(8): 1,462–1,467 (in Chinese)
Wang M B, Li H J, Chai B F (1996). Water ecophysiological characteristics of Caragana korshinskii. Acta Phytoecol Sin, 20(6): 494–501 (in Chinese)
Xu D Y (1993). Tree Hydrology. Beijing: China Forestry Publishing House (in Chinese)
Yang C H, Wang Y Y, Zhou Z F, Zhang G C (2006). Response of gas exchange parameters of Periploca sepium Bunge to soil water content in Loess Plateau. For Res, 19(2): 231–234 (in Chinese)
Yang J W, Liang Z S, Han R L (2004). Water use efficiency and water consumption characteristics of poplar under soil drought conditions. Acta Phytoecol Sin, 28(5): 630–636 (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2007, 27(1): 91–97 [译自: 西北植物学报]
About this article
Cite this article
An, Y., Liang, Z., Han, R. et al. Effects of soil drought on seedling growth and water metabolism of three common shrubs in Loess Plateau, Northwest China. Front. Forest. China 2, 410–416 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11461-007-0065-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11461-007-0065-5