Abstract
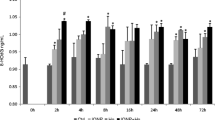
Having multidisciplinary applications, iron oxide nanoparticles can inevitably enter aquatic system and impact inhabitants such as fish. However, the studies in this context have ignored the significance of obvious interaction of iron oxide nanoparticles with other persistent co-contaminants such as mercury (Hg) in the modulation of the toxicity and underlying mechanisms of iron oxide nanoparticles and Hg alone, and concomitant exposures. This study aimed to evaluate lipid peroxidation (LPO) and its control with glutathione (GSH) and associated enzymes (such as glutathione reductase, GR; glutathione peroxidase, GPX; glutathione sulfo-transferase, GST) in European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.) hepatocytes exposed to stressors with following schemes: (i) no silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles functionalized with dithiocarbamate (Fe3O4@SiO2/Si DTC, hereafter called ‘FeNPs’; size range 82 ± 21 to 100 ± 30 nm) or Hg, (ii) FeNPs (2.5 μg L−1) alone, (iii) Hg (50 μg L−1) alone and (iv) FeNPs + Hg concomitant condition during 0 to 72 h. The exhibition of a differential coordination between GSH regeneration (determined as GR activity) and GSH metabolism (determined as the activity of GPX and GST) was perceptible in A. anguilla hepatocytes in order to control FeNPs, Hg and FeNPs + Hg exposure condition-mediated LPO. This study revealed the significance of a fine tuning among GR, GPX and GST in keeping LPO level under control during FeNPs or Hg alone exposure, and a direct role of total GSH (TGSH) in the control of LPO level and impaired GSH metabolism under the concomitant (FeNPs + Hg) exposure. An interpretation of the fish risk to FeNPs in a multi-pollution state should equally consider the potential outcome of the interaction of FeNPs with other contaminants.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahamed M, Alhadlaq HA, Khan MM, Akhtar MJ (2013) Selective killing of cancer cells by iron oxide nanoparticles mediated through reactive oxygen species via p53 pathway. J Nanoparticle Res 15:1225
Ahmad I, Maria V, Pacheco M, Santos M (2009) Juvenile sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax L.) enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidant responses following 17β-estradiol exposure. Ecotoxicology 18:974–982
Anjum NA, Srikanth K, Mohmood I, Sayeed I, Trindade T et al (2014) Brain glutathione redox system significance for the control of silica-coated magnetite nanoparticles with or without mercury co-exposures mediated oxidative stress in European eel (Anguilla anguilla L.). Environ Sci Pollut Res 21:7746–7756
Auffan M, Rose J, Proux O, Masion A, Liu W et al (2012) Is there a Trojan-horse effect during magnetic nanoparticles and metalloid cocontamination of human dermal fibroblasts? Environ Sci Technol 46:10789–10796
Baker MA, Cerniglia GJ, Zaman A (1990) Microtiter plate assay for the measurement of glutathione and glutathione disulfide in large numbers of biological samples. Anal Biochem 190:360–365
Bickley LK, Lange A, Winter MJ, Tyler CR (2009) Evaluation of a carp primary hepatocyte culture system for screening chemicals for oestrogenic activity. Aquat Toxicol 94:195–203
Bird RP, Draper HH (1984) Comparative studies on different methods of malonaldehyde determination. Method Enzymol 105:299–305
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cossu C, Doyotte A, Jacquin MC, Babut M et al (1997) Glutathione reductase, selenium dependent glutathione peroxidase, glutathione levels, and lipid peroxidation in freshwater bivalves, Unio tumidus, as biomarkers of aquatic contamination in field studies. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 38:122–131
Filipak Neto F, Zanata SM, Silva de Assis HC et al (2008) Toxic effects of DDT and methyl mercury on the hepatocytes from Hoplias malabaricus. Toxicol in Vitro 22:1705–1713
García A, Espinosa R, Delgado L, Casals E, González E et al (2011) Acute toxicity of cerium oxide, titanium oxide and iron oxide nanoparticles using standardized tests. Desalination 269:136–141
Girginova PI, Daniel-da-Silva AL, Lopes CB, Figueira P et al (2010) Silica coated magnetite particles for magnetic removal of Hg2+ from water. J Colloid Interface Sci 345:234–240
Grover VA, Hu J, Engates KE, Shipley HJ (2012) Adsorption and desorption of bivalent metals to hematite nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Chem 31:86–92
Hardas SS, Sultana R, Warrier G, Dan M, Florence RL et al (2012) Rat brain pro-oxidant effects of peripherally administered 5 nm ceria 30 days after exposure. Neurotoxicology 33:1147–1155
Kortenkamp A, Backhaus T, Faust M (2009) State of the art on mixture toxicity, Report, April 2011
LeCluyse EL, Alexandre E, Hamilton GA, Viollon-Abadie C et al (2005) Isolation and culture of primary human hepatocytes. Methods Mol Biol 290:207–229
Ma P, Luo Q, Chen J, Gan Y, Du J et al (2012) Intraperitoneal injection of magnetic Fe3O4-nanoparticle induces hepatic and renal tissue injury via oxidative stress in mice. Int J Nanomed 7:4809–4818
Mahmoudi M, Simchi A, Vali H, Imani M, Shokrgozar MA et al (2009) Cytotoxicity and cell cycle effects of bare and poly(vinyl alcohol)-coated iron oxide nanoparticles in mouse fibroblasts. Adv Eng Mater 11:B243–B250
Mahmoudi M, Hofmann H, Rothen-Rutishauser B et al (2011) Assessing the in vitro and in vivo toxicity of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Chem Rev 112:2323–2338
Mieiro C, Ahmad I, Pereira M, Duarte A, Pacheco M (2010) Antioxidant system breakdown in brain of feral golden grey mullet (Liza aurata) as an effect of mercury exposure. Ecotoxicology 19:1034–1045
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Pereira ME, Lillebø AI, Pato P, Válega M et al (2009) Mercury pollution in Ria de Aveiro (Portugal): a review of the system assessment. Environ Monit Assess 155:39–49
Radu M, Munteanu M, Petrache S, Serban AI, Dinu D et al (2010) Depletion of intracellular glutathione and increased lipid peroxidation mediate cytotoxicity of hematite nanoparticles in MRC-5 cells. Acta Biochim Pol 57:355–360
Santos MA, Pacheco M (1996) Anguilla anguilla L. stress biomarkers recovery in clean water and secondary-treated pulp mill effluent. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 35:96–100
Scown TM, Goodhead RM, Johnston BD, Moger J et al (2010) Assessment of cultured fish hepatocytes for studying cellular uptake and (eco)toxicity of nanoparticles. Environ Chem 7:36–49
Singh N, Manshian B, Jenkins GJS, Griffiths SM et al (2009) Nano genotoxicology: the DNA damaging potential of engineered nanomaterials. Biomaterials 30:3891–3914
Søfteland L, Eide I, Olsvik PA (2009) Factorial design applied for multiple endpoint toxicity evaluation in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) hepatocytes. Toxicol in Vitro 23:1455–1464
Srikanth K, Pereira E, Duarte AC, Ahmad I (2013) Glutathione and its dependent enzymes’ modulatory responses to toxic metals and metalloids in fish—a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:2133–2149
Srikanth K, Ahmad I, Rao JV, Trindad T et al (2014) Modulation of glutathione and its dependent enzymes in gill cells of Anguilla anguilla exposed to silica coated iron oxide nanoparticles with or without mercury co-exposure under in vitro condition. Comp Biochem Physiol C 162:7–14
Strober W (1991) Trypan blue exclusion test for cell viability. In: Coligan JE, Kruisbeek AM, Margulies DH et al (eds) Current protocols in immunology. Wiley, New York, pp 3–4
Tavares DS, Daniel-da-Silva AL, Lopes CB, Silva NJO et al (2013) Efficient sorbents based on magnetite coated with siliceous hybrid shells for removal of mercury ions. J Mater Chem A A1:8134–8143
Tavares DS, Lopes CB, Daniel-da-Silva AL, Duarte AC et al (2014) The role of operational parameters on the uptake of mercury by dithiocarbamate functionalized particles. Chem Eng J 254:559–570
Ueda S, Masutani H, Nakamura H, Tanaka T et al (2002) Redox control of cell death. Antioxid Redox Signal 4:405–414
Zhu X, Tian S, Cai Z (2012) Toxicity assessment of iron oxide nanoparticles in zebrafish (Danio rerio) early life stages. PloS One 7:e46286
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) for postdoctoral grants to KS (SFRH/BPD/79490/2011) and NAA (SFRH/BPD/84671/2012), and to the Aveiro University Research Institute/CESAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Henner Hollert
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 57.0 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srikanth, K., Anjum, N.A., Trindade, T. et al. Lipid peroxidation and its control in Anguilla anguilla hepatocytes under silica-coated iron oxide nanoparticles (with or without mercury) exposure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 9617–9625 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4125-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-015-4125-3