Abstract
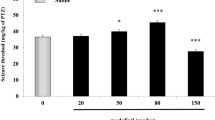
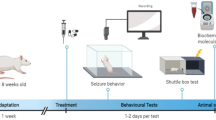
Oleuropein, a well-known olive polyphenol, has been shown to mediate neuroprotection in Alzheimer’s disease and cerebral ischemia. We investigated the effects of oleuropein on pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced seizures in male NMRI mice, with diazepam as the standard drug. We also examined the possible involvement of opioidergic/nitrergic pathways in the probable effects of oleuropein. Intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of different doses of oleuropein (10, 20 and 30 mg/kg) significantly increased the seizure threshold 60 min prior to induction of seizure, in a dose-dependent manner. Administration of naltrexone (10 mg/kg, i.p.), an opioid receptor antagonist, completely reversed the anticonvulsant effects of oleuropein (10 mg/kg). On the other hand, the anticonvulsant effect of oleuropein (10 mg/kg) was blocked by a non-effective dose of nonspecific inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), L-NAME (1 and 10 mg/kg, i.p) and a selective inhibitor of neuronal NOS, 7-nitroindazole (30 mg/kg, i.p.). However, the nitric oxide precursor, l-arginine (30 and 60 mg/kg, i.p.) potentiated the anticonvulsant activity of oleuropein (10 mg/kg). A selective inducible NOS inhibitor, aminoguanidine (100 mg/kg, i.p.) did not change the anticonvulsant activity of oleuropein. It seems that the opioidergic system and constitutive neuronal NOS may be involved in the anticonvulsant properties of oleuropein.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
González-Correa JA, Muñoz-Marín J, Arrebola MM, Guerrero A, Narbona F, López-Villodres JA, De La Cruz JP (2007) Dietary virgin olive oil reduces oxidative stress and cellular damage in rat brain slices subjected to hypoxia–reoxygenation. Lipids 42(10):921–929
González-Correa JA, Navas MD, Lopez-Villodres JA, Trujillo M, Espartero JL, De La Cruz JP (2008) Neuroprotective effect of hydroxytyrosol and hydroxytyrosol acetate in rat brain slices subjected to hypoxia–reoxygenation. Neurosci Lett 446(2):143–146
Kuem N, Song SJ, Yu R, Yun JW, Park T (2014) Oleuropein attenuates visceral adiposity in high-fat diet-induced obese mice through the modulation of WNT10b- and galanin-mediated signalings. Mol Nutr Food Res 58(11):2166–2176
Dekanski D, Selaković V, Piperski V, Radulović Ž, Korenić A, Radenović L (2011) Protective effect of olive leaf extract on hippocampal injury induced by transient global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in Mongolian gerbils. Phytomedicine 18(13):1137–1143
Bu Y, Rho S, Kim J, Kim MY, Lee DH, Kim SY, Choi H, Kim H (2007) Neuroprotective effect of tyrosol on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 414(3):218–221
Mohagheghi F, Bigdeli MR, Rasoulian B, Zeinanloo AA, Khoshbaten A (2010) Dietary virgin olive oil reduces blood brain barrier permeability, brain edema, and brain injury in rats subjected to ischemia-reperfusion. Sci World J 10:1180–1191
De La Cruz JP, Del Río S, Arrebola MM, López-Villodres JA, Jebrouni N, González-Correa JA (2010) Effect of virgin olive oil plus acetylsalicylic acid on brain slices damage after hypoxia-reoxygenation in rats with type 1-like diabetes mellitus. Neurosci Lett 471(2):89–93
Pitozzi V, Jacomelli M, Zaid M, Luceri C, Bigagli E, Lodovici M, Ghelardini C, Vivoli E, Norcini M, Gianfriddo M, Esposto S (2010) Effects of dietary extra-virgin olive oil on behaviour and brain biochemical parameters in ageing rats. Br J Nutr 103(11):1674–1683
Zare L, Esmaeili-Mahani S, Abbasnejad M, Rasoulian B, Sheibani V, Sahraei H, Kaeidi A (2012) Oleuropein, chief constituent of olive leaf extract, prevents the development of morphine antinociceptive tolerance through inhibition of morphine-induced L-type calcium channel overexpression. Phytother Res 26(11):1731–1737
Esmaeili Mahani S, Zare L (2013) Olive (Olea europaea L.) leaf extract and its main component (oleuropein) mitigate the development of morphine physical dependence in rats. Physiol Pharmacol 16(4):360–370
Lauretti GR, Ahmad I, Pleuvry BJ (1994) The activity of opioid analgesics in seizure models utilizing N-methyl-dl-aspartic acid, kainic acid, bicuculline and pentylenetetrazole. Neuropharmacology 33(2):155–160
Foote F, Gale K (1984) Proconvulsant effect of morphine on seizures induced by pentylenetetrazol in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 105(1):179–184
Homayoun H, Khavandgar S, Namiranian K, Gaskari SA, Dehpour AR (2002) The role of nitric oxide in anticonvulsant and proconvulsant effects of morphine in mice. Epilepsy Res 48(1):33–41
Khavandgar S, Homayoun H, Dehpour AR (2003) Mediation of nitric oxide in inhibitory effect of morphine against electroshock-induced convulsions in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74(4):795–801
de la Puerta R, Domínguez ME, RuÍz-GutÍerrez V, Flavill JA, Hoult JR (2001) Effects of virgin olive oil phenolics on scavenging of reactive nitrogen species and upon nitrergic neurotransmission. Life Sci 69(10):1213–1222
Visioli F, Galli C (1994) Oleuropein protects low density lipoprotein from oxidation. Life Sci 55(24):1965–1971
Visioli F, Bellosta S, Galli C (1998) Oleuropein, the bitter principle of olives, enhances nitric oxide production by mouse macrophages. Life Sci 62(6):541–546
Visioli F, Poli A, Gall C (2002) Antioxidant and other biological activities of phenols from olives and olive oil. Med Res Rev 22(1):65–75
Honar H, Riazi K, Homayoun H, Demehri S, Dehghani M, Vafaie K, Ebrahimkhani MR, Rashidi N, Gaskari SA, Dehpour AR (2004) Lithium inhibits the modulatory effects of morphine on susceptibility to pentylenetetrazole-induced clonic seizure in mice: involvement of a nitric oxide pathway. Brain Res 1029(1):48–55
Majewska MD, Bell JA, London ED (1990) Regulation of the NMDA receptor by redox phenomena: inhibitory role of ascorbate. Brain Res 537(1):328–332
Park S, Choi Y, Um SJ, Yoon SK, Park T (2011) Oleuropein attenuates hepatic steatosis induced by high-fat diet in mice. J Hepatol 54(5):984–993
Shafaroodi H, Baradaran N, Moezi L, Dehpour S, Kabiri T, Dehpour AR (2011) Morphine sensitization in the pentylenetetrazole-induced clonic seizure threshold in mice: role of nitric oxide and μ receptors. Epilepsy Behav 20(4):602–606
Rahimi N, Sadeghzadeh M, Javadi-Paydar M, Heidary MR, Jazaeri F, Dehpour AR (2014) Effects of D-penicillamine on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in mice: involvement of nitric oxide/NMDA pathways. Epilepsy Behav 39:42–47
Tsikas D (2007) Analysis of nitrite and nitrate in biological fluids by assays based on the Griess reaction: appraisal of the Griess reaction in the l-arginine/nitric oxide area of research. J Chromatogr 851(1):51–70
Del Vecchio RA, Gold LH, Novick SJ, Wong G, Hyde LA (2004) Increased seizure threshold and severity in young transgenic CRND8 mice. Neurosci Lett 367(2):164–167
Luccarini I, Grossi C, Rigacci S, Coppi E, Pugliese AM, Pantano D, Casamenti F (2015) Oleuropein aglycone protects against pyroglutamylated-3 amyloid-β toxicity: biochemical, epigenetic and functional correlates. Neurobiol Aging 36(2):648–663
Mohagheghi F, Bigdeli MR, Rasoulian B, Hashemi P, Pour MR (2011) The neuroprotective effect of olive leaf extract is related to improved blood–brain barrier permeability and brain edema in rat with experimental focal cerebral ischemia. Phytomedicine 18(2):170–175
Rauwald HW, Brehm O, Odenthal KP (1994) Screening of nine vasoactive medicinal plants for their possible calcium antagonistic activity. Strategy of selection and isolation for the active principles of Olea europaea and Peucedanum ostruthium. Phytother Res 8(3):135–140
Wang L, Geng C, Jiang L, Gong D, Liu D, Yoshimura H, Zhong L (2008) The anti-atherosclerotic effect of olive leaf extract is related to suppressed inflammatory response in rabbits with experimental atherosclerosis. Euro J Nutr 47(5):235–243
Cullinen K (2006) Olive oil in the treatment of hypercholesterolemia. Med Health RI 89(3):113
Owen RW, Giacosa A, Hull WE, Haubner R, Würtele G, Spiegelhalder B, Bartsch H (2000) Olive-oil consumption and health: the possible role of antioxidants. Lancet Oncol 1(2):107–112
Ueda S, Tokuda H, Iwashima A, Nishino H (1994) Chemoprevention of skin and lung cancer by Gardenia iridoid. In: Proceedings International Congress on Natural Products Research
Nekooeian AA, Khalili A, Khosravi MB (2014) Effects of oleuropein in rats with simultaneous type 2 diabetes and renal hypertension: a study of antihypertensive mechanisms. J Asian Nat Prod Res 16(9):953–962
Sardo P, D’Agostino S, Rizzo V, Carletti F, Lonobile G, Ferraro G (2009) In the rat maximal dentate activation model of partial complex epilepsy, the anticonvulsant activity of levetiracetam is modulated by nitric oxide-active drugs. J Neural Transm 116:831–839
Javadian N, Rahimi N, Javadi-Paydar M, Doustimotlagh A, Dehpour AR (2016) The modulatory effect of nitric oxide in pro- and anti-convulsive effects of vasopressin in PTZ-induced seizures threshold in mice. Epilepsy Res 126:134–140
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahimi, N., Delfan, B., Motamed-Gorji, N. et al. Effects of oleuropein on pentylenetetrazol-induced seizures in mice: involvement of opioidergic and nitrergic systems. J Nat Med 71, 389–396 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1071-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11418-017-1071-z