Abstract
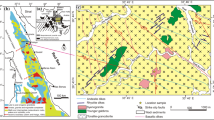
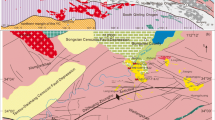
Zircon grains were selected from two types of ultrahigh-pressure (UHP) eclogites, coarse-grained phengite eclogite and fine-grained massive eclogite, in the Yukahe area, the western part of the North Qaidam UHP metamorphic belt. Most zircon grains show typical metamorphic origin with residual cores in some irregular grains and sector, planar or misty internal textures on the cathodoluminescence (CL) images. The contents of REE and HREE of the core parts of grains range from 173 to 1680 μg/g and 170 to 1634 μg/g, respectively, in phengite eclogite, and from 37 to 2640 μg/g and 25.7 to 1824 μg/g, respectively, in massive eclogite. The core parts exhibit HREE-enriched patterns, representing the residual zircons of protolith of the Yukahe eclogite. The contents of REE and HREE of the rim parts and the grains free of residual cores are much lower than those for the core parts. They vary from 13.1 to 89.5 μg/g and 12.5 to 85.7 μg/g, respectively, in phengite eclogite, and from 9.92 to 45.8 μg/g and 9.18 to 43.8 μg/g, respectively, in massive eclogite. Negative Eu anomalies and Th/U ratios decrease from core to rim. Positive Eu anomalies are shown in some grains. These indicate that the presence of garnet and the absence of plagioclase in the peak metamorphic mineral assemblage, and the zircons formed under eclogite facies conditions. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age data indicate that phengite eclogite and massive eclogite have similar metamorphic age of 436±3Ma and 431±4Ma in the early Paleozoic and magmatic protolith age of 783–793 Ma and 748–759 Ma in the Neo-proterozoic. The weighted mean age of the metamorphic ages (434±2 Ma) may represent the UHP metamorphic age of the Yukahe eclogites. The metamorphic age is well consistent with their direct country rocks of gneisses (431±3 Ma and 432±19 Ma) and coesite-bearing pelitic schist in the Yematan UHP eclogite section (423–440 Ma). These age data together with field observation and lithology, allow us to conclude that the Yukahe eclogites were Neo-proterozoic igneous rocks and may have experienced subduction and UHP metamorphism with continental crust at deep mantle during the early Paleozoic, therefore the metamorphic age of 434±2 Ma of the Yukahe eclogites probably represents the continental deep subduction time in this area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Song S G, et a1. Discovery of coesite in the North Qaidam Early Paleozoic ultrahigh pressure (UHP) metamorphic belt, NW China. Acta Geol Sin (in Chinese), 2001, 75(2): 175–179
Song S G, Yang J S, Liou J G, et al. Petrology, geochemistry and isotopic ages of eclogites from the Dulan UHPM Terrane, the North Qaidam, NW China. Lithos, 2003, 70: 195–211
Song S G, Zhang L F, Niu Y L, et al. Early Paleozoic plate-tectonic evolution and deep continental subduction on the northern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geol Bull Chin (in Chinese), 2004, 23(9–10): 918–925
Lu S N, Wang H C, Li H K, et al, Redefinition of the “Dakendaban Group” on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin. Geol Bull Chin (in Chinese), 2002, 21(1): 19–23
Sun S G. Petrology, mineralogy and metamorphic evolution of the Dulan UHP terrane in North Qaidam, NW China, and its tectonic implications. Doctoral thesis (in Chinese), Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing, 2001
Song S, Zhang L, Su L, et al. Geochronology of diamond-bearing zircons in garnet peridotite in the North Qaidam UHPM belt, North Tibetan Plateau: A record of complex histories associated with continental collision. Earth Planet Sci Lett, 2005, 234: 99–118
Song S G, Zhang L F, Chen J, et al. Sodic amphibole exsolution in garnet from garnet-peridotite, North Qaidam UHPM belt, NW China: implications for ultradeep-origin and hydroxyl defects in mantle garnets. Am Mineral, 2005, 90: 814–820
Chen L. Geochemistry of eclogites from north Qaidam and its dynamic significance. Doctoral thesis (in Chinese), Northwest University, Xi’an, 2003
Yang J S, Zhang J X, Meng F C, et al. Ultrahigh pressure eclogites of the North Qaidam and Altun mountains, NW China and their protoliths. Earth Sci Front (in Chinese), 2003, 10(3): 291–314
Meng F C, Zhang J X, Yang J S, et al. Geochemical characteristics of eclogites in Xitieshan area, north Qaidam of northwest China. Acta Petrol Sin (in Chinese), 2003, 19(3): 435–452
Chen D L. Petrology, geochemistry and chronology of Yukahe eclogites. In: 2004 National Workshop on Petrology & Geodynamics, December, 19–24, Haikou, China. Abstract (in Chinese), 14–15
Zhang J X, Yang J S, Mattinson C G, et al. Two contrasting eclogite cooling histories, North Qaidam HP/UHP terrane, western China: Petrological and isotopic constraints. Lithos, 2005, 84: 51–76
Zhang J X, Yang J S, Xu Z Q, et al. Peak and retrograde age of eclogites at the northern margin of Qaidam basin, Northwestern China: evidences from U-Pb and Ar-Ar dates. Geochimica (in Chinese), 2000, 29(3): 217–222
Wang H C, Lu S N, Mo X X, et al. An Early Paleozoic collisional orogen on the northern margin of the Qaidam basin, northwestern China. Geol Bull Chin (in Chinese), 2005, 24(7): 603–612
Chen D L, Sun Y, Liu L, et al. The metamorphic evolution of the Yuka eclogite in the North Qaidam, NW China: evidences from the compositional zonation of garnet and reaction texture in the rock. Acta Petrol Sin (in Chinese), 2005, 21(4): 1039–1048
Yang J S, Song S G, Wu C L, et al. North Qaidam ultrahigh pressure metamorphic(UHPM)belt on the northeastern Qjinghai-Tibei plateau and its eastward extension. Earth Science Front, 2000, 7(suppl.): 241–242
Yuan H L, Gao S, Liu X M, et al. Accurate U-Pb age and trace element determinations of zircon by laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Geostand Geoanal Res, 2004, 11: 357–370
Rubatto D, Williams I S. Imaging, trace element geochemistry and mineral inclusions: linking U-Pb ages with metamorphic Rubatto conditions. EOS Trans, 2000, 21: 2520
Rubatto D. Zircon trace element geochemistry: partitioning with garnet and the link between U-Pb ages and metamorphism. Chem Geol, 2002, 184: 123–138
Whitehouse M J, Platt J P. Dating high-grade metamorphism-constraints from rare-earth elements in zircon and garnet. Contrib Mineral Petrol, 2003, 145: 61–74
Hoskin P W O, Ireland T. Rare earth element chemistry of zircon and its use as a provenance indicator. Geology, 2000, 28(7): 627–630
McDonough W F, Sun S S. The composition of the earth. Chem. Geol, 1995, 120: 223–253
Ludwig K R. Isoplot—a plotting and regression program for radiogenic—isotope data. US Geological Survey Open-File Report, 1991, 39: 91–445
Andersen T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chem Geol, 2002, 192: 59–79
Gebauer D A. P-T-t path for an (Ultra?) high-pressure ultramafic/ mafic rock-association and its felsic country-rocks based on SHRIMP-dating of magmatic and metamorphic zircon domains. Example: Alps Arami Central Swiss Alps. In: Reading the Isotopic Code, Geophysical Monograph 95. Washington D C: Am Geophy Union. 1996. 307–329
Wu Y B, Chen D G, Xia Q K, et al. In-situ trace element analyses of zircons from Dabieshan Huangzhen eclogite: Trace element characteristics of eclogite facies metamorphic zircons. Chin Sci Bull, 2002, 47(16): 1398–1401
Zhang A D, Liu L, Sun Y, et al. SHRIMP U-Pb Dating of Zircons and Its Geological Significance from UHP Granitoid Gneiss in Altyn Tagh. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49(23): 2527–2532
Chen D L, Liu L, Sun Y, et al. LA-ICP-MS Zircon U-Pb dating for high-pressure basic granulite from north Qinling. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49(21): 2296–2302
Yang J S, Xu Z Q, Pei X Z. et al. Discovery of diamond in North Qinling and recognition of Paleozoic and Mesozoic dual deep subduction between North China and Yangtze plates. Acta Geol Sin, 2002, 76(4): 484–495
Su L, Song S G, Song B. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb age of garnet-pyroxenite and Fushui gabbroic complex in Songshugou region and constraints on tectonic evolution of Qinling Orogenic Belt. Chin Sci Bull, 2004, 49(12): 1307–1310
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 40472043, 40372088 and 40572111), the Key Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (Grant No. 306021) and the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. G1999075508)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Sun, Y., Liu, L. et al. In situ LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of ultrahigh-pressure eclogites in the Yukahe area, northern Qaidam Basin. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 50 (Suppl 2), 322–330 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-007-6001-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-007-6001-6