Abstract
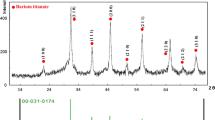
Porous tetragonal BaTiO3 ceramic was successfully prepared by a combination of hydrothermal and low-temperature-sintering method. The hollow TiO2@BaCO3 as the sintering precursor was synthesized via a simple hydrothermal method, and then porous BaTiO3 was generated by calcining the hollow TiO2@BaCO3 precursor at 900 °C without additive. The hollow TiO2@BaCO3 structure plays two important roles in the preparing of the porous BaTiO3 ceramic. First, the TiO2@BaCO3 hollow structure provides high surface areas and increases the contact points between BaCO3 and TiO2, which can reduce the sintering temperature of the BaTiO3 ceramic. Second, the cavity of the ordered arranged TiO2@BaCO3 hollow sphere shows important influence on the porous structure, and the pore size of the as-prepared porous BaTiO3 ceramic can be tuned from several nanometers to hundreds nanomters by changing the sintering temperature. The formation mechanism of the porous BaTiO3 ceramic was proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Setter N, Waser R. Electroceramic materials. Acta Mater, 2000, 48: 151–178
Hennings D, Klee M, Waser R. Advanced dielectrics: Bulk ceramics and thin films. Adv Mater, 1991, 3: 334–340
Haertling GH. Ferroelectric ceramics: History and technology. J Am Ceram Soc, 1999, 82: 797–818
Fuentes S, Zárate RA, Chávez E, Muñoz P, Ayala M, Espinoza-González R, Leyton P. Synthesis and characterization of BaTiO3 nanoparticles in oxygen atmosphere. J Alloys Compd, 2010, 505: 568–572
Xu J, Zhai J, Yao X. Structure and dielectric nonlinear characteristics of BaTiO3 thin films prepared by low temperature process. J Alloys Compd, 2009, 467: 567–571
Rae A, Chu M, Ganine V. Physical and electromechanical properties of barium zirconium titanate synthesized at low-sintering-temperature. J Am Ceram Soc, 1999, 100: 1–12
Reynolds TG III. Application space influences electronic ceramic materials. J Am Ceram Soc, 2001, 80: 29–33
Yao LR, Wang D, Peng W, Hu WW, Yuan HM, Feng SH. Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of rare-earth ruthenate pyrochlore compounds R2Ru2O7 (R = Pr3+, Sm3+-Ho3+). Sci China Chem, 2011, 54 (6): 941–946
Li GS, Li LP, Zheng J. Understanding the defect chemistry of oxide nanoparticles for creating new functionalities: A Critical review. Sci China Chem, 2011, 54 (6): 876–886
Chang CY, Huang CY, Wu YC, Su CY, Huang CL. Synthesis of submicron BaTiO3 particles by modified solid-state reaction method. J Alloys Compd, 2010, 495: 108–112
Hamid NZ, Carsten G, Werner O, Torsten R. Low temperature sintering of barium titanate based ceramics with high dielectric constant for LTCC applications. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2011, 31: 589–596
Dong WJ, Zhao HX, Li CR, Mei J, Chen BY, Tang WH, Shi Z, Feng SH. Hetero-nanostructure of silver nanoparticles on MOx (M = Mo, Ti and Si) and their applications. Sci China Chem, 2011, 54 (6): 865–875
Sebastianl MT, Jantunen H. Low loss dielectric materials for LTCC applications: A review. Int Mater Rev, 2008, 53(2): 57–90
Sharma PK, Varadan VV, Varadan VK. Porous behavior and dielectric properties of barium strontium titanate synthesized by sol-gel method in the presence of triethanolamine. Chem Mater, 2000, 12: 2590–2596
Hou RZ, Ferreira P, Vilarinho PM. Nanoporous BaTiO3 crystallites. Chem Mater, 2009, 21: 3536–3541
Hou RZ, Ferreira P, Vilarinho PM. A facile route for synthesis of mesoporous barium titanate crystallites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater, 2008, 110: 392–396
Bowen CR, Perry A, Lewis ACF, Kara H. Processing and properties of porous piezoelectric materials with high hydrostatic figures of merit. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2004, 24: 541–545
Buscaglia MT, Buscaglia V, Alessio R. Coating of BaCO3 crystals with TiO2: Versatile approach to the synthesis of BaTiO3 tetragonal nanoparticles. Chem Mater, 2007, 19: 711–718
Buscaglia MT, Viviani M, Zhao Z, Buscaglia V, Nanni P. Synthesis of BaTiO3 core-shell particles and fabrication of dielectric ceramics with local graded structure. Chem Mater, 2006, 18: 4002–4010
Buscaglia MT, Buscaglia V, Viviani M, Dondero G, Röhrig S, Rudiger A, Nanni P. Ferroelectric hollow particles obtained by solid-state reaction. Nanotechnology, 2008, 19: 225602–225609
Ruzimuradov O, Hasegawa G, Kanamori K, Nakanishi K. Preparation of hierarchically porous nanocrystallinne CaTiO3, SrTiO3 and BaTiO3 perovskite monoliths. J Am Ceram Soc, 2011, 10: 3335–3339
Zhong HR, Ferreira P, Vilarinho PM. Fabrication of BaTiO3-carbon nano-composite and porous BaTiO3. Cryst Growth Des, 2012, ASAP
Werner S, Arthur F, Emst B. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci, 1968, 26: 62–69
Lee DW, Ihm SK, Lee KH. Mesostructure control using a titania-coated silica nanosphere framework with extremely high thermal stability. Chem Mater, 2005, 17: 4461–4467
Tian XL, Li J, Chen K, Han J, Pan SL, Wang YJ, Fan XY, Li F, Zhou ZX. Nearly monodisperse ferroelectric BaTiO3 hollow nanoparticles: Size-related solid evacuation in ostwald-ripening-induced hollowing process. Cryst Growth Des, 2010, 10: 3990–3995
Dong WJ, Li BJ, Li Y, Wang XB, An LN, Li CR, Chen BY, Wang G, Shi Z. A general approach to well-defined perovskite MTiO3 (M = Ba, Sr, Ca and Mg) nanostructures. J Phys Chem C, 2011, 115: 3918–3925
Beauger A, Mutin JC, Niepce JC. Synthesis reaction of metatitanate BaTiO3. J Mater Sci, 1983, 18: 3041–3046
Graff A, Senz S, Voltzke D, Abicht HP, Hesse D. Microstructure evolution during BaTiO3 formation by solid-state reactions on rutile single crystal surfaces. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2005, 25: 2201–2206
Li CC, Jean JH. Dissolution and dispersion behavior of barium carbonate in aqueous suspensions. J Am Ceram Soc, 2002, 85: 2977–2983
Bae HS, Lee MK, Kim WW, Rhee CK. Dispersion properties of TiO2 nano-powder synthesized by homogeneous precipitation process at low temperatures. Colloids Surf A, 2003, 220: 169–177
Shi Y, Wu Y, Li G. Surface and rheology characterization of NH4PAA-stabilized nanosized TiO2 suspensions. J Dispersion Sci Technol, 2003, 24: 739–743
Ando C, Yanagawa R, Chazono H, Kishi H, Senna M. Nuclei growth optimization for fine-grained by precision controlled mechanical pretreatment of starting powder mixture. J Mater Res, 2004, 19: 3592–3599
Niepce JC, Thomas G. About the mechanism of the solid way synthesis of barium metatitanate, industrial consequences. Solid State Ionics, 1990, 43: 69–76
Hsiang HI, Chang YL, Fang JS, Yen FS. Polythyleneimine surfactant effect on the formation of nano-sized BaTiO3 powder via a solid state reaction. J Alloys Compd, 2011, 509: 7632–7638
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liu, H., Liu, F. et al. A simple approach to porous low-temperature-sintering BaTiO3 . Sci. China Chem. 55, 1765–1769 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4554-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4554-5