Abstract
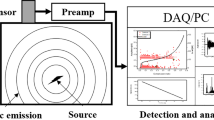
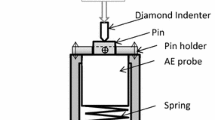
The aim of this study is to monitor the subsurface damage mechanisms of commercial cold-work tool steel by observing acoustic emissions generated in a spherical indentation test. Monotonic loads are applied in the elastic and plastic ranges to damage the specimen. Two types of damage prior to the occurrence of cracking are found: carbide breakage and plastic deformation. The phenomena are confirmed by microscopic images and the good agreement between the estimated carbide fracture strength and previous results. The two types of damage gives rise to different acoustic emission signals: a burst-type, high-amplitude signal for the breakage of carbides and a continuous-type, low-amplitude signal for plastic deformation. It is thus possible to detect and differentiate the incipient damage mechanisms on the subsurface in real time in a spherical indentation test.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a :
-
Radius of contact between ball indenter and specimen surface
- AE:
-
Acoustic emission
- AR :
-
Aspect ratio
- D max :
-
Maximum diameter
- D min :
-
Minimum diameter
- E :
-
Young’s modulus
- E’ :
-
Young’s modulus indenter
- ECD :
-
Equivalent diameter
- p 0 :
-
Indentation stress
- P :
-
Normal load
- P c :
-
Critical normal load
- P γ :
-
Yield load
- r 0 :
-
Radius of spherical-indentation circular cracks
- R :
-
Ball indenter radius
- RMS:
-
Root mean square
- SF :
-
Shape factor
- σ n :
-
Principal normal stress n
- σ RC :
-
Fracture strength of primary carbides
- τ RC :
-
Fracture shear stress of primary carbides
- ε :
-
Strain
- υ :
-
Poisson’s ratio
- υ′:
-
Poisson’s ratio of the indenter
- Ψ :
-
Sphericity
References
Advanced High Strength Steel (AHSS). Application Guidelines. Version 4.1. (June 2009) International Iron & Steel Institute. Committee on Automotive Applications. http://www.worldautosteel.org. Accessed 1 June 2013
Picas I, Hernandez R, Casellas D, Valls I (2010) Strategies to increase the tool performance in punching operations of UHSS. R. Kollek (Ed.), Proc. IDDRG, Graz, Austria, 325–334.
Mishnaevsky L Jr, Lippmann N, Schmander S (2003) Micromechanisms and modeling of crack initiation and growth in tool steels: role of primary carbides. Matter Res Adv Technol 94(6):676–681
Fukaura K, Yokoyama Y, Yokoi D, Tsujii N, Ono K (2004) Fatigue of cold-work tool steels: effect of heat treatment and carbide morphology on fatigue crack formation, life and fracture surface observations. Metall Mater Trans A 35:1289–1300
Berns H, Broeckmann C (1997) Fracture of hot formed ledeburitic tool steels. Eng Fract Mech 58(4):311–325
Picas I, Cuadrado N, Casellas D, Goez A, Llanes L (2010) Microstructural effects on the fatigue crack nucleation in cold work tool steels. Proced Eng 2(1):1777–1785, Fatigue 2010
Martinez-Gonzalez E, Picas I, Casellas D, Romeu J (2013) Detection of crack nucleation and growth in tool steels using fracture tests and acoustic emission. Meccanica. doi:10.1007/s11012-013-9858-9
Johnson L (1985) Contact mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lawn BR (1998) Indentation of ceramics with spheres: a century after Hertz. J Am Ceram Soc 81:1977–1994
Lawn BR, Wilshaw TR (1975) Indentation fracture: principles and applications. J Mater Sci 10(161):1049–1081
Ramirez G, Tarres E, Casas B, Valls I, Martinez R, Llanes L (2009) Contact fatigue behavior of PVD-coated steel. Plasma Process Polym 6:S588–S591
Ramirez G, Mestra A, Casas B, Valls I, Martinez R, Bueno R, Góez A, Mateo A, Llanes L (2012) Influence of substrate microstructure on the contact fatigue strength of coated cold-work tool steels. Surf Coat Technol 206:3069–3081
Padture NP, Lawn BR (1994) Toughness properties of a silicon carbide with an in-situ induced heterogeneous grain structure. J Am Ceram Soc 77(10):2518–2522
Faisal NH, Ahmed R, Reuben RL (2011) Indentation testing and its acoustic emission response: applications and its emerging trends. Int Mater Rev 56(2):98–142
Wereszczak AA, Johanss KE (2008) Spherical indentation of SiC, in Advances in Ceramic Armor II: Ceram Eng & Sci Proc 27(7), John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ, USA. Doi: 10.1002/9780470291368.ch4
Bouras S, Zerizer I, Gheldane F, Bouazza MT, Bouzabata B (2008) Study of the resistance to crack propagation in alumina by acoustic emission. Ceram Int 34:1857–1865
Wereszczak AA, Daloz WL, Strong KT, Jadaan OM (2011) Effect of indenter elastic modulus on hertzian ring crack initiation in silicon carbide. Int J App Ceram Technol 8:885–894
Fischer-Cripps AC, Lawn BR (1996) Indentation stress–strain curves for “quasi ductile” ceramics. Acta Mater 44(2):519–527
Pavon J, Jiménez-Pique E, Anglada M, Saiz E, Tomsia AP (2006) Monotonic and cyclic Hertzian fracture of a glass coating on titanium-based implants. Acta Mater 54:3593–3603
Zhang H, Fang ZZ (2008) Characterization of quasi-plastic deformation of WC–Co composite using Hertzian indentation technique. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 26:106–114
Tarrés E, Ramírez G, Gaillard Y, Jiménez-Piqué E, Llanes L (2009) Contact fatigue behavior of PVD-coated hardmetals. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater 27:323–331
Lee SK, Wuttiphan S, Lawn BR (1997) Role of microstructure in Hertzian contact damage in silicone nitride: I. Mechanical Characterization. J Am Ceram Soc 80(9):2367–2381
Swain MV, Lawn BR (1969) A Study of dislocation arrays at spherical indentation in LiF as a function of indentation stress and strain. Physica Datatus Solidi 35(2):909–923
Swain MV, Hagan JT (1976) Indentation plasticity and the ensuing fracture of glass’. J Phys D Appl Phys 9:2201–2214
Frank FC, Lawn BR (1967) On the theory of Hertzian fracture. Proc R Soc Lond A299(1458):291–306
Picas, I (2012) Mechanical behaviour of tools for shearing Ultra High-Strength Steels: influence of the microstructure on fracture and fatigue micro-mechanisms of tool steels and evaluation of micro-mechanical damage in tools. PhS. Dissertation. Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya (UPC). http://hdl.handle.net/10803/112059
Huang M, Jiang L, Liaw PK, Brooks CR, Seeley R, Klarstrom DL (1998) Using acoustic emission in fatigue and fracture materials research. J Mater 50(11)
Martinez-Gonzalez E, Picas I, Romeu J, Casellas D (2013) Filtering of acoustic emission signals for the accurate identification of fracture/ mechanisms in bending tests. Mater Trans 54(7):1087–1094
Stachowiak GW, Batchelor AW (2005) Engineering tribology, 3rd edn. Elsevier Butterworh-Heinemann, Burlington, pp 571–593
Gere JM, Timoshenko SP (1997) Mechanics of materials. London PWS Publishing Company, Boston
Johnson L (1968) Engineering plasticity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 341
Studman CJ, Field JE (1977) The indentation of hard metals: the role of residual stresses. J Mater Sci 12(2):215–218
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted within the framework of the oPtiMa project and was partially support by the DPI2007-66688-CO2-01 project. The authors acknowledge funding received from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness and the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez-Gonzalez, E., Ramirez, G., Romeu, J. et al. Damage Induced by a Spherical Indentation Test in Tool Steels Detected by Using Acoustic Emission Technique. Exp Mech 55, 449–458 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-014-9959-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11340-014-9959-y