Abstract
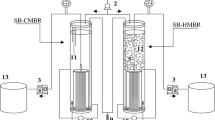
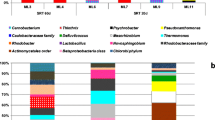
It is known that an increase of COD/N ratio can result in an enhanced removal of nutrients in membrane bioreactors (MBRs); however, impacts of doing so on membrane filtration performance remain unclear. In this work, comparison of membrane filtration performance, microbial community, and microbial products under low temperature was carried out in anoxic/oxic (A/O) MBRs with COD/N ratios of 9.9 and 5.5 g COD/g N in influent. There was no doubt that an improvement of nitrogen removal under high COD/N ratio was observed; however, severer membrane fouling was found compared to the MBR fed with low COD/N ratio wastewater. The increase of COD/N ratio resulted in an elevated production of humic acids in soluble microbial product (SMP) and carbohydrates, proteins, and humic acids in loosely bound extracellular polymeric substance (LB-EPS). Quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) analysis showed that the adsorption capability of SMP and LB-EPS was higher in the MBR with higher COD/N ratio. Four hundred fifty four high-throughput pyrosequencing revealed that the higher COD/N ratio led to the enrichment of Bacteroidetes at phylum level and Azospira, Thauera, Zoogloea, etc. at genus level. Bacteroidetes are considered to potentially release EPS, and Azospira, Thauera, and Zoogloea, etc. have denitrification activity. The change in microbial communities is consistent with MBR performance.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association, America
Cherchi C, Onnis-Hayden A, El-Shawabkeh I, Gu AZ (2009) Implication of using different carbon sources for denitrification in wastewater treatments. Water Environ Res 81:788–799
Chu HQ, Dong BZ, Zhang YL, Zhou XF, Yu ZX (2012) Pollutant removal mechanisms in a bio-diatomite dynamic membrane reactor for micro-polluted surface water purification. Desalination 293:38–45
Contreras AE, Steiner Z, Miao J, Kasher R, Li QL (2011) Studying the role of common membrane surface functionalities on adsorption and cleaning of organic foulant susing QCM-D. Environ Sci Technol 45:6309–6315
Courtens ENP, de Clippeleir H, Vlaeminck SE, Jordaens R, Park H, Chandran K, Boon N (2015) Nitric oxide preferentially inhibits nitrite oxidizing communities with high affinity for nitrite. J Biotechnol 193:120–122
Dannenberger O, Buck M, Grunze M (1999) Self-assembly of n-alkanethiols: a kinetic study by second harmonic generation. J Phys Chem B103:2202–2213
Enders D, Nagao T, Nakayama T, Aono M (2007) In situ surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy for the analysis of the adsorption and desorption process of Au nanoparticles on the SiO2/Si surface. Langmuir 23:6119–6125
Fabio SD, Malamis S, Katsou E, Vecchiato G, Cecchi F, Fatone F (2013) Are centralized MBRs coping with the current transition of large petrochemical areas? A pilot study in Porto-Marghera (Venice). Chem Eng J 214:68–77
Fatone F, Battistoni P, Pavan P, Cecchi F (2006) Application of a membrane bioreactor for the treatment of low loaded domestic wastewater for water re-use. Water Sci Technol 53:111–121
Furman O, Usenko S, Lau BLT (2013) Relative importance of the humic and fulvic fractions of natural organic matter in the aggregation and deposition of silver nanoparticles. Environ Sci Technol 47:1349–1356
Gao DW, Zhang T, Tang CYY, Wu WM, Wong CY, Lee YH, Yeh DH, Criddle CS (2010) Membrane fouling in an anaerobic membrane bioreactor: differences in relative abundance of bacterial species in the membrane foulant layer and in suspension. J Membr Sci 364:331–338
Gutman J, Walker SL, Freger V, Herzberg M (2013) Bacterial attachment and viscoelasticity: physicochemical and motility effects analyzed using quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation (QCM-D). Environ Sci Technol 47:398–404
Han XM, Wang ZW, Zhu CW, Wu ZC (2013) Effect of ultrasonic power density on extracting loosely bound and tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances. Desalination 329:35–40
Heulin T, Barakat M, Christen R, Lesourd M, Sutra L, de Luca G, Achouak W (2003) Ramlibactertataouinensis gen. nov., spnov., and Ramlibacterhenchirensisspnov., cyst-producing bacteria isolated from subdesert soil in Tunisia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:589–594
Hunter WJ (2007) An Azospiraoryzae (synDechlorosomasuillum) strain that reduces selenate and selenite to elemental red selenium. Curr Microbiol 54:376–381
Kavitha S, Selvakumar R, Sathishkumar M, Swaminathan K, Lakshmanaperumalsamy P, Singh A, Jain SK (2009) Nitrate removal using Brevundimonasdiminuta MTCC 8486 from ground water. Water Sci Technol 60:517–524
Kimura K, Yamato N, Yamamura H, Watanabe Y (2005) Membrane fouling in pilot-scale membrane bioreactors (MBRs) treating municipal wastewater. Environ Sci Technol 39:6293–6299
Kojima H, Watanabe T, Iwata T, Fukui M (2014) Identification of major planktonic sulfur oxidizers in stratified freshwater lake. Plos One 9:e93877
Kong YH, Xia Y, Nielsen JL, Nielsen PH (2007) Structure and function of the microbial community in a full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plant. Microbiology 153:4061–4073
Kumar M, Lee PY, Fukusihma T, WhangLM LJG (2012) Effect of supplementary carbon addition in the treatment of low COD/N high-technology industrial wastewater by MBR. Bioresource Technol 113:148–153
Laspidou CS, Rittmann BE (2002) A unified theory for extracellular polymeric substances, soluble microbial products, and active and inert biomass. Water Res 36:2711–2720
Lee NM, Welander T (1996) The effect of different carbon sources on respiratory denitrification in biological wastewater treatment. J Ferment Bioeng 82:277–285
Lim JH, Baek SH, Lee ST (2009) Ferruginibacteralkalilentus gen. nov., sp. nov. and Ferruginibacterlapsinanis sp. nov., novel members of the family ‘Chitinophagaceae’ in the phylum Bacteroidetes, isolated from freshwater sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2394–2399
Luo JF, Lin WT, Guo Y (2011) Functional genes based analysis of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria community in sulfide removing bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 90:769–778
Ma JX, Wang ZW, Yang Y, Mei XJ, Wu ZC (2013a) Correlating microbial community structure and composition with aeration intensity in submerged membrane bioreactors by 454 high-throughput pyrosequencing. Water Res 47:859–869
Ma JX, Wang ZW, Zhu CW, Li SM, Wang QY, Wu ZC (2013b) Analysis of nitrification efficiency and microbial community in a membrane bioreactor fed with low COD/N-ratio wastewater. Plos One 8:e63059
Müller R, Gerth K (2006) Development of simple media which allow investigations into the global regulation of chivosazol biosynthesis with SorangiumcellulosumSo ce56. J Biotechnol 121:192–200
Osaka T, Yoshie S, Tsuneda S, Hirata A, Iwami N, Inamori Y (2006) Identification of acetate- or methanol-assimilating bacteria under nitrate-reducing conditions by stable-isotope probing. Microb Ecol 52:253–266
Park H, Sundar S, Ma YW, Chandran K (2015) Differentiation in the microbial ecology and activity of suspended and attached bacteria in a nitritation-anammox process. Biotechnol Bioeng 112:272–279
Parks DH, Beiko RG (2010) Identifying biologically relevant differences between metagenomic communities. Bioinformatics 26:715–721
Pynaert K, Smets BF, Beheydt D, Verstraete W (2004) Start-up of autotrophic nitrogen removal reactors via sequential biocatalyst addition. Environ Sci Technol 38:1228–1235
Qiu GL, Song YH, Zeng P, Duan L, Xiao SH (2013) Characterization of bacterial communities in hybrid upflow anaerobic sludge blanket (UASB)- membrane bioreactor (MBR) process for berberine antibiotic wastewater treatment. Bioresource Technol 142:52–62
Rahn JR, Hallock RB (1995) Antibody binding to antigen-coated substrates studied with surface plasmonoscillations. Langmuir 11:650–654
Sauerbrey G (1959) Verwendung von schwingquarzen zur wägung dünner schichten und zur mikrowägung. Z Phys 155:206–222 (in German)
Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, Lesniewski RA, Oakley BB, Parks DH, Robinson CJ, Sahl JW, Stres B, Thallinger GG, van Horn DJ, Weber CF (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:7537–7541
Straub KL, Schönhuber WA, Buchholz-Cleven BEE, Schink B (2004) Diversity of ferrous iron-oxidizing, nitrate-reducing bacteria and their involvement in oxygen-independent iron cycling. Geomicrobiology J21:371–378
Sweity A, Ying W, Belfer S, Oron G, Herzberg M (2011a) pH effects on the adherence and fouling propensity of extracellular polymeric substances in a membrane bioreactor. J Membr Sci 378:186–193
Sweity A, Ying W, Ali-Shtayeh MS, Yang F, Bick A, Oron G, Herzberg M (2011b) Relation between EPS adherence, viscoelastic properties, and MBR operation: biofouling study with QCM-D. Water Res 45:6430–6440
Thomsen TR, Kong Y, Nielsen PH (2007) Ecophysiology of abundant denitrifying bacteria in activated sludge. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60:370–382
Velusamy K, Krishnani KK (2013) Heterotrophic nitrifying and oxygen tolerant denitrifying bacteria from green watersystem of coastal aquaculture. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 169:1978–1992
Verhagen FJ, Laanbroek HJ (1991) Competition for ammonium between nitrifying and heterotrophic bacteria in dual energy-limited chemostats. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:3255–3263
Wang ZW, Wu ZC, Tang SJ (2009a) Characterization of dissolved organic matter in a submerged membrane bioreactor by using three-dimensional excitation and emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy. Water Res 43:1533–1540
Wang ZW, Wu ZC, Tang SJ (2009b) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) properties and their effects on membrane fouling in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Water Res 43:2504–2512
Wang ZW, Wu ZC, Tang SJ, Ye SF (2011) Role of EPS in membrane fouling of a submerged anaerobic-anoxic-oxic (A-A-O) membrane bioreactor for municipal wastewater treatment. Desalin Water Treat 34:88–93
Wang QY, Wang ZW, Wu ZC, Ma JX, Jiang ZY (2012a) Insights into membrane fouling of submerged membrane bioreactors by characterizing different fouling layers formed on membrane surfaces. Chem Eng J 179:169–177
Wang XH, Hu M, Xia Y, Wen XH, Ding K (2012b) Pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial diversity in 14 wastewater treatment systems in China. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:7042–7047
Wang Z, Zhang XX, Huang KL, Miao Y, Shi P, Liu B, Long C, Li AM (2013) Metagenomic profiling of antibiotic resistance genes and mobile genetic elements in a tannery wastewater treatment plant. Plos One 8:e76079
Xia Y, Kong YH, Thomsen TR, Nielsen PK (2008) Identification and ecophysiological characterization of epiphytic protein-hydrolyzing Saprospiraceae (“Candidatus Epiflobacter” spp.) in activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2229–2238
Ye L, Shao MF, Zhang T, Tong AHY, Lok S (2011) Analysis of the bacterial community in a laboratory-scale nitrification reactor and a wastewater treatment plant by 454-pyrosequencing. Water Res 45:4390–4398
Ying W, Yang F, Bick A, Oron G, Herzberg M (2010) Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) in a hybrid growth membrane bioreactor (HG-MBR): viscoelastic and adherence characteristics. Environ Sci Technol 44:8636–8643
Zhang B, Sun BS, Jin M, Gong TS, Gao ZH (2008) Extraction and analysis of extracellular polymeric substances in membrane fouling in submerged MBR. Desalination 227:286–294
Zhang T, Shao MF, Ye L (2012) 454 Pyrosequencing reveals bacterial diversity of activated sludge from 14 sewage treatment plants. ISME J 6:1137–1147
Zhu PT, Long GY, Ni JR, Tong MP (2009) Deposition kinetics of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) on silica in monovalent and divalent salts. Environ Sci Technol 43:5699–5704
Acknowledgments
We thank the Shanghai Rising-Star Program (14QA1403800), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51422811), and National Science & Technology Pillar Program (2012BAJ21B05) for financial support of this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Gerald Thouand
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 470 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, X., Wang, Z., Ma, J. et al. Membrane bioreactors fed with different COD/N ratio wastewater: impacts on microbial community, microbial products, and membrane fouling. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 11436–11445 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4376-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4376-z