Abstract
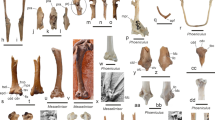
The taxonomy, age and environment status of the Yuanmou hominoids had been controversial since their discovery. We launched new excavations and investigations in the Yuanmou Basin and analyzed both old and newly collected data. We conclude that all hominoids from the Yuanmou Basin and the so-called Pliocene hominids can be attributed into a single species, and its valid nomination is Lufengpithecus hudienensis. It is different from Lufengpithecus lufengensis and Lufengpithecus keiyuanensis. Based on the faunal comparison and paleomagnetic correlation, the strata yielding the Yuanmou hominoids are older than those of Lufeng hominoids and younger than those of the Kaiyuan hominoids. The age of the Yuanmou hominoids is Late Miocene. The environments of the Yuanmou hominoids were subtropical, hilly, with some dense forestry and partial transitional bushes and seasonal climate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woo, J. K., Dryopithecus teeth from Keiyuan, Yunnan Province, Vert PalAs, 1957, 1(1): 25–32.
Woo, J. K., New materials of Dryopithecus from Keiyuan, Yunnan, Vert PalAs, 1958, 2(1): 38–43.
Xu, Q. H., Lu, Q. W., Pan, Y. R. et al., The fossil mandible of Ramapithecus lufengensis, Kexue Tongbao, 1978, 23(9): 554–556.
Lu, Q. W., Xu, Q. H., Zheng, L., Preliminary research on the cranium of Sivapithecus yunnanensi, Vert PalAs, 1981, 19(2): 101–106.
Zhang, X. Y., Lin, Y. P., Jiang, C. et al., A new species of Ramapithecus from Yuanmou, Yunnan Province, Sixiangzhanxian, 1987, (3): 54–56.
Jiang, N. R., Sun, R., Liang, Q. Z., The discovery of Yuanmou early ape man teeth fossils and their significance, J, Yunnan Geol., 1987, 6(2): 157–162.
Zhang, X. Y., Lin, Y. P., Jiang, C. et al., A new species of Homo from Yuanmou, Yunnan, Sixiangzhanxian, 1987, (3): 57–60.
Zhang, X. Y., Zheng, L., Gao, F., New genus Sinopithecus and its anthropological significance, Sixiangzhanxian, 1990, (2): 53–58.
Zheng, L., Zhang, X. Y., Hominoid Fossils, Yuanmou Hominoid Fauna (ed. He, Z. Q.), Kunming: Yunnan Science & Technology Press, 1997, 21–60.
Zhou, G. X., A study of fossil hominid and cultural remains in Yuanmou Basin, in Collected Works for “The 30th Anniversary of Yuanmou Man Discovery and the International Conference on Palaeoanthropological Studies” (eds. Cheng, J., Jiang, Z., Ji, X.), Kunming: Yunnan Science & Technology Press, 1998, 203–227.
Harrison, T., Ji, X., Su, D., On the systematic status of the Late Neogene hominoids from Yunnan Province, China, J. Hum. Evol., 2002, 43: 207–227.
Zong, G. F., The Neogene strata of the Yuanmou Basin, Yunnan, J. Stratigraphy, 1996, 20(2): 138–145.
Qian, F., Determination of geological age, in Yuanmou Hominoid Fauna (ed. He, Z. Q.), Kunming: Yunnan Science & Technology Press, 1997, 161–178.
Wu, R. K., A revision of the classification of the Lufeng great apes, Acta Anthrop. Sin., 1987, 6(4): 265–271.
Chaimanee, Y., Suteethorn, V., Jintasakul, P. et al., A new orang-utan relative from the Late Miocene of Thailand, Nature, 2004, 427, 439–441.
Kelley, J., The hominoid radiation in Asia, in The Primate Fossil Record (ed. Hartwig, W. C.), Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002, 369–384.
Jiang, C., Xiao, L., Li, J. M., Hominoid teeth fossil from Leilao, Yuanmou, Yunnan, Acta Anthrop. Sinica, 1993, 12(2): 97–102.
Liu, W., Zheng, L., Jiang, C., Statistical analyses of metric data of hominoid teeth found in Yuanmou of China, Chinese Science Bulletin, 1999, 45(10): 936–942.
Liu, W., Zheng, L., Walker, A., Three-dimensional morphometric analyses of hominoid lower molars from Yunnan Province, China, Acta Anthrop. Sinica, 2001, 20(3): 163–177.
Zhao, L. X., Zheng, L., Gao, F., Jiang, C., Study on enamel microstructure of Yuanmou hominoid, Science in China, Ser. D, 2002, 32(11): 921–927.
Zong, G. F., Primary correlation of Yuanmou hominoid fauna and discussion of relative problems, in Yuanmou Hominoid Fauna (ed. He, Z. Q.), Kunming: Yunnan Science & Technology Press, 1997, 122–131.
Dong, W., Miocene mammalian fauna of Xiaolongtan, Kaiyuan, Yunnan Province, Vert PalAs, 1987, 25(2): 116–123.
Dong, W., Upper Cenozoic stratigraphy and paleoenvironment of Xiaolongtan Basin, Kaiyuan, Yunnan Province, in Proceedings of the Eighth Annual Meetings of Chinese Society of Vertebrate Paleontology (eds. Deng, T., Wang, Y.), Beijing: China Ocean Press, 2001, 91–100.
Ni, X. J., Qiu, Z. D., The micromammalian fauna from the Leilao, Yuanmou hominoid locality: Implication for Biochronology and Paleoecology, J. Hum. Evol., 2002, 42: 535–546.
Qi, G. Q., Stratigraphic summarization of Ramapithecus fossil locality, Lufeng, Yunnan, Acta Anthrop. Sinica, 1985, 4(1): 55–69.
Flynn, L. J., Qi, G., Age of the Lufeng, China, hominoid locality, Nature, 1982, 298: 746–747.
Badgley, C., Qi, G., Chen, W. et al., Paleoecology of a Miocene, tropical, upland fauna: Lufeng, China, Nat. Geogr. Res., 1988, 4: 178–196.
Yue, L., Zhang, Y. X., Qi, G. Q. et al., Paleomagnetic age and palaeobiological significance of hominoid fossil strata of Yuanmou Basin in Yunnan, Science in China, Ser. D, 2004, 47: 405–411.
Zhu, R. X., Liu, Q. S., Yao, H. T. et al., Magnetostratigraphic dating of hominoid-bearing sediments at Zhupeng, Yuanmou Basin, southwestern China, EPSL, 2005, 236: 559–568.
Cande, S. C., Kent, D. V., Revised calibration of the geomagnetic polarity timescale for the Late Cretaceous and Cenozoic, J. Geophys. Res., 1995, 100: 6093–6095.
Andrews, P., Paleoecology of Miocene fauna from Pasala, Turkey, J. Hum. Evol., 1990, 19: 569–582.
Han, D. F., The Artiodactyla of Ramapithecus Site, Lufeng, Yunnan, Acta Anthrop. Sinica, 1985, 4(1): 44–54.
Dong, W., Liu, J. H., Pan, Y. R., A new Euprox from the Late Miocene of Yuanmou, Yunnan Province, China, with interpretation of its paleoenvironment, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(5): 485–491.
Bubenik, A., Epigenetical, morphological, physiological, and behavioral aspects of evolution of horns, prohorns and antlers, in Horns, Prohorns and Antlers (eds. Bubenik, G. A., Bubenik, A. B.), New York: Springer-Verlag, 1990, 1–113.
Bubenik, A., Evolution of cranial protuberances of Cervoids from velericorn stage into annually deciduous antlers, in Deer of China, (eds. Ohtaishi, N., Sheng, H. L.), Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers B V, 1993, 44–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, G., Dong, W., Zheng, L. et al. Taxonomy, age and environment status of the Yuanmou hominoids. CHINESE SCI BULL 51, 704–712 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0704-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-006-0704-5