Abstract
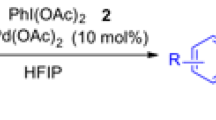
A new kind of intermolecular indole C-H amidation reaction catalyzed by the most frequently used palladium catalyst has been developed. Sulfonyl azide was employed as an innovative nitrogen source and environmentally benign nitrogen was produced as the only byproduct.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hili R, Yudin AK. Making carbon-nitrogen bonds in biological and chemical synthesis. Nat Chem Biol, 2006, 2: 284–287
Ricci A. Amino Group Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2008
Evano G, Blanchard N, Toumi M. Copper-mediated coupling reactions and their applications in natural products and designed biomolecules synthesis. Chem Rev, 2008, 108: 3054–3131
Rao H, Fu H. Copper-catalyzed coupling reactions. Synlett, 2011, 6: 745–769
Tye JW, Weng Z, Johns AM, Incarvito CD, Hartwig JF. Copper complexes of anionic nitrogen ligands in the amidation and imidation of aryl halides. J Am Chem Soc, 2008, 130: 9971–9983
Hartwig JF. Evolution of a fourth generation catalyst for the amination and thioetherification of aryl halides. Acc Chem Res, 2008, 41: 1534–1544
Wolfe JP, Wagam S, Marcoux JF, Buchwald SL. Rational development of practical catalysts for aromatic carbon-nitrogen bond formation. Acc Chem Res, 1998, 31: 805–818
Paul F, Patt J, Hartwig JF. Palladium-catalyzed formation of carbon-nitrogen bonds. Reaction intermediates and catalyst improvements in the hetero cross-coupling of aryl halides and tin amides. J Am Chem Soc, 1994, 116: 5969–5970
Guram AS, Buchwald SL. Palladium-catalyzed aromatic aminations with in situ generated aminostannanes. J Am Chem Soc, 1994, 116: 7901–7902
For recent reviews on direct C-H amination: a) Wencel-Delord J, Droge T, Liu F, Glorius F. Towards mild metal-catalyzed C-H bond activation. Chem Soc Rev, 2011, 40: 4740–4761
Cho SH, Kim JY, Kwak J, Chang S. Recent advances in the transition metal-catalyzed twofold oxidative C-H bond activation strategy for C-C and C-N bond formation. Chem Soc Rev, 2011, 40: 5068–5083
Song G, Wang F, Li X. C-C, C-O and C-N bond formation via rhodium(III)-catalyzed oxidative C-H activation. Chem Soc Rev, 2012, 41: 3651–3678
Stokes BJ, Driver TG. Transition metal-catalyzed formation of N-heterocycles via aryl- or vinyl-C-H bond amination. Eur J Org Chem, 2011: 4071–4088
Lu H, Zhang XP. Catalytic C-H functionalization by metalloporphyrins: recent developments and future directions. Chem Soc Rev, 2011, 40: 1899–1909
Collet F, Lescot C, Dauban P. Catalytic C-H amination: the stereoselectivity issue. Chem Soc Rev, 2011, 40: 1926–1936
Roizen JL, Harvey ME, Du Bios J. Metal-catalyzed nitrogen-atom transfer methods for the oxidation of aliphatic C-H bonds. Acc Chem Res, 2012, 45: 911–922
For recent reviews on C-H activation, see: a) Rouquet G, Chatani N. Catalytic functionalization of C(sp2)-H and C(sp3)-H bonds by using bidentate directing groups. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2013, 52: 11726–11743
Li BJ, Shi ZJ. From C(sp2)-H to C(sp3)-H: systematic studies on transition metal-catalyzed oxidative C-C formation. Chem Soc Rev, 2012, 41: 5588–5598
Kuhl N, Hopkinson MN, Wencel-Delord J, Glorius F. Beyond directing groups: transition-metal-catalyzed C-H activation of simple arenes. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2012, 51: 10236–10254
Ackermann L, Kapdi AR, Potukuchi HK, Kozhushkov SI. Synthesis via C-H bond functionalizations. In: Li CJ, Ed. Handbook of Green Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH, 2012. 259
Neufeldt SR, Sanford MS. Controlling site selectivity in palladium-catalyzed C-H bond functionalization. Acc Chem Res, 2012, 45: 936–946
Colby DA, Tsai AS, Bergman RG, Ellman JA. Rhodium catalyzed chelation-assisted C-H bond functionalization reaction. Acc Chem Res, 2012, 45: 814–825
Engle KM, Mei TS, Wasa M, Yu JQ. Weak coordination as a powerful means for developing broadly useful C-H functionalization reactions. Acc Chem Res, 2012, 45: 788–802
Arockiam PB, Bruneau C, Dixueuf PH. Ruthenium(II)-catalyzed C-H bond activation and functionalization. Chem Rev, 2012, 112: 5879–5918
Ackermann L. Carboxylate-assisted transition-metal-catalyzed C-H bond functionalizations: mechanism and scope. Chem Rev, 2011, 111: 1315–1345
Xu LM, Li BJ, Yang Z, Shi ZJ. Organopalladium(IV) chemistry. Chem Soc Rev, 2010, 39: 712–733
For examples of oxidative amination of activated arenes: a) Wang Q, Schreiber SL. Copper-mediated amidation of heterocyclic and aromatic C-H bonds. Org Lett, 2009, 11: 5178–5180
Monguchi D, Fujiwara T, Furukawa H, Mori A. Direct amination of azoles via catalytic C-H, N-H coupling. Org Lett, 2009, 11: 1607–1610.
For examples of oxidative direct amination of arenes bearing directing group: c) Xiao B, Gong TJ, Xu J, Liu ZJ, Liu L. Palladium-catalyzed intermolecular directed C-H amidation of aromatic ketones. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 1466–1474
John A, Nicholas KM. Copper-catalyzed amidation of 2-phenylpyridine with oxygen as the terminal oxidant. J Org Chem, 2011, 76: 4158–4162
Kawano T, Hirano K, Satoh T, Miura M. A new entry of amination reagents for heteroaromatic C-H bonds: copper-catalyzed direct amination of azoles with chloroamines at room temperature. J Am Chem Soc, 2010, 132: 6900–6901
Sun K, Li Y, Xiong T, Zhang J, Zhang Q. Palladium-catalyzed C-H aminations of anilides with N-fluorobenzenesulfonimide. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 1694–1697
Yoo EJ, Ma S, Mei TS, Chan KSL, Yu JQ. Pd-catalyzed intermolecular C-H amination with alkylamines. J Am Chem Soc, 2011, 133: 7652–7655
Ng KH, Zhou Z, Yu WY. Rhodium(III)-catalyzed intermolecular direct amination of aromatic C-H bonds with N-chlo-roamines. Org Lett, 2012, 14: 272–275
Grohmann C, Wang H, Glorius F. Rh[III]-catalyzed direct C-H amination using N-chloroamines at room temperature. Org Lett, 2012, 14: 656–659
Kim JY, Park SH, Ryu J, Cho SH, Kim SH, Chang S. Rhodium-catalyzed intermolecular amidation of arenes with sulfonyl azides via chelation-assisted C-H bond activation. J Am Chem Soc, 2012, 134: 9110–9113
For recent transition-metal catalyzed amidation reaction with sulfonyl azide as nitrogen source, see: a) Zheng QZ, Liang YF, Qin C, Jiao N. Ru(II)-catalyzed intermolecular C-H amidation of weakly coordinating ketones. Chem Commun, 2013, 49: 5654–5656
Yu DG, Suri M, Glorius F. Rh(III)/Cu(II)-cocatalyzed synthesis of 1H-indazoles through C-H amidation and N-N bond formation. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135: 8802–8805
Thirunavukkarasu VS, Raghuvanshi K, Ackermann L. Expedient C-H amidations of heteroaryl arenes catalyzed by versatile ruthenium(II) catalysts. Org Lett, 2013, 15: 3286–3289
Kim J, Kim J, Chang S. Ruthenium-catalyzed direct C-H amidation of arenes including weakly coordinating aromatic ketones. Chem Eur J, 2013, 19: 7328–7333
Bhanuchandra M, Yadav MR, Rit RK, Kuram MR, Sahoo AK. Ru(II)-catalyzed intermolecular ortho-C-H amidation of aromatic ketones with sulfonyl azides. Chem Commun, 2013, 49: 5225–5227
Shi J, Zhou B, Yang Y, Li Y. Rhodium-catalyzed regioselective amidation of indoles with sulfonyl azides via C-H bond activation. Org Biomol Chem, 2012, 10: 8953–8955
Yadav MR, Rit RJ, Sahoo AK. Sulfoximine directed intermolecular o-C-H amidation of arenes with sulfonyl azides. Org Lett, 2013, 15: 1638–1641
Lee D, Kim Y, Chang S. Iridium-catalyzed direct arene C-H bond amidation with sulfonyl- and arylazides. J Org Chem, 2013, 78: 11102–11109
For recent transition-metal catalyzed amination reaction with other types of azide as nitrogen source, see: a) Ryu J, Kwak J, Shin K, Lee D, Chang S. Ir(III)-catalyzed mild C-H amidation of arenes and alkenes: an efficient usage of acyl azides as the nitrogen source. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135: 12861–12868
Lian Y, Hummel JR, Bergman RG, Ellman JA. Facile synthesis of unsymmetrical acridines and phenazines by a Rh(III)-catalyzed amination/cyclization/aromatization cascade. J Am Chem Soc, 2013, 135: 12548–12551
Ryu J, Shin K, Park SH, Kim JY, Chang S. Rhodium-catalyzed direct C-H amination of benzamides with aryl azides: a synthetic route to diarylamines. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2012, 51: 9904–9908
Shin K, Baek Y, Chang S. Direct C-H amination of arenes with alkyl azides under rhodium catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed, 2013, 52: 8031–8036
Tang C, Yuan Y, Cui Y, Jiao N. Rh-catalyzed diarylamine synthesis by intermolecular C-H amination of heteroarylarenes. Eur J Org Chem, 2013, 2013: 7480–7483
Sundberg RJ. Indoles. San Diego: Academic Press, 1996
Katrizky AR, Ress CW. Comprehensive Heterocyclic Chemistry. 2nd Ed. Pergamon, 1996. 119
For some recent reviews: see a) Humphrey GR, Kuethe JT. Practical methodologies for the synthesis of indoles. Chem Rev, 2006, 106: 2875–2911
Vicente R. Recent advances in indole syntheses: new routes for a classic target. Org Biomol Chem, 2011, 9: 6469–6480
Cacchi S, Fabrizi G. Synthesis and functionalization of indoles through palladium-catalyzed reactions. Chem Rev, 2011, 111: 215–283
Oda Y, Matsuyama N, Hirano K, Satoh T, Miura M. Dehydrogenative synthesis of C3-azolylindoles via copper-promoted annulative direct coupling of o-alkynylanilines. Synthesis, 2012: 1515–1520
Peng J, Zhao J, Hu Z, Liang D, Huang J, Zhu Q. Palladium-catalyzed C(sp2)-H cyanation using tertiary amine derived isocyanide as a cyano source. Org Lett, 2012, 14: 4966–4969
Peng J, Liu L, Hu Z, Huang J, Zhu Q. Direct carboxamidation of indoles by palladium-catalyzed C-H activation and isocyanide insertion. Chem Commun, 2012, 48: 3772–3774
Bahadur GA, Bailey AS, Scott PW, Vandrevala MH. The reactions of four derivatives of pyrrolo[1,2-a]indole with arene-sulphonyl azides. J Chem Soc, Perkin Trans 1, 1980: 2870–2877
Harmon RE, Wellman G, Gupta SK. Reaction of arylsulfonyl azides with N-methylindole. J Org Chem, 1973, 38: 11–16. Two reports involving the reaction of indole with sulfonyl azides to give 3-amidated indole have been published. However, there are several pivotal differences between our procedure and the published reports: i) Palladium catalyst and PPh3 are prerequisite for our procedure; however, catalyst was not nessesary in the published reports; ii) N-H free indoles were suitable substrates for our procedure; but only N-H alkyl substituted indoles were applied in the published reports; iii) C3-position amidated indoles generated directly in our procedure; yet C3-position amidated indoles generated through indole C2 amidation followed by C2 C3 transformation in flash column chromatography in Ref. i) Palladium catalyst and PPh3 are prerequisite for our procedure; however, catalyst was not nessesary in the published reports; ii) N-H free indoles were suitable substrates for our procedure; but only N-H alkyl substituted indoles were applied in the published reports; iii) C3-position amidated indoles generated directly in our procedure; yet C3-position amidated indoles generated through indole C2 amidation followed by C2 C3 transformation in flash column chromatography in Ref. [14b]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Z., Luo, S. & Zhu, Q. Palladium-catalyzed intermolecular C-H amidation of indoles with sulfonyl azides. Sci. China Chem. 58, 1349–1353 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5369-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-015-5369-y