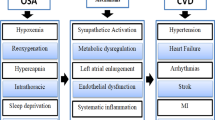
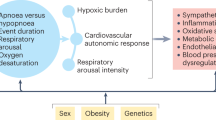
Abstract
Purpose
A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies was conducted to clarify the association between obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) and future risk of all-cause mortality.
Methods
Eligible studies were identified by searching the PubMed and EMBASE databases up to July 2015. Pooled hazard ratios (HRs) and their corresponding 95 % confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated to estimate the association between OSA and risk of all-cause mortality. Sources of heterogeneity were identified by subgroup and meta-regression analyses.
Results
Twelve prospective cohort studies involving 34,382 participants were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled HR of all-cause mortality was 1.262 (95 % CI 1.093–1.431) with significant heterogeneity. Subgroup analyses indicated that the pooled HRs of all-cause mortality in patients with mild, moderate and severe OSA were 0.945 (95 % CI 0.810–1.081), 1.178 (95 % CI 0.978–1.378) and 1.601 (95 % CI 1.298–1.902), respectively. OSA severity could be a possible sources of heterogeneity. Existing publication bias produced a minor contribution to effect size.
Conclusion
Severe, but not mild to moderate, OSA is significantly associated with increased risk of all-cause mortality.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee W, Nagubadi S, Kryger MH, Mokhlesi B (2008) Epidemiology of obstructive sleep apnea: a population-based perspective. Expert Rev Respir Med 2:349–364
De Miguel-Diez J, Carrasco-Garrido P, Jimenez-Garcia R, Puente-Maestu L, Hernandez-Barrera V, Lopez DAA (2015) Obstructive sleep apnea among hospitalized patients in Spain, analysis of hospital discharge data 2008–2012. Sleep Breath 19:1–8
Ge X, Han F, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Yang T, Bai C, Guo X (2013) Is obstructive sleep apnea associated with cardiovascular and all-cause mortality? PLoS One 8:e69432
Wang X, Ouyang Y, Wang Z, Zhao G, Liu L, Bi Y (2013) Obstructive sleep apnea and risk of cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality: a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int J Cardiol 169:207–214
Bradley TD, Floras JS (2009) Obstructive sleep apnoea and its cardiovascular consequences. Lancet 373:82–93
Marshall NS, Wong KK, Liu PY, Cullen SR, Knuiman MW, Grunstein RR (2008) Sleep apnea as an independent risk factor for all-cause mortality: the Busselton Health Study. Sleep 31:1079–1085
Partinen M, Jamieson A, Guilleminault C (1988) Long-term outcome for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome patients. Mortality Chest 94:1200–1204
Veale D, Chailleux E, Hoorelbeke-Ramon A, Reybet-Degas O, Humeau-Chapuis MP, Alluin-Aigouy F, Fleury B, Jonquet O, Michard P (2000) Mortality of sleep apnoea patients treated by nasal continuous positive airway pressure registered in the ANTADIR observatory. Association Nationale pour le Traitement A Domicile de l’Insuffisance Respiratoire chronique. Eur J Respir 15:326–331
Johansson P, Alehagen U, Svanborg E, Dahlstrom U, Brostrom A (2012) Clinical characteristics and mortality risk in relation to obstructive and central sleep apnoea in community-dwelling elderly individuals: a 7-year follow-up. Age Ageing 41:468–474
Korostovtseva LS, Sviryaev YV, Zvartau NE, Konradi AO, Kalinkin AL (2011) Prognosis and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in prospective study of hypertensive patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in St Petersburg, Russia. Med Sci Monit 17:CR146–CR153
Lindberg E, Janson C, Sv Rdsudd K, Gislason T, Hetta J, Boman G (1998) Increased mortality among sleepy snorers: a prospective population based study. Thorax 53:631–637
Punjabi NM, Caffo BS, Goodwin JL, Gottlieb DJ, Newman AB, O’Connor GT, Rapoport DM, Redline S, Resnick HE, Robbins JA, Shahar E, Unruh ML, Samet JM (2009) Sleep-disordered breathing and mortality: a prospective cohort study. PLoS Med 6:e1000132
Young T, Finn L, Peppard PE, Szklo-Coxe M, Austin D, Nieto FJ, Stubbs R, Hla KM (2008) Sleep disordered breathing and mortality: eighteen-year follow-up of the Wisconsin sleep cohort. Sleep 31:1071–1078
Lavie P, Lavie L, Herer P (2005) All-cause mortality in males with sleep apnoea syndrome: declining mortality rates with age. Eur J Respir 25:514–520
Yaggi HK, Concato J, Kernan WN, Lichtman JH, Brass LM, Mohsenin V (2005) Obstructive sleep apnea as a risk factor for stroke and death. N Engl J Med 353:2034–2041
Mant A, King M, Saunders NA, Pond CD, Goode E, Hewitt H (1995) Four-year follow-up of mortality and sleep-related respiratory disturbance in non-demented seniors. Sleep 18:433–438
Johansson P, Alehagen U, Ulander M, Svanborg E, Dahlstrom U, Brostrom A (2011) Sleep disordered breathing in community dwelling elderly: associations with cardiovascular disease, impaired systolic function, and mortality after a six-year follow-up. Sleep Med 12:748–753
Gooneratne NS, Richards KC, Joffe M, Lam RW, Pack F, Staley B, Dinges DF, Pack AI (2011) Sleep disordered breathing with excessive daytime sleepiness is a risk factor for mortality in older adults. Sleep 34:435–442
Marshall NS, Delling L, Grunstein RR, Peltonen M, Sjostrom CD, Karason K, Carlsson LM, Hedner J, Stenlof K, Sjostrom L (2011) Self-reported sleep apnoea and mortality in patients from the Swedish Obese Subjects study. Eur J Respir 38:1349–1354
Yeboah J, Redline S, Johnson C, Tracy R, Ouyang P, Blumenthal RS, Burke GL, Herrington DM (2011) Association between sleep apnea, snoring, incident cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in an adult population: MESA. Atherosclerosis 219:963–968
Martinez-Garcia MA, Campos-Rodriguez F, Catalan-Serra P, Soler-Cataluna JJ, Almeida-Gonzalez C, De la Cruz MI, Duran-Cantolla J, Montserrat JM (2012) Cardiovascular mortality in obstructive sleep apnea in the elderly: role of long-term continuous positive airway pressure treatment: a prospective observational study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 186:909–916
Lee JE, Lee CH, Lee SJ, Ryu Y, Lee WH, Yoon IY, Rhee CS, Kim JW (2013) Mortality of patients with obstructive sleep apnea in Korea. J Clin Sleep Med 9:997–1002
Marshall NS, Wong KK, Cullen SR, Knuiman MW, Grunstein RR (2014) Sleep apnea and 20-year follow-up for all-cause mortality, stroke, and cancer incidence and mortality in the Busselton Health Study cohort. J Clin Sleep Med 10:355–362
Mirrakhimov AE (2013) Supine fluid redistribution: should we consider this as an important risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea? Sleep Breath 17:511–523
Guo Y, Pan L, Ren D, Xie X (2013) Impact of continuous positive airway pressure on C-reactive protein in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep Breath 17:495–503
Leung RS, Comondore VR, Ryan CM, Stevens D (2012) Mechanisms of sleep-disordered breathing: causes and consequences. Pflugers Arch 463:213–230
Lavie P, Herer P, Lavie L (2007) Mortality risk factors in sleep apnoea: a matched case-control study. J Sleep Res 16:128–134
Muraja-Murro A, Eskola K, Kolari T, Tiihonen P, Hukkanen T, Tuomilehto H, Peltonen M, Mervaala E, Toyras J (2013) Mortality in middle-aged men with obstructive sleep apnea in Finland. Sleep Breath 17:1047–1053
Rich J, Raviv A, Raviv N, Brietzke SE (2012) All-cause mortality and obstructive sleep apnea severity revisited. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 147:583–587
Campos-Rodriguez F, Pena-Grinan N, Reyes-Nunez N, De la Cruz-Moron I, Perez-Ronchel J, De la Vega-Gallardo F, Fernandez-Palacin A (2005) Mortality in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea patients treated with positive airway pressure. Chest 128:624–633
Jennum P, Tonnesen P, Ibsen R, Kjellberg J (2015) All-cause mortality from obstructive sleep apnea in male and female patients with and without continuous positive airway pressure treatment: a registry study with 10 years of follow-up. Nat Sci Sleep 7:43–50
Nakamura H, Kanemura T, Takara C, Tsukayama A, Tohyama K, Matsumoto T, Iseki K (2009) A retrospective analysis of 4000 patients with obstructive sleep apnea in Okinawa, Japan. Sleep Biol Rhythms 7:103–112
Marti S, Sampol G, Munoz X, Torres F, Roca A, Lloberes P, Sagales T, Quesada P, Morell F (2002) Mortality in severe sleep apnoea/hypopnoea syndrome patients: impact of treatment. Eur Respir J 20:1511–1518
Punjabi NM (2015) Counterpoint: is the AHI the best way to quantify the severity of sleep disordered breathing? No Chest. doi:10.1378/chest.14-2261
Kendzerska T, Gershon AS, Hawker G, Leung RS, Tomlinson G (2014) Obstructive sleep apnea and risk of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality: a decade-long historical cohort study. PLoS Med 11:e1001599
Eckert DJ, White DP, Jordan AS, Malhotra A, Wellman A (2013) Defining phenotypic causes of obstructive sleep apnea. Identification of novel therapeutic targets. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 188:996–1004
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Xuzhou Science and Technology Bureau provided financial support in the form of social development funding (XZZD1345). The sponsor had no role in the design or conduct of this research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Lei Pan, Xiaomei Xie and Dayue Liu contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, L., Xie, X., Liu, D. et al. Obstructive sleep apnoea and risks of all-cause mortality: preliminary evidence from prospective cohort studies. Sleep Breath 20, 345–353 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-015-1295-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-015-1295-7