Abstract
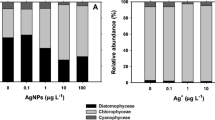
Autotrophic biofilms are complex and fundamental biological compartments of many aquatic ecosystems. Since microbial species differ in their sensitivity to stressors, biofilms have long been proposed for assessing the quality of aquatic ecosystems. Among the many stressors impacting aquatic ecosystems, eutrophication and metal pollution are certainly the most common. Despite that these stressors often occur together, their effects on biofilms have been far much studied separately than interactively. In this study, we evaluated the interactive effects of silver (Ag), a reemerging contaminant, and phosphorus (P), a nutrient often associated with freshwater eutrophication, on the structure and functioning of two types of autotrophic biofilms, one dominated by diatoms and another one dominated by cyanobacteria. We hypothesized that P would alleviate the toxic effects of Ag, either directly, through the contribution of P in metal detoxification processes, or indirectly, through P-mediated shifts in biofilm community compositions and associated divergences in metal tolerance. Results showed that Ag impacted biofilm community structure and functioning but only at unrealistic concentrations (50 μg/L). P availability led to significant shifts in biofilm community composition, these changes being more pronounced in diatom- than those in cyanobacteria-dominated biofilm. In addition, P tended to reduce the impact of Ag but only for the cyanobacteria-dominated biofilm. More generally, our results highlight the preponderant role of the initial community structure and nutrient level on biofilm response to metallic pollutants.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Admiraal W, Blanck MH, Buckert-De Jong M, Guasch H, Ivorra N, Lehmann V, Nystroe BAH (1999) Short term toxicity of zinc to microbenthic algae and bacteria in a metal polluted stream. Water Res 33:1989–1996
AFNOR (1990) Eaux, Méthodes d’essais: recueil de normes françaises. Association Française de Normalisation, Paris
Arce Funck J, Clivot H, Felten V, Rousselle P, Guérold F, Danger M (2013a) Phosphorus availability modulates the toxic effect of silver on aquaticfungi and leaf litter decomposition. Aquat Toxicol 144–145:199–207
Arce Funck J, Danger M, Gismondi E, Cossu-Leguille C, Guérold F, Felten V (2013b) Behavioural and physiological responses of Gammarus fossarum (Crustacea Amphipoda) exposed to silver. Aquat Toxicol 142–143:73–84
Barranguet C, Charantoni E, Plans M, Admiraal W (2000) Short-term response of monospecific and natural algal biofilms to copper exposure. Eur J Phycol 35:397–406
Battin TJ, Kaplan LA, Newbold JD, Hansen CME (2003) Contributions of microbial biofilms to ecosystem processes in stream mesocosms. Nature 426:439–442
Bérard A, Dorigo U, Humbert JF, Leboulanger C, Seguin F (2002) Application of the pollution-induced community tolerance (PICT) method to algal communities: its values as a diagnostic tool for ecotoxicological risk assessment in the aquatic environment. Ann Limnol Int J Limnol 38:247–261
Blanck H, Wänkberg SA, Molander S (1988) Pollution-induced community tolerance - a new ecotoxicological tool. In: Cairs J, Pratt JR (eds) Functional testing of aquatic biota for estimating hazards of chemicals. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, pp 219–230
Boston HL, Hill WR, Stewart AJ (1991) Evaluating direct toxicity and food-chain effects in aquatic systems using natural periphyton communities. In: Gorsuch JW, Lower WR, Wang W (eds) Plants for toxicity assessment, vol 2. American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, pp 126–145
Cardinale M, Brusetti L et al (2004) Comparison of different primer sets for use in automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of complex bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6147–6156
Cattaneo A (1987) Periphyton in lakes of different trophy. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44:296–302
Chao TT, Jenne EA, Heppting LM (1968) Adsorption of traces of silver on sample containers. In: Geological Survey Research, chapter D, pp. 13–15
Clements WH, Kiffney PM (1994) Integrated laboratory and field approach for assessing impacts of heavy metals at the Arkansas River, Colorado. Environ Toxicol Chem 13:397–404
Einhellig FA (2004) Mode of allelochemical action of phenolic compounds. In: Macias FA, Galindo JCG, Molinillo JMG, Cutler HG (eds) Allelopathy - chemistry and mode of action of allelochemicals. CRC Press, London, pp 217–238
Fisher MM, Triplett EW (1999) Automated approach for ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis of microbial diversity and its application to freshwater bacterial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4630–4636
García-Meza JV, Barranguet C, Admiraal W (2005) Biofilm formation by algae as a mechanism for surviving on mine tailings. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:573–581
Garland JL (1996a) Analytical approaches to the characteriztion of samples of microbial communities using patterns of potential C sources utilization. Soil Biol Biochem 28:213–221
Garland JL (1996b) Patterns of potential C source utilization by rhizosphere communities. Soil Biol Biochem 28:223–230
Genter RB, Cherry DS, Smith EP, Cairns J Jr (1987) Algal-periphyton population and community changes from zinc stress in stream mesocosms. Hydrobiologia 153:261–275
Genty B, Briantais JM et al (1989) The relationship between the quantum yield of photosynthetic electron-transport and quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence. Biochim Biophys Acta 990:87–92
Guasch H, Martí E, Sabater S (1995) Nutrient enrichment effects on biofilm metabolism in a Mediterranean stream. Freshwat Biol 33:373–383
Guasch H, Paulsson M, Sabater S (2002) Effect of copper on algal communities from oligotrophic calcareous streams. J Phycol 38:241–248
Guasch H, Admiraal W, Sabater S (2003) Contrasting effects of organic and inorganic toxicants on freshwater periphyton. Aquat Toxicol 64:165–175
Guasch H, Navarro E, Serra A, Sabater S (2004) Phosphate limitation influences the sensitivity to copper in periphytic algae. Freshwat Biol 49:463–473
Hadoux E, Plaire M, et al. (2010) PHYTOBS v2.0: Outil de comptage du phytoplancton et de calcul de biovolumes en laboratoire. Version 2.0. Application JAVA
Herbert HPF, Li-Chong X, Kwong-Yu C (2002) Effects of toxic metals and chemicals on biofilm and biocorrosion. Water Res 36:4709–4716
Hillebrand H, Durselen CD et al (1999) Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. J Phycol 35:403–424
Hogstrand C, Wood CM (1998) Toward a better understanding of the bioavailability, physiology, and toxicity of silver in fish: Implications for water quality criteria. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:547–561
Huber-Pestalozzi G (1938) Das Phytoplankton des Susswassers : Systematik und Biologie. Stuttgart, E. Schweizerbart’sche Verlagsbuchhandlung
Ivorra N, Bremer S, Guasch H, Kraak MHS, Admiraal W (2000) Differences in sensitivity of benthic microalgae to Zn and Cd regarding biofilm development and exposure history. Environ Toxicol Chem 19:1332–1339
Izaguirre G (1992) A copper-tolerant Phormidium species from lake Mathews, California, that produces 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin. Water Sci Technol 25:217–223
Juneau P, El Berdey A, Popovic R (2002) PAM fluorometry in the determination of the sensitivity of Chlorella vulgaris, selenastrum capricornutum, and chlamydomonas reinhardtii to copper. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 42:155–164
Kilham SS, Kreeger DA et al (1998) COMBO: a defined freshwater culture medium for algae and zooplankton. Hydrobiologia 377:147–159
Komárek J, Anagnostidis K (1998) Cyanoprokaryota 1. Teil: Chroococcales. Stuttgart, In Ettl H, Gärtner G, Heynig H, Mollenhauer D (eds), Süsswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 19/1, Gustav Fischer, Jena-Stuttgart-Lübeck-Ulm, 548 pp.
Koukal B, Guéguen C, Pardos M, Dominik J (2003) Influence of humic substances on the toxic effects of cadmium and zinc to the green alga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Chemosphere 53:953–961
Küster A, Altenburger R (2007) Development and validation of a new fluorescence-based bioassay for aquatic macrophyte species. Chemosphere 67:194–201
Leflaive J, Danger M, Lacroix G, Lyautey E, Oumarou C, Ten-Hage L (2008) Nutrient effects on genetic and functional diversity of bacterial communities. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 66:379–390
Liu J, Hurt RH (2010) Ion release kinetics and particle persistence in aqueous nano-silver colloids. Environ Sci Technol 44:2169–2175
López-Flores R, Quintana XD, Salvadó V, Hidalgo M, Sala LL, Moreno-Amich R (2003) Comparison of nutrient and contaminant fluxes in two areas with different hydrological regimes (Emporda’ Wetlands, NE Spain). Water Res 37:3034–3046
Luoma SN (2008) Silver nanotechnologies and the environment: Old problems or New challenges? Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars, Washington DC
Luoma SN, Rainbow PS (2008) Metal contamination in aquatic environments: science and lateral management. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Marambio-Jones C, Hoek EMV (2010) A review of the antibacterial effects of silvernanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environ-ment. J Nanopart Res 12:1531–1551
Marks JC, Lowe RL (1989) The independent and interactive effects of snail grazing and nutrient enrichment on structuring periphyton communities. Hydrobiologia 185:9–17
Massee R, Maessen FJMJ, De Goeij JJM (1981) Losses of silver, arsenic, cadmium, selenium and zinc traces from distilled water and artificial sea-water by sorption on various container surfaces. Anal Chim Acta 127:181–193
McCormick PA, Stevenson RJ (1998) Periphyton as a tool for ecological assessment and management in the Florida Everglades. J Phycol 4:726–733
Moffett JW, Brand LE (1996) Production of strong, extracellular Cu chelators by marine cyanobacteria in response to Cu stress. Limnol Oceanogr 41:388–395
Murdock JN, Wetzel DL (2012) Macromolecular response of individual algal cells to nutrient and atrazine mixtures within biofilms. Micro Ecol 63:761–772
Murdock JN, Shields FD Jr, Lizotte RE Jr (2013) Periphyton responses to nutrient and atrazine mixtures introduced through agricultural runoff. Ecotoxicology 22:215–230
Navarro E, Guasch H, Sabater S (2002) Use of microbenthic algal communities on ecotoxicological tests for the assessment of water quality. J Appl Phycol 14:41–48
Ndungu K (2011) Dissolved silver in the Baltic Sea. Environ Res 111:45–49
Nichols JW, Brown S, Wood CM, Walsh PJ, Playle RC (2006) Influence of salinity and organic matter on silver accumulation in Gulf toadfish (Opsanus beta). Aquat Toxicol 78:253–261
Pringle CM (1987) Effects of water and substratum nutrient supplies on lotic periphyton growth: an integrated bioassay. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 44:619–629
Proia L, Cassio F, Pascoal C, Tlili A, Romani AM (2012) The use of attached microbial communities to assess ecological risks of pollutants in river ecosystems: the role of heterotrophs. In: Guasch H (ed) Emerging and priority pollutants in rivers, Hdb Env Chem. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 55–84
Project on Emerging Nanotechnology (2012) Consumer Products Inventories for Nanotechnology Products http://www.nanotechproject.org/inventories/consumer/analysis
Ranjard L, Poly F et al (2001) Characterization of bacterial and fungal soil communities by automated ribosomal intergenic spacer analysis fingerprints: biological and methodological variablitity. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:4479–4487
Ratte HT (1999) Bioaccumulation and toxicity of silver compounds: a review. Environ Toxicol Chem 18:89–108
Roháček K, Barták M (1999) Technique of the modulated chlorophyll fluorescence: basic concepts, useful parameters, and some applications. Photosynthetica 37:339–363
Roussel H, Ten-Hage L, Joachim S, Le Cohu R, Gauthier L, Bonzom J-M (2007) A long-term copper exposure on freshwater ecosystem using lotic mesocosms: primary producer community responses. Aquat Toxicol 81:168–182
Say PJ, Whitton BA (1981) Chemistry and plant ecology of zinc rich streams in Northern Pennines. In: Say PJ, Whitton BA (eds) Heavy metals in Northern England: environmental and biological aspects. University of Durham, Durham, pp 53–63
Sabater S, Guasch H, Ricart M, Romaní A, Vidal G, Klünder C, Schmitt-Jansen M (2007) Monitoring the effect of chemicals on biological communities. The biofilm as an interface. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:1425–1434
Schmitt-Jansen M, Altenburger R (2008) Community-level microalgal toxicity assessment by multiwavelength-excitation PAM fluorometry. Aquat Toxicol 86:49–58
Schreiber U (1998) Chlorophyll fluorescence: new instruments for special applications. In: Garab G (ed) Photosynthesis: mechanisms and effects, vol V. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 4253–4258
Serra A, Guasch H (2009) Effects of chronic copper exposure on fluvial systems: Linking structural and physiological changes of fluvial biofilms with the in-stream copper retention. Sci Total Environ 407:5274–5282
Serra A, Guasch H, Admiraal W, Van der Geest HG, Van Beusekom SAM (2010) Influence of phosphorus on copper sensitivity of fluvial periphyton: the role of chemical, physiological and community-related factors. Ecotoxicology 19:770–780
Shea K, Roxburgh SH, Rauschert ESJ (2004) Moving from pattern to process: coexistence mechanisms under intermediate disturbance regimes. Ecol Lett 7:491–508
Smith VH, Tilman GD, Nekola JC (1999) Eutrophication: impacts of excess nutrient inputs on freshwater, marine, and terrestrial ecosystems. Environ Poll 100:179–196
Soldo D, Behra R (2000) Long-term effects of copper on the structure of freshwater periphyton communities and their tolerance to copper, zinc, nickel and silver. Aquat Toxicol 47:181–189
Stevenson RJ, Bothwell ML, Lowe RL (1996) Algal ecology: freshwater benthic ecosystems. Academic, San Diego
Tetu SG et al. (2013) Impact of DNA damaging agents on genome-wide transcriptional profiles in two marine Synechococcus species. Front Microbiol 4
Tlili A, Bérard A, Roulier J-L, Volata B, Montuelle B (2010) PO4 3− dependence of the tolerance of autotrophic and heterotrophic biofilm communities to copper and diuron. Aquat Toxicol 98:165–177
Twiss MR, Nalewajko C (1992) Influence of phosphorus nutrition on copper toxicity to three strains of Scenedesmus acutus (Chlorophyceae). J Phycol 28:291–298
Wetzel RG (1983) Opening remarks. In: Wetzel RG (ed) Periphyton of freshwater ecosystems. Dr W. Junk Publisher, The Hague, pp 3–4
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the ICARE EC2CO MicrobiEn program to MD. We are grateful to P. Rousselle for his help during chemical analyses and to P Bonin, R Duran, and D Faure for their invitation to participate to this special issue. We also thank anonymous reviewers for their useful and constructive comments on an earlier draft of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible editor: Philippe Garrigues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leflaive, J., Felten, V., Ferriol, J. et al. Community structure and nutrient level control the tolerance of autotrophic biofilm to silver contamination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22, 13739–13752 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3860-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-014-3860-1