Abstract
Purpose
The concerns of the public on safe handling of nuclear energy power facilities have increased due to the recent nuclear plant accidents in Japan and others. Cesium, cobalt, and strontium are a few of the major radionuclides released from nuclear power plant accidents. The objectives of this study are to investigate binding, distribution, fractionation, and transformation of cesium (Cs), cobalt (Co), and strontium (Sr) in a US coastal soil under saturated paste (SP) and field capacity (FC) moisture regimes.
Materials and methods
There are four major nuclear power plants in the coast region around the northern Gulf of Mexico where coastal soil often undergoes soil moisture change. A coastal soil was taken from the middle region of these major nuclear power plants and spiked with different concentrations of cesium, cobalt, and strontium salts. The sequential selective dissolution technique was used to investigate the transformation and fractionations of these metals in the coastal soils affected by moisture regime, a key factor in the coastal environment.
Results and discussion
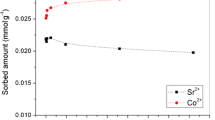
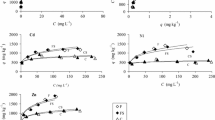
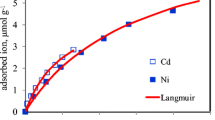
The adsorption kinetics showed that both Co and Sr reached the adsorption plateau even after 5 h of adsorption, indicating a fast initial adsorption process in the coastal soil. Cesium, cobalt, and strontium were dominantly presented in the soluble and exchangeable form (EXC) (Cs > Co and Sr), which linearly increased with the addition levels, possessing the high bioavailability, mobility, and ecotoxicity. Saturated regime significantly reduced the soluble and exchangeable form compared to field capacity moisture regime.
Conclusions
The current study provides the fundamental understanding for designing the cost-effective remediation technology to remediate these metals in coastal soil by targeting on the soluble and exchangeable forms and better prepare the USA for future potentially nuclear power plant accidents.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agapkina GL, Tikhomirov FA, Shcheglov AL, Kracke W, Bunz LK (1995) Association of Chernobyl-derived 239+240Pu, 241Am, 90Sr, and 137Cs with organic matter in the soil solution. J Environ Radioact 29:57–269
Amano H, Matsunaga T, Nagao S, Hanzawa Y, Watanabe M, Ueno T, Onuma Y (1999) The transfer capability of long-lived Chernobyl radionuclides from surface soil to river water in dissolved forms. Organic Geochem 30(6):437–442
Arapis G, Petrayev E, Shagalova E, Zhukova O, Sokolik G, Ivanona T (1997) Effective migration velocity of 137Cs and 90 Sr as a function of the type of soils in Belarus. J Environ Radioact 34:171–185
Beak DG, Kirby JK, Hettiarachchi GM, Wendling LA, McLaughlin MJ, Khatiwada R (2011) Cobalt distribution and speciation: effect of aging, intermittent submergence, in situ rice roots. J Environ Qual 40(3):679–695
Bohn HL, McNeal L, O’Connor GA (1979) Soil chemistry. Wiley, New York
Bunzl K, Kracke W, Schimmack W, Zelles L (1998) Forms of fallout 137Cs and 239 + 240Pu in successive horizons of a forest soil. J Environ Radioact 39(1):55–68
Casacuberta N, Masque P, Garcia-Orellana J, Garcia-Tenorio R, Buesseler KO (2013) 90Sr and 89Sr in seawater off Japan as a consequence of the Fukushima Dai-ichi nuclear accident. Biogeosciences 10:3649–3659
Gommers A, Gafvert T, Smolders E, Merckx R, Vandenhove H (2005) Radio cesium soil-to-wood transfer in commercial willow short rotation coppice on contaminated farm land. J Environ Radioact 78:267–287
Govindaraju K (1994) Compilation of working values and description for 383 geostandards. Geostand Newslett 18:1–158
Grin N, Stammose D, Guillou P, Genet M (1999) Mobility of 137Cs and 90Sr related to speciation studies in contaminated soils of the Chernobyl area. Proc. 5th Int Conf Biogeochem Trace Elements, Vienna
Grybos M, Davranche M, Gruau G, Petitjea P (2007) Is trace metal release in wetland soils controlled by organic matter mobility or Fe-oxyhydroxides reduction? Colloid Interface Sci 314(2):490–501
Han FX, Banin A, Kingery WL, Li ZP (2002) Pathways and kinetics of transformation of cobalt among solid-phase components in arid-zone soils. J Environ Sci Health, Part A 137:175–194
Han FX, Banin A (2000) Long-term transformations of Cd, Co, Cu, Ni, Zn, V, Mn and Fe in the native arid-zone soils under saturated condition. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 31:943–957
Han FX, Banin A (1996) Solid-phase manganese fractionation changes in saturated arid-zone soils: pathways and kinetics. Soil Sci Soc Am J 60:1072–1080
Han FX, Banin A (2001) The fractional loading isotherm of heavy metals in an arid-zone soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 32:2691–2708
Han FX, Kingery WL, Hargreaves JE, Walker TW (2007) Effects of land uses on solid-phase distribution of micronutrients in selected vertisols of the Mississippi River Delta. Geoderma 142:96–103
Han FX, Su Y, Monts DL, Sridhar BBM (2004) Distribution, transformation and bioavailability of trivalent and hexavalent chromium in contaminated soil. Plant Soil 265:243–252
Han FX, Su Y, Monts DL, Waggoner CA, Plodinec MJ (2006) Binding, distribution, and plant uptake of mercury in a soil from Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. Sci Total Environ 368:753–768
Han FX (2007) Biogeochemistry of trace elements in arid environments. Springer, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Han FX, Banin A, Triplett GB (2001) Redistribution of heavy metals in arid-zone soils under a wetting-drying soil moisture regime. Soil Sci 166(1):18–28
Han FX, Banin A (1997) Long-term transformations and redistribution of potentially toxic heavy metals in arid-zone soils. I: under saturated conditions. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 95:399–423
Han FX, Banin A (1999) Long-term transformations and redistribution of potentially toxic heavy metals in arid-zone soils. II: under the field capacity regime. Water, Air, Soil Pollut 114:221–250
Hinton TG, Kaplan DI, Knox AS, Coughlin D, Rice R, Watson SL (2006) Use of illite clay for in situ remediation of 137Cs-contaminated water bodies: field demonstration of reduced biological uptake. Environ Sci Technol 40:4500–4505
Kabata-Pendias HA, Mukherjee AB (2007) Trace elements from soil to human. Springer
Kagan LM, Kadatsky VB (1996) Depth migration of Chernobyl originated 137Cs and 90Sr in soils of Belarus. J Environ Radioact 33:27–39
Kaplan DI, Gergely V, Dernovics M, Fodor P (2005) Cesium-137 partitioning to wetland sediments and uptake by plants. J Radioanal Nuclear Chem 264:393–399
Kashparov V, Colle C, Zvarich S, Yoschenko V, Levchuk S, Lundin S (2005) Soil-to-plant halogens transfer studies 1. Root uptake of radioiodine by plants J Environ Radioact 79:187–204
Kerstin AB, Efurd DW, Finnegan DL, Rokop DJ, Smith DK, Thompson JL (1999) Migration of plutonium in groundwater at the Nevada Test Site. Nature 397:56–59
Klute A (1986) Methods of soil analysis, Part 1, Physical and mineralogical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI
Korobova E, Ermakov A, Linnik V (1998) 137Cs and 90Sr mobility in soils and transfer in soil–plant systems in the Novozybkov district affected by the Chernobyl accident. Appl Geochem 13:803–814
Mason B (1979) Chapter B. Cosmochemistry. Part I. Meteorites. In: Fleischer M (ed) Data of geochemistry, Sixth Edition, Geological survey professional papers 440-B-1. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington
Mico C, Li HF, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (2008) Use of Co speciation and soil properties to explain variation in Co toxicity to root growth of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) in different soils. Environ Pollut 156:883–890
Mondini C, Cesco S, Bini C (1995) Pedogenic evolution and 137Cs contents in soils of eastern Alps (Friuli-Venezia-Giulia, Italy). Mineralogica Petrographica Acta 38:129–143
Nakao A, Funakawa S, Kosaki T (2003) Kinetics of Cs adsorption on soils with different mineralogical composition. Proceeding of International Symposium Radioecology and Environmental Dosimetry, pp 191–195
Pavlotskaya FI, Goriachenkova TA, Blokhina MI (1976) Behavior of Sr-90, in the system: ammonium humate-stable strontium-iron (III). Pochvovedenie 11:33
Reimann C, de Caritat P (1998) Chemical elements in the environment. Springer, Berlin
Seliman AF, Borai EH, Lasheen YF, Abo-Aly MM, DeVol TA, Powell BA (2010) Mobility of radionuclides in soil/groundwater system: comparing the influence of EDTA and four of its degradation products. Environ Pollut 158:3077–3084
Shuman LM (1982) Separating soil iron and manganese-oxide fractions for micronutrient analysis. Soil Sci Soc Am J 46:1099–1102
Sparks DL (1996) Methods of soil analysis, Part 3. Chemical methods. Soil Science Society of America, Madison, WI
Su Y, Sridhar BBM, Han FX, Diehl SV, Monts DL (2007) Effects of bioaccumulation of Cs and Sr natural isotopes on foliar structure and plant spectral reflectance of Indian mustard (Brassica Juncea). Water, Air, Soil Pollut 180:65–74
Tani Y, Miyata N, Ohashi M, Iwahori K, Soma M, Seyma H (2003) Interaction of Co(II), Zn(II) and As(III/V) with manganese oxides formed by Mn-oxidizing fungus. 16 International Symposium of Environmental Biogeochemistry, Oirase, Japan
Tessier A, Cambell PGC, Bisson M (1979) Sequential extraction procedure for the speciation of particulate trace metals. Anal Chem 51:844–851
Tsukada H, Takeda A, Hisamatsu S, Inaba J (2008) Concentration and specific activity of fallout Cs-137 in extracted and particle-size fraction of cultivated soils. J Environ Radioact 99:875–881
Wasserman MA, Bartoly F, Portilho AP, Rochedo ERR, Viana AG, Perez DV, Conti CC (2008) The effect of organic amendment on potential mobility and bioavailability of 137Cs and 60Co in tropical soils. J Environ Radioact 99:554–562
Wasserman MA, Perez DV, Viana AG, Bartoly F, Silva MM, Ferreira AC, Wasserman JC, Bourg A (2005) A sequential extraction protocol proposed to evaluate phytoavailability and potential mobility of radionuclides in soils. XIII International Conference on Heavy metals in the Environment, Brazil, In
Welp G, Brümmer GW (1999) Adsorption and solubility of ten metals in soil samples of different composition. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 162:155–161
Yasunari TJ, Stohl A, Hayano RS, Burkhart JF, Eckhardt S, Yasunarie T (2011) Cesium-137 deposition and contamination of Japanese soils due to the Fukushima nuclear accident. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 8(49):19530–19534
Yoshida N, Kanda J (2012) Tracking the Fukushima radionuclides. Science 336:1115–1116
Yoshida N, Takahashi Y (2012) Land-surface contamination by radionuclides from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident. Elements 8:201–206
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC–HQ-12-G-38-0038).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Jan Schwarzbauer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lawson, L.S., McComb, J.Q., Dong, R. et al. Binding, fractionation, and distribution of Cs, Co, and Sr in a US coastal soil under saturated and field capacity moisture regimes. J Soils Sediments 16, 497–508 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1228-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-015-1228-x