Abstract
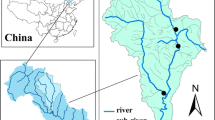
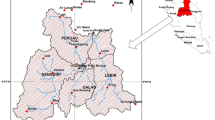
Non-point source pollution is a significant environmental issue in small watersheds in China. To study the effects of rainfall on pollutants transported by runoff, rainfall was monitored in Xueyan town in the Taihu Lake Basin (TLB) for over 12 consecutive months. The concentrations of different forms of nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P), and chemical oxygen demand, were monitored in runoff and river water across different land use types. The results indicated that pollutant loads were highly variable. Most N losses due to runoff were found around industrial areas (printing factories), while residential areas exhibited the lowest nitrogen losses through runoff. Nitrate nitrogen (NO3-N) and ammonia nitrogen (NH4-N) were the dominant forms of soluble N around printing factories and hotels, respectively. The levels of N in river water were stable prior to the generation of runoff from a rainfall event, after which they were positively correlated to rainfall intensity. In addition, three sites with different areas were selected for a case study to analyze trends in pollutant levels during two rainfall events, using the AnnAGNPS model. The modeled results generally agreed with the observed data, which suggests that AnnAGNPS can be used successfully for modeling runoff nutrient loading in this region. The conclusions of this study provide important information on controlling non-point source pollution in TLB.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bian B, Hua GF, Li L, Wu HS (2014) Elimination of agricultural nonpoint source pollution using a pre-dam in the Taihu Lake basin: perspective from a laboratory study. Desalin Water Treat 52(40–42):7450–7459
Chahor Y, Casalí J, Giménez R, Bingner RL, Campo MA, Goñi M (2014) Evaluation of the AnnAGNPS model for predicting runoff and sediment yield in a small Mediterranean agricultural watershed in Navarre (Spain). Agr Water Manage 134:24–37
Fouz PS, Avalos JMM, Vázqueza EV, Gonzáleza AP (2009) Phosphorus Contents and Loads at the Outlet of an Agroforestry Catchment in Northwestern Spain. Commun Soil Sci Plan. 40(1):660–671
Guo HY, Wang XR, Zhu JG (2004) Quantification and index of non-point source pollution in Taihu Lake region with GIS. Environ Geochem Health 26(2–3):147–156
Haregeweyn N, Yohannes F (2003) Testing and evaluation of the agricultural non-point source pollution model (AGNPS) on Augucho catchment, western Hararghe, Ethiopia. Agric Ecosyst Environ 99:201–212
Hatfield JL, McMullen LD, Jone CS (2009) Nitrate-nitrogen patterns in the Raccoon River Basin related to agricultural practices. J Soil Water Conserv 64(3):190–199
Kim SW, Park JS, Kim D, Oh JM (2014) Runoff characteristics of non-point pollutants caused by different land uses and a spatial overlay analysis with spatial distribution of industrial cluster: a case study of the Lake Sihwa watershed. Environ Earth Sci 71(1):483–496
Liu RM, Wang JW, Shi JH, Chen YX, Sun CC, Zhang PP, Shen ZY (2014) Runoff characteristics and nutrient loss mechanism from plain farmland under simulated rainfall conditions. Sci Total Environ 468–469:1069–1077
McKee L, Eyre B, Hossain S (2000) Intra- and inter annual export of nitrogen and phosphorus in the subtropical Richmond River catchment, Australia. Hydrol Proc 14(10):1787–1809
National Environmental Bureau (1991) Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis methods (4th Edition)
Ouyang W, Song K, Wang X, Hao F (2014) Non-point source pollution dynamics under long-term agricultural development and relationship with landscape dynamics. Ecol Indic 45:579–589
Owens LB, Shipitalo MJ, Bonta JV (2008) Water quality response time to pasture management changes in small and large watersheds. J Soil Water Conserv 63:292–299
Qiao J, Yang LZ, Yan TM, Xue F, Zhao D (2012) Nitrogen fertilizer reduction in rice production for two consecutive years in the Taihu Lake area. Agr Ecosyst Environ 146(1):103–112
Sharpley AN, Kleinman PJA, Heathwaite AL (2008) Phosphorus loss from an agricultural watershed as a function of storm size. J Environ Qual 37(2):362–368
Shen Z, Qiu J, Hong Q, Chen L (2014) Simulation of spatial and temporal distributions of non-point source pollution load in the three gorges reservoir region. Sci Total Environ 493:138–146
Shen ZY, Zhong Y, Huang Q, Chen L (2015) Identifying non-point source priority management areas in watersheds with multiple functional zones. Water Res 68:563–671
Taguas EV, Yuan Y, Bingner RL, Gómez JA (2012) Modeling the contribution of ephemeral gully erosion under different soil managements: a case study in an olive orchard microcatchment using the AnnAGNPS model. Catena 98:1–16
Wang X, Zhang W, Huang Y, Li S (2004) Modeling and simulation of point-non-point source effluent trading in Taihu Lake area: perspective of non-point sources control in China. Sci Total Environ 325(1–3):39–50
Xu K, Wang YP, Su H, Yang JX, Li LL, Liu C (2013) Effect of land-use changes on nonpoint source pollution in the Xizhi River watershed, Guangdong, China. Hydrol Process 27(18):2557–2566
Zhang QL, Chen YX, Jilani G, Shamsi IH, Yu QG (2010) Model AVSWAT apropos of simulating non-point source pollution in Taihu lake basin. J Hazard Mater 174(1–3):824–830
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support for this work from the Natural Science Fund Project in Jiangsu Province (BK20130834) and the National Higher Education Institution for General Research and Development Funding (2012B00714).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Highlights
• Runoff production and nutrient losses increased with increasing rainfall intensity.
• Land use changes from industrial and urban to rural had the greatest effects on nutrient loss but smaller on COD.
• AnnAGNPS can be used effectively to model runoff and nutrient loads in the complex TLB region.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Q.D., Sun, J.H., Hua, G.F. et al. Runoff characteristics and non-point source pollution analysis in the Taihu Lake Basin: a case study of the town of Xueyan, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 15029–15036 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4709-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4709-y